V2.20
D-Link DGS-3100 SERIES GIGABIT STACKABLE MANAGED SWITCH
User Manual
Warnung
FCC Warning
CE Mark Warning
Precaución
Table of Contents
Defining SNMP Host Table
Configuring Port Security
Safety Cautions General Precautions for Rack-Mountable Products
Preface
DGS-3100 Series Gigabit Stackable Managed Switch User Manual
System Overview Viewing the Device Device Management Methods
DGS-3100 Series Front Panel
System Overview
Viewing the Device
Figure 1 DGS-3100 Series 48 Port Front Panel
Web Based Management Interface
Device Management Methods
Command Line Console
SNMP-Based Management
Notes, Notices, and Cautions
Safety Cautions
User Guide Overview
NOTE A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your device
An object has fallen into the product
The power cable, extension cable, or plug is damaged
Unplug the power cable before removing the power supply
The product has been exposed to water
General Precautions for Rack-Mountable Products
Battery Handling Reminder
Protecting Against Electrostatic Discharge
Understanding the D-Link Embedded Web Interface
Using the Web-Based User Interface
GETTING STARTED
View
2. Device
Figure 1-1. Device Information Page
1. Tree View
Information View
Locating Devices
Using the Tool Menu
Displaying the Stack Status
1. Click Device Locator. The Device Locator Page opens
Field Http TFTP
Backing up and Restoring Configuration Files
Figure 1-3 Config Backup and Restore Page
Figure 1-4 Factory Reset Page
Resetting the Device
1. Click Reset. The Factory Reset Page opens
Figure 1-5 Firmware Download Page
Downloading the Firmware
1. Click Firmware Download. The Firmware Download Page opens
Field HTTP Download TFTP Download
Figure 1-6 System Reboot Page
Rebooting the System
1. Click System Reboot. The System Reboot Page opens
2. Define the Select Unit to Reboot field
Name
Using the Web System Components
Component
Description
CONFIGURING BASIC CONFIGURATION
Field Device Type System Contact System Name System Location
Viewing Device Information
Figure 2-1 Device Information Page
Firmware Version Hardware Version System Time System Up Time
Safeguard Engine SNMP Trap SSL GVRP Setting Jumbo Frames
Field Boot Version MAC Address IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
Login Timeout minutes Time Source 802.1D Spanning Tree DHCP Client
BPDU Forwarding IGMP Snooping Broadcast Storm Control 802.1X Status
3. Define the System Location and Login Timeout minutes fields
Defining System Information
System Contact System Name System Location Login Timeout minutes
Figure 2-2 System Information Page
Figure 2-3 IP Address Page
Defining IP Addresses
1. Click Configuration IP Address. The IP Address Page opens
Field
Advanced Stacking
Managing Stacking
Managing Stacking Modes
Allocating Unit IDs
Defining a Stacking Master
Master Enabled Stacking Members
Assigning Unit IDs
Defining a Stacking Back Up Master
Electing a Stacking Master
Stack Startup Process
Discovering the Stacking Master
Unit and Stacking Port Configuration
Allocating Unit IDs/Resolving Unit ID Conflicts
Managing a Self-Ordered Stack
Building Stacks - Quick Start
Stack Resiliency
