SUPPORT FOR LONG PIECES
![]() WARNING: Turn off tool and disconnect from power source before attempting to move it, changing accesso- ries or making any adjustments accept as written in laser adjustment instructions.
WARNING: Turn off tool and disconnect from power source before attempting to move it, changing accesso- ries or making any adjustments accept as written in laser adjustment instructions.
ALWAYS SUPPORT LONG PIECES
Support long workpieces using any convenient means such as sawhorses or similar devices to keep the ends from dropping. For best results, use the DW7080 exten- sion work support to extend the table width of your saw.
CUTTING PICTURE FRAMES, SHADOW BOXES AND OTHER FOUR SIDED PROJECTS
To best understand how to make the items listed here, we suggest that you try a few simple projects using scrap wood until you develop a “FEEL” for your saw.
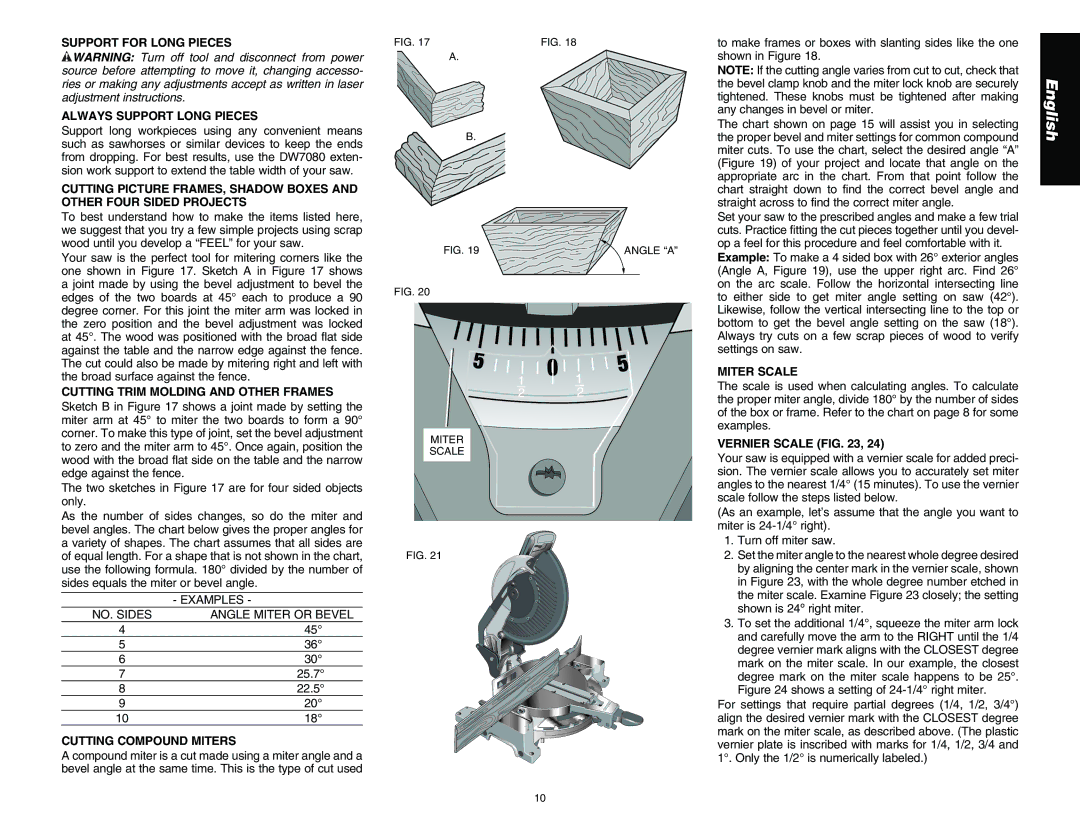
Your saw is the perfect tool for mitering corners like the one shown in Figure 17. Sketch A in Figure 17 shows a joint made by using the bevel adjustment to bevel the edges of the two boards at 45° each to produce a 90 degree corner. For this joint the miter arm was locked in the zero position and the bevel adjustment was locked at 45°. The wood was positioned with the broad flat side against the table and the narrow edge against the fence. The cut could also be made by mitering right and left with the broad surface against the fence.
