IPv4 host
| IPv4 network |
IPv4 Router | IPv6/IPv4 Router |
| |
IPv6/IPv4 host |
|
Figure 4: router-to-host tunnel configuration
IPv4 host
IPv6 host
IPv6 host
6. 6to4
6to4 is an automatic
6to4 further defines an address assignment scheme that allows a site to obtain an unique externally routable prefix if the site has at least one globally unique IPv4 address. The Internet Assigned Number Authority has assigned the unique prefix 2002::/16 for 6to4 mechanism. The site border dual stack router should have at least one global IPv4 address, a 6to4 prefix can be generated by concatenating the 2002:: prefix to the global IPv4 address. For example, if the dual stack router has an IPv4 address 15.13.136.1, then its 6to4 prefix will be 2002:0f0d:8801::/48. The embedded IPv4 address will be used as the tunnel endpoint address by the 6to4 mechanism.
|
|
| IPv6 host |
6to4 host |
|
|
|
| IPv4 network | 6to4 relay router | IPv6 host |
6to4 router |
| ||
|
| ||
|
|
| |
6to4 host |
|
| IPv6 host |
|
|
| |
| 6to4 router |
|
|
6to4 host6to4 host
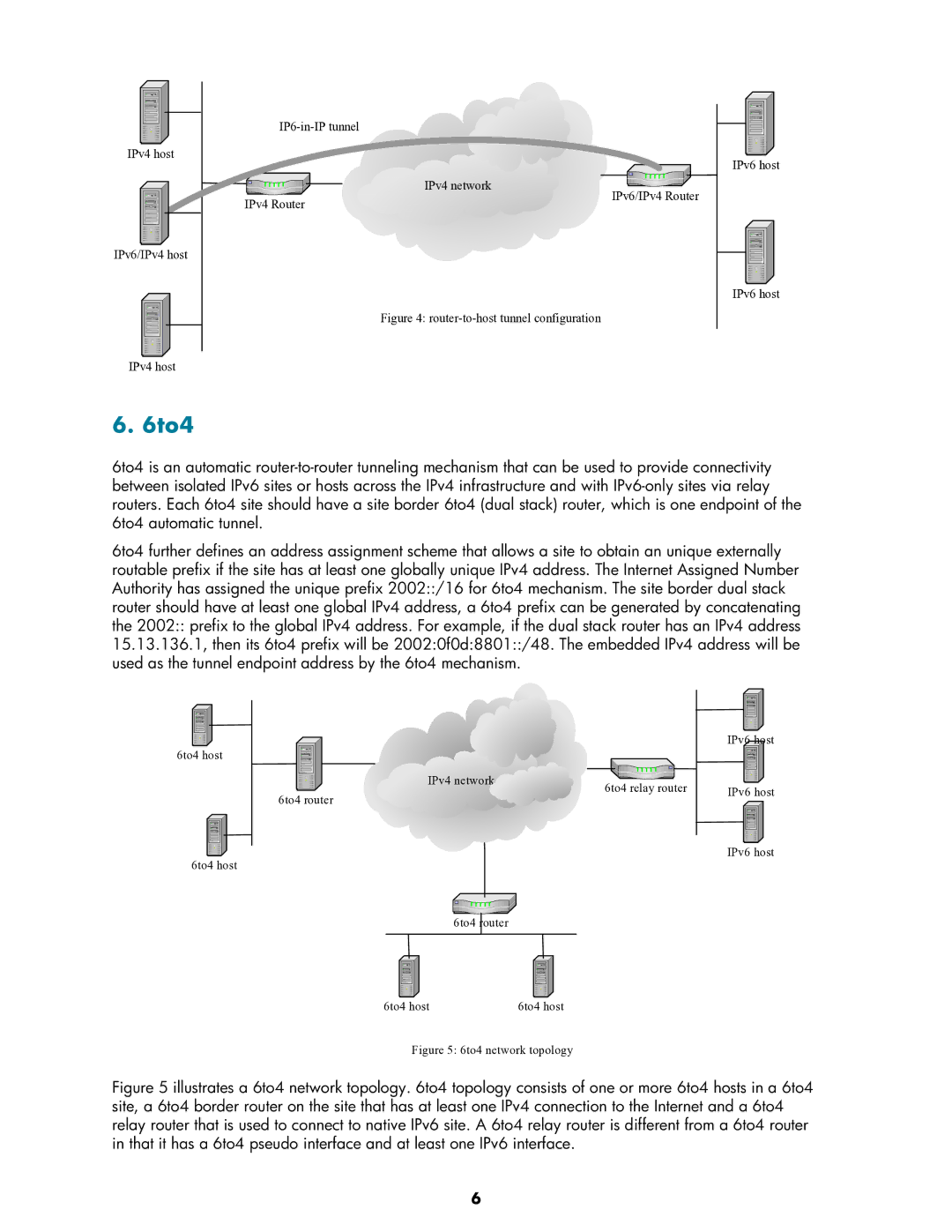
Figure 5: 6to4 network topology
Figure 5 illustrates a 6to4 network topology. 6to4 topology consists of one or more 6to4 hosts in a 6to4 site, a 6to4 border router on the site that has at least one IPv4 connection to the Internet and a 6to4 relay router that is used to connect to native IPv6 site. A 6to4 relay router is different from a 6to4 router in that it has a 6to4 pseudo interface and at least one IPv6 interface.
6