Managing a New Manually Ordered Stack
Building New Manually Ordered Stacks
Stack Management Examples
Replacing Failed Stacking-Members in a Running Stack
Adding Stacking Members to an Existing Manually Ordered Stack
Replacing a Failed Stack Master
Dividing Stacks
Page
Inserting Excess Stacking Members
Merging Stacks
Stacking Cable Failure
When switches are added to a running stack, the Unit ID Allocation and Duplicate ID Conflict Resolution process detects an error if too many switches are present in the stack, and no changes are to stacking members that originally belonged to the group managed by the newly elected master. The original switches retain their ID assignments and configurations. The stacking members that originally belonged to the group managed by the Stack Master that lost the Master Election process are shut down
Field Stacking Master Current Stack ID New Stack ID after reset
Configuring Stacking
Figure 2-4 Stacking Settings Page
Figure 2-5 Port Setting Page
Configuring Port Properties
Defining Ports
Field Unit From Port To Port State Speed
Field Flow Control Learning
Unit
Viewing Port Properties
Figure 2-6 Port Description Page
From Port
Figure 2-7 ARP Settings Page
ARP Settings
1. Click Configuration ARP Settings. The ARP Settings Page opens
Static ARP Settings
Field User Name New Password Access Right Confirm New Password
Configuring User Accounts
1. Click Configuration User Accounts. The User Accounts Page opens
Figure 2-8 User Accounts Page
2. Click 3. Define the value
2. Click . The user account is deleted, and the device is updated
To edit the User Accounts Page 1. Select a name on the User List
1. Select an entry
Index
Managing System Logs
Figure 2-9 System Log Host Page
Severity
Example
Configuring SNTP
Stratum Stratum Stratum Stratum
Time level T1 T2 T3 T4
Time Source
Figure 2-10 Time Settings Page
Field Time Setting Time in HH MM SS
Current Time
Configuring Daylight Savings Time
Figure 2-11 TimeZone Settings Page
Daylight Saving Time Offset in Minutes Time Zone Offsetfrom GMT
DST Repeating Settings Sections
Field Daylight Savings Time State
Field From Which Week of the Month From Day of Week From Month
DST Annual Settings Section
Field FromMonth FromDay FromTime ToMonth ToDay ToTime
Configuring SNMP
Parameters Authentication Privacy Key Management
Field View Name Subtree OID View Type
Defining SNMP Views
Figure 2-12 SNMP View Table Page
2. Define the View Name, Subtree OID and View Type fields
Field Group Name Read View Name Write View Name
Defining SNMP Groups
Figure 2-13 SNMP Group Table Page
Community/View TestReadView PWriteView PrivateView
Field Notify View Name Security Model Security Level
Figure 2-14 SNMP User Table Page
Defining SNMP Users
Auth-Protocol by Password Password Confirm Password
Field User Name Group Name SNMP V3 Encryption
2. Define the User Name, Group Name, and SNMP V3 Encryption fields
Auth-Protocol by Key
Confirm Key
2. Define the Community Name, and View Name, Access Right fields
Defining SNMP Communities
Access Rights
Figure 2-15 SNMP Community Table Page
Figure 2-16 SNMP Host Table Page
Defining SNMP Host Table
To define the SNMP Host Table Page
