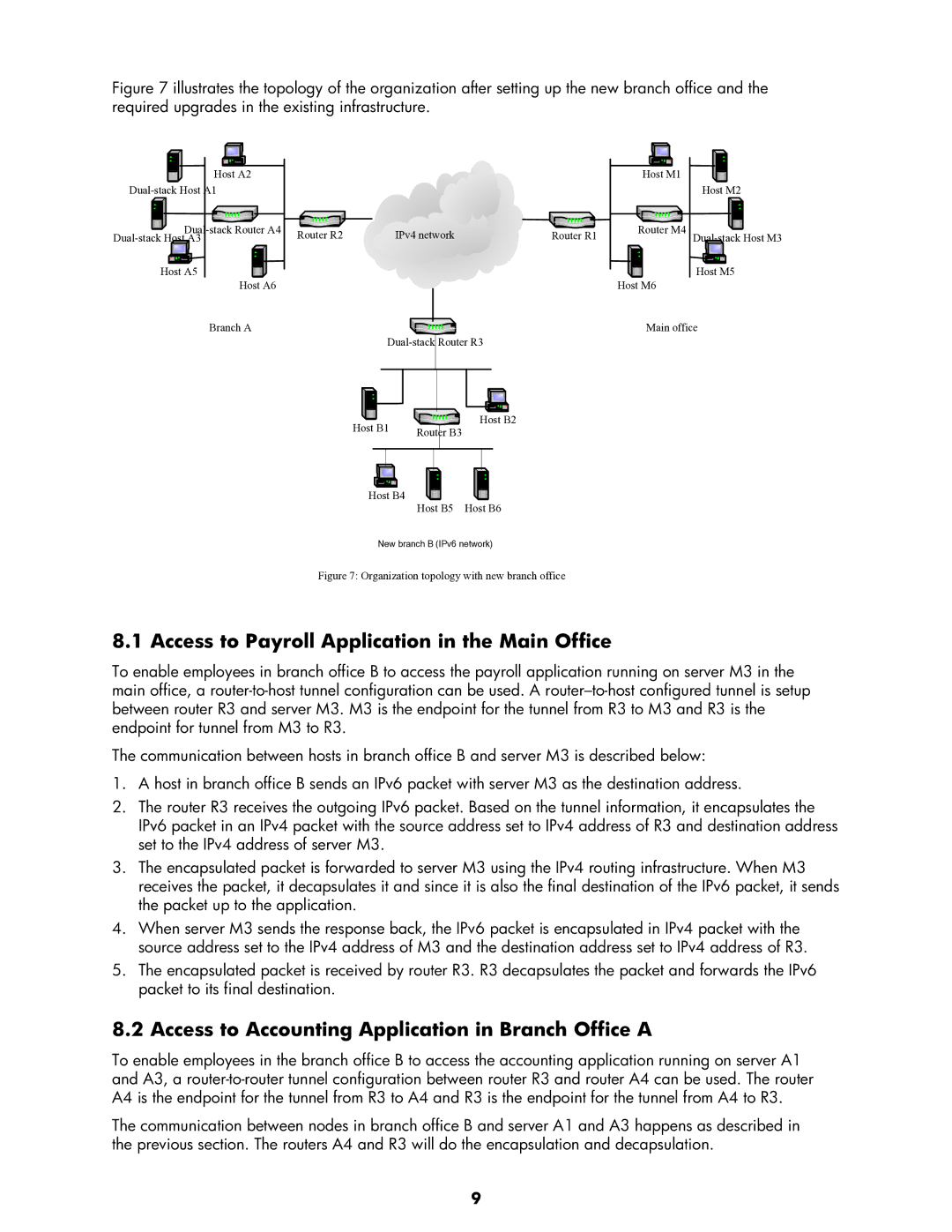
Figure 7 illustrates the topology of the organization after setting up the new branch office and the required upgrades in the existing infrastructure.
Host A2 |
|
|
| Host M1 |
|
|
|
|
| Host M2 | |
Router R2 | IPv4 network | Router R1 | Router M4 | ||
| |||||
Host A5 |
|
|
|
| Host M5 |
Host A6 | Host M6 |
Branch A | Main office |
|
Host B1 | Host B2 | |
Router B3 | ||
|
Host B4
Host B5 Host B6
New branch B (IPv6 network)
Figure 7: Organization topology with new branch office
8.1 Access to Payroll Application in the Main Office
To enable employees in branch office B to access the payroll application running on server M3 in the main office, a
The communication between hosts in branch office B and server M3 is described below:
1.A host in branch office B sends an IPv6 packet with server M3 as the destination address.
2.The router R3 receives the outgoing IPv6 packet. Based on the tunnel information, it encapsulates the IPv6 packet in an IPv4 packet with the source address set to IPv4 address of R3 and destination address set to the IPv4 address of server M3.
3.The encapsulated packet is forwarded to server M3 using the IPv4 routing infrastructure. When M3 receives the packet, it decapsulates it and since it is also the final destination of the IPv6 packet, it sends the packet up to the application.
4.When server M3 sends the response back, the IPv6 packet is encapsulated in IPv4 packet with the source address set to the IPv4 address of M3 and the destination address set to IPv4 address of R3.
5.The encapsulated packet is received by router R3. R3 decapsulates the packet and forwards the IPv6 packet to its final destination.
8.2 Access to Accounting Application in Branch Office A
To enable employees in the branch office B to access the accounting application running on server A1 and A3, a
The communication between nodes in branch office B and server A1 and A3 happens as described in the previous section. The routers A4 and R3 will do the encapsulation and decapsulation.
9