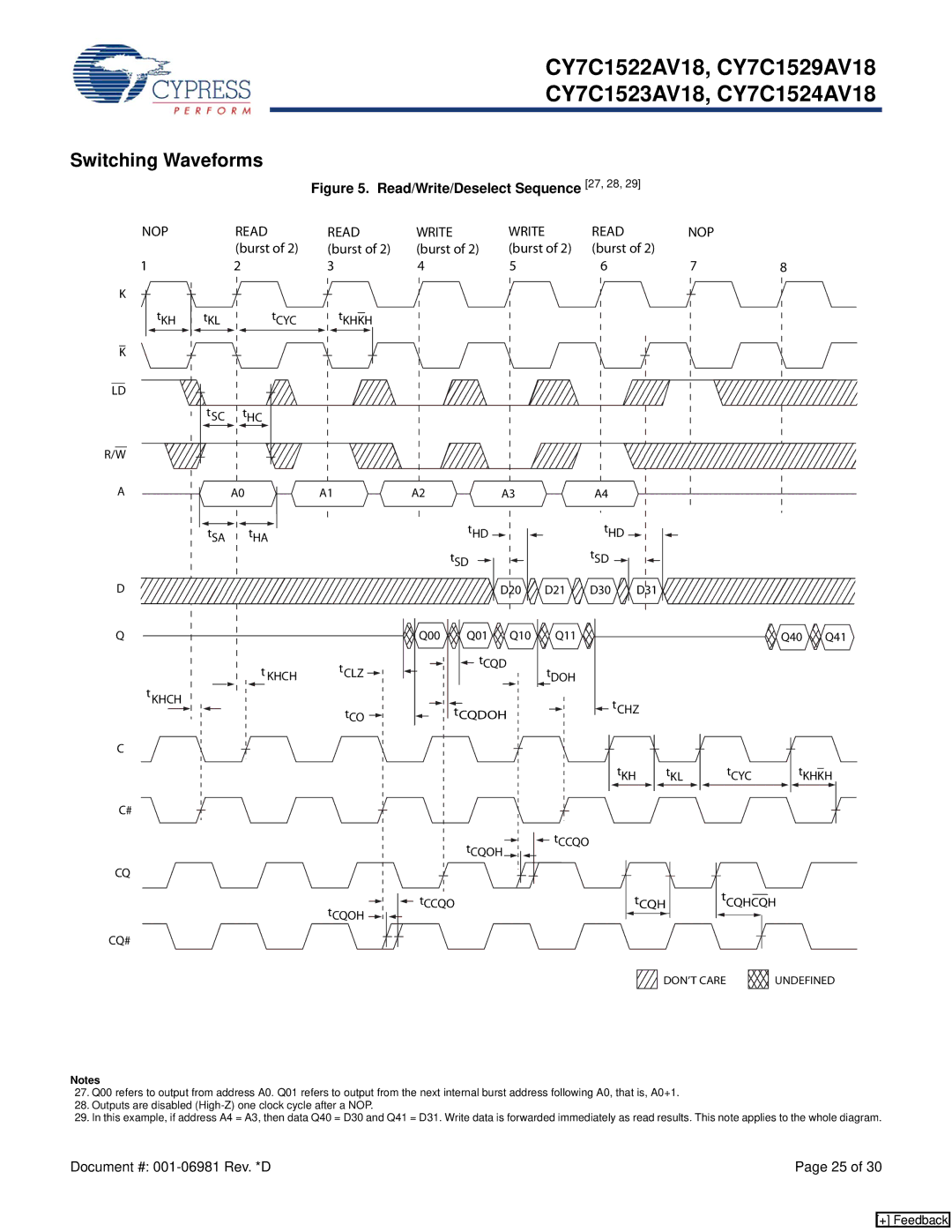
CY7C1529AV18, CY7C1523AV18, CY7C1524AV18, CY7C1522AV18 specifications
Cypress Semiconductor has established itself as a prominent player in the memory solutions market, and its family of high-performance synchronous static random-access memory (SRAM) devices has garnered significant attention. Among these, the CY7C1522AV18, CY7C1524AV18, CY7C1523AV18, and CY7C1529AV18 stand out due to their advanced features and reliable performance.The CY7C1522AV18 is a 2 Megabit SRAM device designed to deliver fast access times with a dual-port architecture. This memory solution supports a 3.0V to 3.6V power supply range. With a high-speed operation of up to 167 MHz, it is ideal for applications that require rapid data processing and retrieval. Its unique architecture allows simultaneous read and write operations, which enhances throughput and efficiency in data handling.
Conversely, the CY7C1524AV18 is a 4 Megabit SRAM that builds upon these capabilities, offering an even larger storage option while maintaining similar speed and voltage specifications. Both devices come with Cyclical Redundancy Check (CRC) for data integrity, ensuring reliability in mission-critical applications. Additionally, these SRAMs feature a simple asynchronous interface, making integration into existing systems remarkably straightforward.
The CY7C1523AV18 offers a balance of features with its 3 Megabit capacity. Similar to its counterparts, this device also presents dual-port capabilities, which facilitate quick data access without bottlenecks, proving advantageous in high-performance computing environments.
Lastly, the CY7C1529AV18 rounds out the family with its impressive 9 Megabit capacity, providing ample memory for more extensive applications. Its enhanced architecture makes it suitable for advanced embedded systems where speed and reliability are paramount.
All four devices leverage Cypress’s innovative Synchronous SRAM technology, which offers low latency and high bandwidth, making them suited for high-performance applications such as networking, telecommunications, and industrial control systems. The memory chips are built with robust features including low power consumption modes and wide operating temperature ranges, enhancing their versatility in various environments.
In conclusion, the CYPRESS CY7C1522AV18, CY7C1524AV18, CY7C1523AV18, and CY7C1529AV18 are exemplary SRAM solutions that combine speed, capacity, and reliability, catering to a broad spectrum of contemporary electronic systems. Whether for embedded applications or high-speed network devices, these memory solutions continue to be at the forefront of technology advancements.