Community String / SNMPv3 User Name
Host IP Address
SNMP Version
Figure 2-17 SNMP Engine ID Page
Defining SNMP Engine ID
Field Engine ID Use Default
Field SNMP Traps SNMP Authentication Traps
Enabling SNMP Traps
Figure 2-18 SNMP Configuration Trap Page
Field DHCP Auto Configuration
DHCP Auto Configuration
Figure 2-19 DHCP Auto Configuration Page
Field Unit Image Version Update Time
Dual Image Services
Firmware Information
Figure 2-20 Firmware Information Page
Defines the image file used for reboot. The possible values are
Config Firmware Image
Figure 2-21 Config Firmware Image Page
Image
CONFIGURING L2 FEATURES
Figure 3-1. Jumbo Frame Page
Enabling Jumbo Frames
1. Click L2 Features Jumbo Frame. The Jumbo Frame Page opens
Field Jumbo Frame
VLAN Description
Configuring VLANs
Understanding IEEE 802.1p Priority
Notes about VLANs on the DGS-3100 Series
Term Untagging Ingress port Egress port
Figure 3-2. IEEE 802.1Q Packet Forwarding
Figure 3-4. Adding an IEEE 802.1Q Tag
802.1Q VLAN Tags
Figure 3-3. IEEE 802.1Q Tag
Ingress Filtering
Port VLAN ID
Tagging and Untagging
VLAN Status
Default VLANs
VLAN and Trunk Groups
Switch Ports
Figure 3-5. VLAN Configuration Page
Defining VLAN Properties
1. Click L2 Features 802.1Q VLAN. The VLAN Configuration Page opens
Field VID VLAN Name Untag VLAN Ports Tag VLAN Ports
Figure 3-6. Add/Edit VLAN Information Page
Figure 3-7. GVRP Setting Page
Configuring GVRP
1. Click L2 Features GVRP Settings. The GVRP Setting Page opens
4. Define the PVID, GVRP, Ingress, and Acceptable Frame Type fields
Field GRVP Global Setting Unit From Port To Port PVID GVRP Ingress
Acceptable Frame Type
Figure 3-8. Trunking Configuration Page
Defining Trunking
1. Click L2 Features Trunking. The Trunking Configuration Page opens
Field Unit Group ID Type Ports
Notes about Trunking on the DGS-3100 Series
Source Ports
Traffic Segmentation
Figure 3-9. Traffic Segmentation Page
Forwarding Ports
Timeout
Configuring LACP
Figure 3-10. LACP Port Settings Page
4. Define the Port-Priority and LACP Timeout fields
Leave Timer
Defining IGMP Snooping
1. Click L2 Features IGMP Snooping. The IGMP Snooping Page opens
Figure 3-11. IGMP Snooping Page
Static Router Port Setting Edit button
Host Timeout
Router Timeout
2. Click . The Static Router Ports Settings Page opens
Dynamic Router Ports
Static Router Ports
Ports
Figure 3-13. Port Mirroring Page
Configuring Port Mirroring
1. Click L2 Features Port Mirroring. The Port Mirroring Page opens
Field Status Unit Target Port Source Port
Defines that port mirroring is not applied to the ports
4. Define the Unit, Tx, and Rx. fields under Source Port Setting
Field None
2. Define the Status, Unit, and Target fields
Configuring Spanning Tree
Version Classic STP Rapid STP Multiple STP
STP Status
Defining Spanning Tree Global Parameters
Figure 3-14. STP Bridge Global Settings Page
STP Version
Bridge Hello Time 1
Bridge Priority 0
Bridge Max Age 6
Bridge Forward Delay
Field Unit From Port To Port Cost 0=Auto
Defining STP Port Settings
Figure 3-15. STP Port Settings Page
Field Edge Forwarding BPDU P2P State
Configuration Name
Defining Multiple Spanning Tree Configuration Identification