CUTTING TRIM MOLDING AND OTHER FRAMES
Sketch B in Figure 17 shows a joint made by setting the miter arm at 45° to miter the two boards to form a 90° corner. To make this type of joint, set the bevel adjustment to zero and the miter arm to 45°. Once again, position the wood with the broad flat side on the table and the narrow edge against the fence.
The two sketches in Figure 17 are for four sided objects only.
As the number of sides changes, so do the miter and bevel angles. The chart below gives the proper angles for a variety of shapes. The chart assumes that all sides are of equal length. For a shape that is not shown in the chart, use the following formula. 180° divided by the number of sides equals the miter or bevel angle.
| - EXAMPLES - |
NO. SIDES | ANGLE MITER OR BEVEL |
4 | 45° |
5 | 36° |
6 | 30° |
7 | 25.7° |
8 | 22.5° |
9 | 20° |
10 | 18° |
CUTTING COMPOUND MITERS
A compound miter is a cut made using a miter angle and a bevel angle at the same time. This is the type of cut used
FIG. 17
A.
B.
FIG. 19
FIG. 20
MITER
SCALE
FIG. 21
FIG. 18 |
| to make frames or boxes with slanting sides like the one |
|
| shown in Figure 18. |
|
| NOTE: If the cutting angle varies from cut to cut, check that |
|
| the bevel clamp knob and the miter lock knob are securely |
|
| tightened. These knobs must be tightened after making |
|
| any changes in bevel or miter. |
|
| The chart shown on page 15 will assist you in selecting |
|
| the proper bevel and miter settings for common compound |
|
| miter cuts. To use the chart, select the desired angle “A” |
|
| (Figure 19) of your project and locate that angle on the |
|
| appropriate arc in the chart. From that point follow the |
|
| chart straight down to find the correct bevel angle and |
|
| straight across to find the correct miter angle. |
|
| Set your saw to the prescribed angles and make a few trial |
|
| cuts. Practice fitting the cut pieces together until you devel- |
| ANGLE “A” | op a feel for this procedure and feel comfortable with it. |
| Example: To make a 4 sided box with 26° exterior angles | |
|
| |
|
| (Angle A, Figure 19), use the upper right arc. Find 26° |
|
| on the arc scale. Follow the horizontal intersecting line |
|
| to either side to get miter angle setting on saw (42°). |
|
| Likewise, follow the vertical intersecting line to the top or |
|
| bottom to get the bevel angle setting on the saw (18°). |
|
| Always try cuts on a few scrap pieces of wood to verify |
|
| settings on saw. |
|
| MITER SCALE |
|
| The scale is used when calculating angles. To calculate |
|
| the proper miter angle, divide 180° by the number of sides |
|
| of the box or frame. Refer to the chart on page 8 for some |
|
| examples. |
VERNIER SCALE (FIG. 23, 24)
Your saw is equipped with a vernier scale for added preci- sion. The vernier scale allows you to accurately set miter angles to the nearest 1/4° (15 minutes). To use the vernier scale follow the steps listed below.
(As an example, let’s assume that the angle you want to miter is
1. Turn off miter saw.
2. Set the miter angle to the nearest whole degree desired by aligning the center mark in the vernier scale, shown in Figure 23, with the whole degree number etched in the miter scale. Examine Figure 23 closely; the setting shown is 24º right miter.
3. To set the additional 1/4°, squeeze the miter arm lock and carefully move the arm to the RIGHT until the 1/4 degree vernier mark aligns with the CLOSEST degree mark on the miter scale. In our example, the closest degree mark on the miter scale happens to be 25°. Figure 24 shows a setting of
For settings that require partial degrees (1/4, 1/2, 3/4°) align the desired vernier mark with the CLOSEST degree mark on the miter scale, as described above. (The plastic vernier plate is inscribed with marks for 1/4, 1/2, 3/4 and 1°. Only the 1/2° is numerically labeled.)
English
10