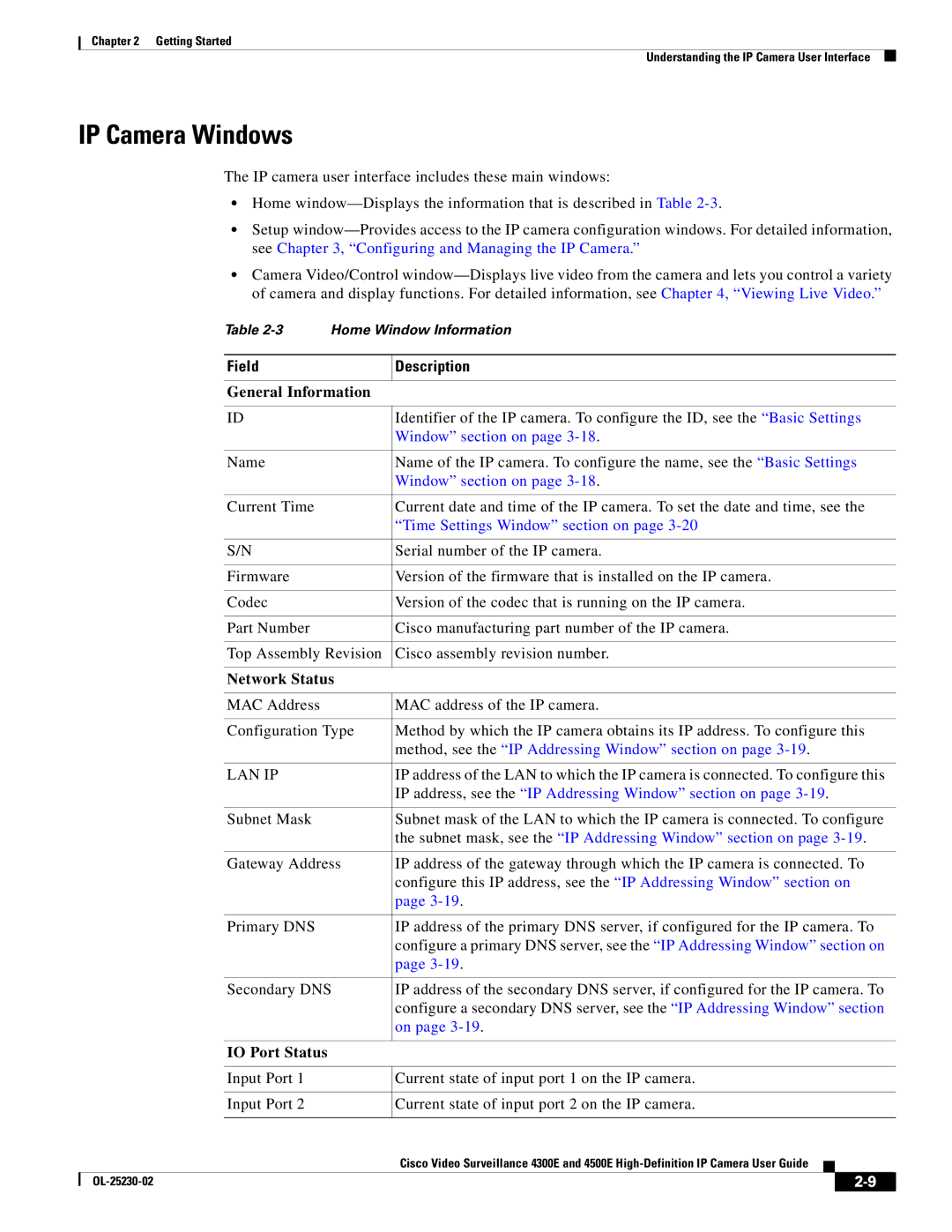
4300E specifications
The Cisco Systems 4300E Series is an advanced integrated service router designed to deliver high-performance, scalable, and secure networking solutions for enterprises. This versatile platform caters to a wide range of applications while ensuring reliability and flexibility in dynamic environments.One of the standout features of the Cisco 4300E is its modular architecture, which allows organizations to tailor the router to their specific needs by adding or changing modules. This modularity is crucial for enterprises that require agility to adapt to evolving network demands. The router supports various network interface modules (NIMs), service modules (SMs), and high-speed WAN interface cards (HWICs), enabling seamless integration of various interfaces and features.
The Cisco 4300E is designed with performance in mind, capable of delivering high throughput and low latency, which is essential for applications such as voice, video, and data traffic. It supports robust performance with the capability of handling up to 2 Gbps of throughput, making it suitable for mid-sized to large enterprise branch offices.
Another key technology associated with the 4300E is Cisco’s Unified Communications and Collaboration suite. This integration facilitates voice, video, and messaging services across the network, ensuring efficient communication within organizations. Security features include advanced threat protection through Cisco’s integrated security services, such as firewall capabilities, VPN support, and intrusion prevention, ensuring that sensitive data remains secure.
The Cisco 4300E also supports Cisco’s DNA (Digital Network Architecture) capabilities, allowing for automation, analytics, and enhanced network visibility. This integration empowers network administrators to manage their infrastructure proactively, ensuring optimal performance and quick resolution of issues.
Additionally, the router is equipped with enhanced Quality of Service (QoS) capabilities, enabling prioritization of critical applications and traffic types. This feature is vital for maintaining high performance across diverse application requirements.
In conclusion, the Cisco 4300E Series routers stand out for their modular architecture, high performance, integrated security, and support for advanced networking technologies. These characteristics make them ideal for enterprises seeking a robust, flexible, and secure solution to meet their networking needs in an ever-evolving digital landscape. With the ability to seamlessly integrate various services and applications, the 4300E is a reliable choice for any organization looking to future-proof its network infrastructure.