Figure 3-16. MST Configuration Identification Page
Revision Level
Field Unit Port Instance ID Internal Path Cost Priority Status
Defining MSTP Port Information
Figure 3-17. MSTI Config Information Page
Field Role
4. Define the Internal Path Cost and Priority fields
Figure 3-18. Unicast Forwarding Page
Defining Forwarding and Filtering
Defining Unicast Forwarding
Field Aging Time VID MAC Address Unit Port
Multicast MAC Address
Defining Multicast Forwarding
Figure 3-19. Multicast Forwarding Page
Egress
The entry is deleted, and the device is updated
4. Click To restore the default settings 1. Click
The default settings are restored
3. Select either all, or individual ports
CONFIGURING QUALITY OF SERVICE
Configuring 1p
Figure 4-1. Mapping QoS on the Switch
Understanding QoS
Figure 4-2. Bandwidth Control Page
Defining Bandwidth Settings
1. Click QoS Bandwidth Control. The Bandwidth Control Page opens
No Limit
Field Unit From Port To Port Storm Control Type State Threshold 3500
Configuring Storm Control
Figure 4-3. Traffic Control Settings Page
Broadcast Storm Broadcast and Multicast Storm
2. Define the Unit, From Port, To Port, Prioirity fields
Mapping Ports to Packet Priorities
Figure 4-4. 802.1P Default Priority Page
Field Priority Class ID
Mapping Priority to Classes Queues
Figure 4-5. 802.1P User Priority Page
Figure 4-6. QoS Scheduling Mechanism Page
Configuring QoS Scheduling Mechanism
Field Class ID Mechanism Weight
Defining Multi-Layer CoS Settings
Figure 4-7. Multi-Layer CoS Setting Page
SECURITY FEATURES
Figure 5-8. Safeguard Engine Page
Configuring Safeguard Engine
1. Click Security Safeguard Engine. The Safeguard Engine Page opens
Field Safeguard Engine
1. Click Security Trusted Host. The Trusted Host Page opens
Configuring Trust Host
Field IP1 Access to Switch IP2 Access to Switch IP3 Access to Switch
Figure 5-9.Trusted Host Page
1. Click Security Port Security. The Port Security Page opens
Configuring Port Security
Field Unit From Port To Port Admin State Max Address0-64 Port
Figure 5-10. Port Security Page
1. Click Security Guest Vlan. The Guest VLAN Page opens
Configuring Guest VLANs
Field Max Learning Addr
Figure 5-11 Guest VLAN Page
State Controlled Access Uncontrolled Access
Configuring Port Authentication
Component Authenticators Supplicants/Clients Authentication Server
SuppTimeout 1-65535 sec
1. Click Security 802.1X Setting. The 802.1X Setting Page opens
Figure 5-12. 802.1X Setting Page
ServerTimeout 1-65535 sec
Control
Mode
ServerTimeout 1-65535 sec
1. Click Security 802.1X Setting. The 802.1X Setting Page opens
SuppTimeout 1-65535 sec
ReAuthEnabled
Control
Field
Description
Unit
Page
DGS-3100 Series Gigabit Stackable Managed Switch User Manual
DGS-3100 Series Gigabit Stackable Managed Switch User Manual
Field Succession RADIUS Server Authentic Port Accounting Port Key
Defining RADIUS Settings
Figure 5-13. Authentic RADIUS Server Page
Configuring Secure Socket Layer Security
1. Click Security SSL. The SSL Configuration Settings Page opens
Figure 5-14. SSL Configuration Settings Page
Field SSL Status Ciphersuite Status
Field SSH Server Status Port
