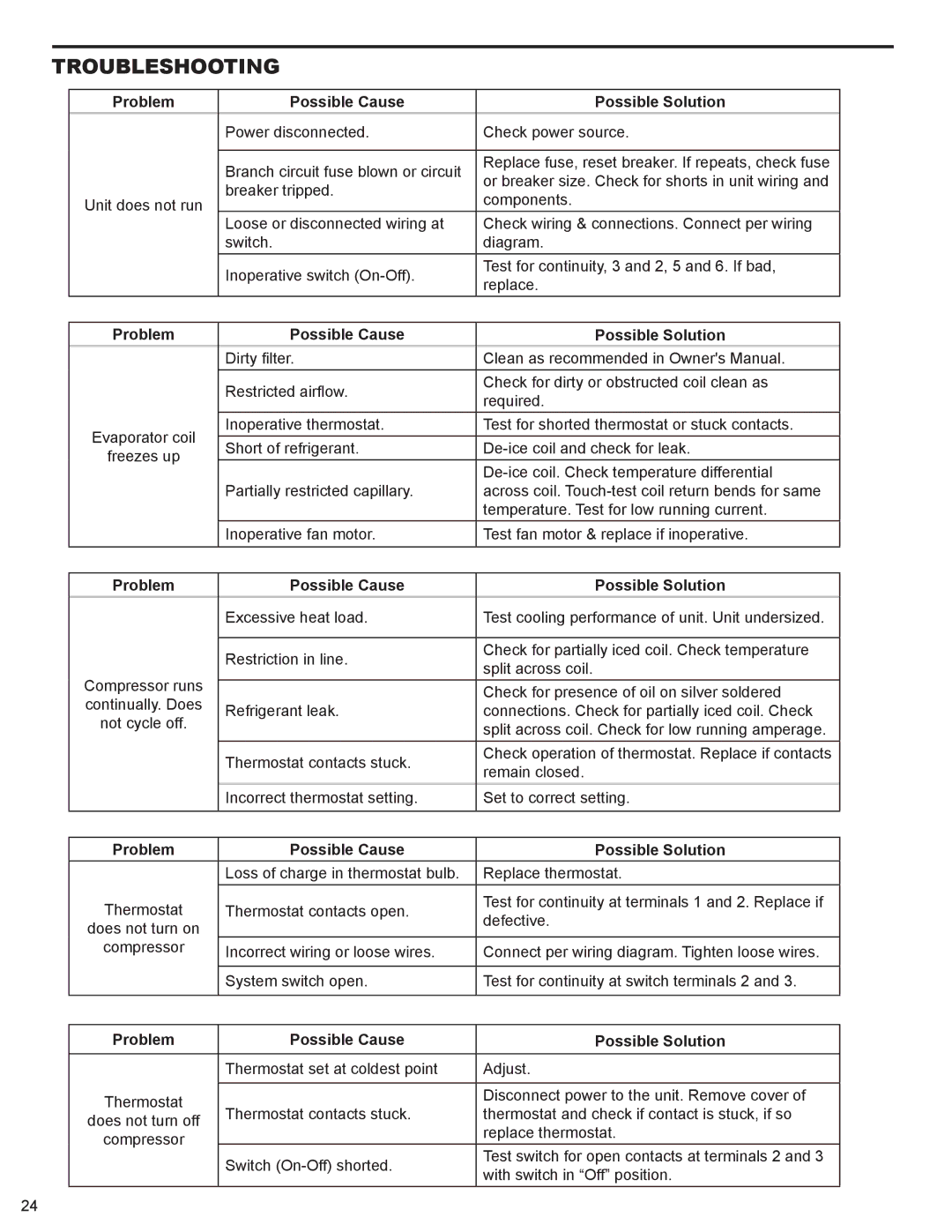
R-410A specifications
Friedrich R-410A is an advanced refrigerant widely used in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, known for its high efficiency and environmental friendliness. As a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) blend, R-410A has become the preferred alternative to R-22, which is being phased out due to its ozone-depleting potential. One of the main features of R-410A is its high latent heat of vaporization, which allows for efficient heat transfer and improved cooling performance in air conditioning units.Technologically, R-410A operates at higher pressures than older refrigerants, meaning systems designed for R-410A need to be built with more robust components to safely handle these pressures. This results in a more compact system design that offers enhanced performance and reliability. The dual-component nature of R-410A—composed of difluoromethane (R-32) and pentafluoroethane (R-125)—provides an optimal balance of thermodynamic properties, leading to superior energy efficiency, especially in variable speed applications.
In terms of characteristics, R-410A has a higher cooling capacity, which enables HVAC systems to effectively cool larger spaces or run more efficiently when cooling smaller areas. The refrigerant is non-toxic and non-flammable, which enhances safety during its use. In addition, R-410A has a lower global warming potential relative to other refrigerants, making it a more environmentally responsible choice for modern cooling systems.
Moreover, R-410A systems typically require less refrigerant charge due to their efficiency, contributing to reduced greenhouse gas emissions. The adoption of R-410A aligns with regulatory trends aimed at minimizing the environmental impact of refrigerants in cooling applications.
Overall, the Friedrich R-410A refrigerant embodies a combination of technology and environmental stewardship, making it a cornerstone of contemporary HVAC design. Its ability to provide effective and energy-efficient cooling solutions while being compliant with modern environmental regulations positions R-410A as the refrigerant of choice for engineers and installers focused on sustainability and performance in air conditioning systems.