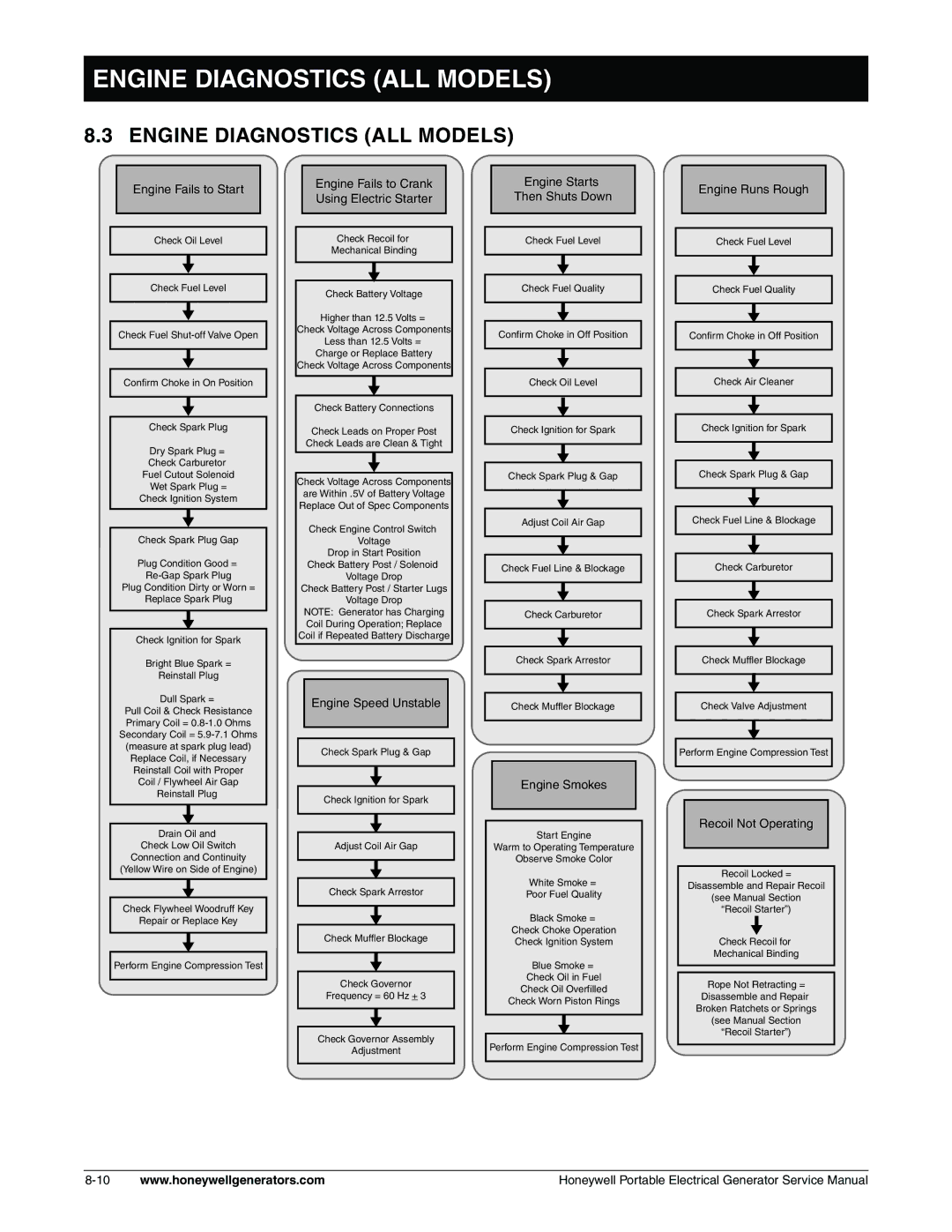
hw400, HW3000, L specifications
Honeywell is renowned for its innovative solutions in various domains, including manufacturing, aerospace, and building technologies. Among its many offerings, the Honeywell L, HW3000, and HW400 series stand out for their advanced features, technologies, and characteristics, tailored to meet the evolving demands of industries worldwide.The Honeywell L Series is recognized for its versatility and reliability in process control applications. Designed to accommodate a range of industrial needs, these controllers provide enhanced flexibility with modifiable configurations that suit diverse operating conditions. With advanced user interfaces, intuitive programming options, and robust execution capabilities, they optimize performance while simplifying system maintenance.
The HW3000 series takes innovation a notch higher, featuring cutting-edge process automation technologies. It leverages advanced algorithms and communication protocols, facilitating seamless integration with existing systems and enhancing overall efficiency. This series is designed for high-performance operations, offering real-time data monitoring and control. The HW3000's modular architecture allows for easy upgrades and scalability, making it ideal for businesses planning for growth.
On the other hand, the Honeywell HW400 series is engineered for precision and reliability. It is equipped with state-of-the-art sensors and control mechanisms that ensure optimal performance in demanding environments. The HW400 model emphasizes sustainability, incorporating energy-efficient technologies that align with global initiatives for greener operations. Users benefit from advanced diagnostics and predictive maintenance capabilities, which minimize downtime and enhance productivity.
All three series—L, HW3000, and HW400—share a commitment to security and data integrity. Honeywell incorporates cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive information and facilitate secure communications. Moreover, they embrace a user-friendly design philosophy, ensuring that operators can easily interface with the systems, regardless of their technical background.
In summary, Honeywell's L, HW3000, and HW400 series highlight the company’s dedication to innovation, efficiency, and reliability. With advanced technologies and robust features, these products cater to a wide range of industrial applications, making them essential tools for businesses aiming to optimize their operations. Whether for process control, automation, or precision management, Honeywell continues to provide solutions that drive success in the modern industrial landscape.