Configuring Secure Shell Security
Figure 5 -15. SSH Configuration Page
Defining SSH Algorithm Settings
Public Key Algorithm
Figure 5-16. SSH Algorithm Settings Page
Public key
Data Integrity Algorithm
Field Application Login Method List Enable Method List
Defining Application Authentication Settings
Figure 5-17. Application Authentication Settings Page
Timeout 1-30secs
Configuring Authentication Server Hosts
Figure 5-18. Authentication Server Host Page
Protocol
Field Method List Name Method Method
Defining Login Methods
Figure 5-19. Login Method Lists Page
Field Method Method
Description are
Field Method List Name Method
Defining Enable Methods
Figure 5-20. Enable Method Lists Page
Field Method Method Method
Old Local Enable Password
Configuring Local Enable Password
Figure 5-21. Configure Local Enable Password Page
Provide the current network Enable password
MONITORING THE DEVICE
Figure 6-1 Stacking Information Page
Viewing Stacking Information
Field Master ID Backup ID Box ID Runtime version H/W version
Figure 6-2. CPU Utilization Page
Viewing CPU Utilization
1. Click Monitoring CPU Utilization. The CPU Utilization Page opens
Field Utilization Time Interval Record Number Show/Hide
Field Unit Port Utilization Time Interval Record Number Show/Hide
Viewing Port Utilization
Figure 6-3. Port Utilization Page
Figure 6-4. Packet Size Page
Viewing Packet Size Information
1. Click Monitoring Packet Size. The Packet Size Page opens
Field Unit Port Packet Size Analysis - Selected Port Number
Figure 6-5. ReceivedRX Page
Viewing Received Packet Statistics
1. Click Monitoring Packets ReceivedRX. The ReceivedRX Page opens
Field Unit Port Bytes Packets Time Interval Record Number Show/Hide
Figure 6-6. UMBcastRX Page
Viewing UMBcast Packet Statistics
1. Click Monitoring Packets UMBcastRX. The UMBcastRX Page opens
Field Unit Port Unicast Multicast Broadcast Time Interval
Field Unit Port Bytes Packets Time Interval
Viewing Transmitted Packet Statistics
Figure 6-7. TransmittedTX Page
Field Record Number Show/Hide
Field Time Interval Server UDP Port Timeouts Requests Challenges
Viewing RADIUS Authenticated Session Statistics
Figure 6-8. RADIUS Authentication Page
Accepts Rejects
Field VLAN Name IP Address Total Entries MAC Address Type
Viewing ARP Table
Figure 6-9 Browse ARP Table Page
Field VID Unit Port
Viewing Router Ports
Figure 6-10 Browse Router Port Page
Field ID From User Privilege Name
Viewing Session Table
Figure 6-11 Browse Session Table Page
Field VID VLAN Name VLAN Name Multicast Group MAC Address Port
Viewing IGMP Group Information
Figure 6-12 IGMP Snooping Group Page
Field Unit Port VLAN Name MAC Address VID Type
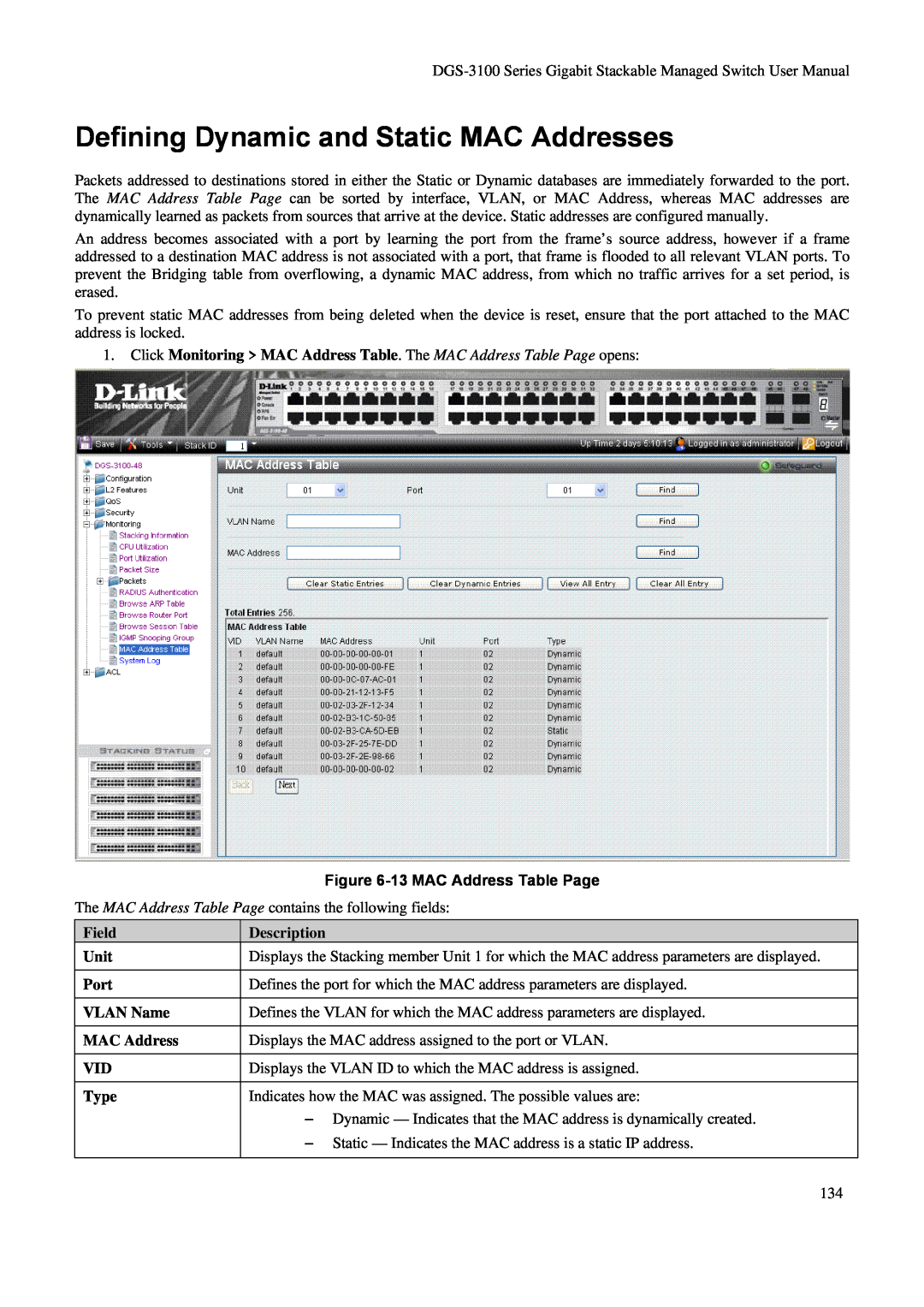
Defining Dynamic and Static MAC Addresses
Figure 6-13 MAC Address Table Page
To view all entries, click To clear static entries, click
2. Select the Stacking member in the Unit field
3. Define the Port, VLAN Name, and MAC Address fields 4. Click
To clear dynamic entries, click
Figure 6-14 System Log Page
Viewing System Log
1. Click Monitoring System Log. The System Log Page opens
Field ID Time Log Description Severity
MANAGING POWER OVER ETHERNET DEVICES
Figure 7-1 PoE Port Setting Page
Defining PoE System Information
1. Click PoE PoE Port Setting. The PoE Port Setting Page opens
PoE Enable
Normal - Indicates that the power supply unit is functioning
Indicates the power consumption is 7W
Indicates the power consumption is 15.4W
Off - Indicates that the power supply unit is not functioning
Figure 7-2 PoE System Setting Page
Displaying and Editing PoE System Information
1. Click PoE PoE System Setting. The PoE System Setting Page opens
System Power Threshold
DEFINING ACCESS PROFILE LISTS
Service Type
ACL Configuration Wizard
Figure 8-1 ACL Configuration Wizard Page
From
UDPAll - Specifies a UDP Packets filtering
TCP Source Port - Matches the packet to the TCP Source Port
TCP Destination Port - Matches the packet to the TCP Destination Port
UDP Source Port - Matches the packet to the UDP Source Port
Displays the access rule
Defining Access Profile Lists
1. Click ACL Access Profile List. The ACL Profile List Page opens
Adding ACL Profiles
L3 ACL
Figure 8-3 Add ACL Profile Page
L2 ACL
To define L2 MAC Address ACL profile
Defining Level 2 ACL
Figure 8-4 ACL Profile L2 ACL Tagged Page
Figure 8-5 ACL Profile L2 ACL Tagged MAC Address Page
To define L2 802.1Q VLAN ACL profile
Source MAC Mask
Destination MAC Mask
Figure 8-6 ACL Profile L2 ACL Tagged VLAN Page
To define L2 Ether Type ACL profile
Figure 8-7 ACL Profile L2 ACL Tagged Ether Type Page
Figure 8-9 Add ACL Profile L3 Page
Defining Level 3 ACL
Figure 8-8 ACL Profile L2 ACL Untagged Page
To define L3 IPv4 Address ACL profile
To define L3 IPv4 DSCP ACL profile
Figure 8-10 ACL Profile L3 ACL ICMP IPv4 DSCP Page
Figure 8-11 ACL Profile L3 ACL ICMP IPv4 Address Page
ICMP Type
To define L3 ICMP ACL profile
Figure 8-12 ACL Profile L3 ACL ICMP Page
ICMP Code
Figure 8-14 ACL Profile L3 IGMP Selected Page
To define L3 IGMP ACL profile
Figure 8-13 ACL Profile L3 IGMP Page
Figure 8-16 ACL Profile L3 TCP Port Page
Figure 8-15 ACL Profile L3 TCP Page
To define L3 TCP Port ACL profile
To define L3 TCP Flag ACL Profile
Figure 8-17 ACL Profile L3 TCP Flag Page
Figure 8-19 ACL Profile L3 UDP Port Page
If L3 ACL UDP is selected, the page updates as follows
Figure 8-18 ACL Profile L3 UDP Page
Description
Figure 8-20 Access Profile List Page
Defining Access Rules Lists
Click ACL Access Profile List The Access Profile List Page opens
Filter
Access ID
1. Click . The Add Access Rule Page opens
Figure 8-21 Add Access Rule Page IP based ACL
Source ID
3. Click . The rule is changed, and the device is updated
2. Define the Rule Detail fields
Figure 8-22 ACL Finder Page
Finding ACL Rules
1. Click ACL ACL Finder The ACL Finder Page opens
Profile ID list box
Destination MAC
Figure 8-23 Rule Detail Page
Source MAC
Ether Type
Notes about ‘IP’ and ‘MAC’ Based ACLs in the DGS-3100 Series
Notes about ACLs capacity in the DGS-3100 Series
Limited Lifetime Warranty for the product is defined as follows
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
Product Registration
Product Type
LIMITED WARRANTY
Warranty Period
What You Must Do For Warranty Service
What Is Not Covered
is not contemplated in the documentation for the product, or if the model or serial number has been altered, tampered with, defaced or removed
Copyright Statement
FCC Warning
Trademarks
Tech Support for customers within the United States
TECHNICAL SUPPORT
Technical Support
Tech Support for customers within Canada
D-Link UK & Ireland Technical Support over the Internet
For Customers within The United Kingdom & Ireland
For Customers within Canada
D-Link UK & Ireland Technical Support over the Telephone
Technische Unterstützung
Support technique destiné aux clients établis au Canada
Assistance technique
Support technique destiné aux clients établis en France
Link
Asistencia Técnica de D-Link a través de Internet
Asistencia Técnica
Asistencia Técnica de D-Link por teléfono
D-Link Mediterraneo S.r.L
Supporto tecnico
Supporto tecnico per i clienti residenti in Italia
Gli ultimi aggiornamenti e la documentazione sono
Tech Support for customers within Belgium
Technical Support
Tech Support for customers within the Netherlands
Tech Support for customers within Luxemburg
Pomoc techniczna
webové stránce firmy D-Link
Technická podpora
Aktualizované verze software a uživatelských příruček najdete na
D-Link poskytuje svým zákazníkům bezplatnou technickou podporu
Technikai Támogatás
D-Link Magyarország
D-Link Teknisk telefon Support
Teknisk Support
Teknisk Support
Du kan finne programvare oppdateringer og bruker
Tlf. 7026
D-Link teknisk support på Internettet
D-Link teknisk support over telefonen
Hverdager kl. 0800
Tuotteen takuun voimassaoloajan Tekninen tuki palvelee seuraavasti
Teknistä tukea asiakkaille Suomessa
D-Link tarjoaa teknistä tukea asiakkailleen
Arkisin klo. 9 - 21 numerosta
uppdateringar och annan användarinformation
Teknisk Support för kunder i Sverige
På vår hemsida kan du hitta mer information om mjukvaru
D-Link tillhandahåller teknisk support till kunder i Sverige
Você pode encontrar atualizações de software e documentação de
Suporte Técnico
Suporte Técnico para clientes no Portugal
Assistência Técnica
Τηλεφωνική υποστήριξη D-Link
Τεχνική Υποστήριξη
Για πελάτες εντός του Ελλαδικού χώρου
Τηλ 210 86 11 Φαξ 210 86 53 Δευτέρα-Παρασκευή
India
Tech Support for customers in
Australia
Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore and Thailand
http//support.dlink-me.com
Technical Support
Tech Support for customers in
e-mail amostafa@dlink-me.com
доступны на Интернет-сайте D-Link
Техническая поддержка
Обновления программного обеспечения и документация
D-Link предоставляет бесплатную поддержку для клиентов
Asistencia Técnica
Telefone
Suporte Técnico
Suporte Técnico para clientes no Brasil
São Paulo +11-2185-9301 Segunda à sexta Das 8h30 às 18h30
D-Link 免付費技術諮詢專線
D-Link 友訊科技 台灣分公司 技術支援資訊
電子郵件:dssqaservice@dlink.com.tw
0800-002-615
Update perangkat lunak dan dokumentasi pengguna dapat
Dukungan Teknis
Dukungan Teknis untuk pelanggan
diperoleh pada situs web D-Link
办公地址:北京市东城区北三环东路 36 号 环球贸易中心 B 座 26F 02-05 室 邮编
技术支持
您可以在 D-Link 的官方網站找到產品的軟件升級和使用手冊
技术支持中心电话:8008296688 技术支持中心传真:02885176948
International Offices
Product Model
Product installed in type of computer
Registration Card All Countries and Regions Excluding USA
Product Serial No