About the WebQoS API
Overview
Overview
Using the WebQoS API, an application can reassign the classification rule class of a session and the process group of a process. This allows more fine-tuning of the assigned class(es). WebQoS must be configured to allow these changes to be made. Refer to the Installing and Configuring WebQoS on HP-UXmanual for more information about configuring WebQoS.
The following figures show how the WebQoS API can be used to change the class of a classification rule and process group. The first two figures represent a single session.
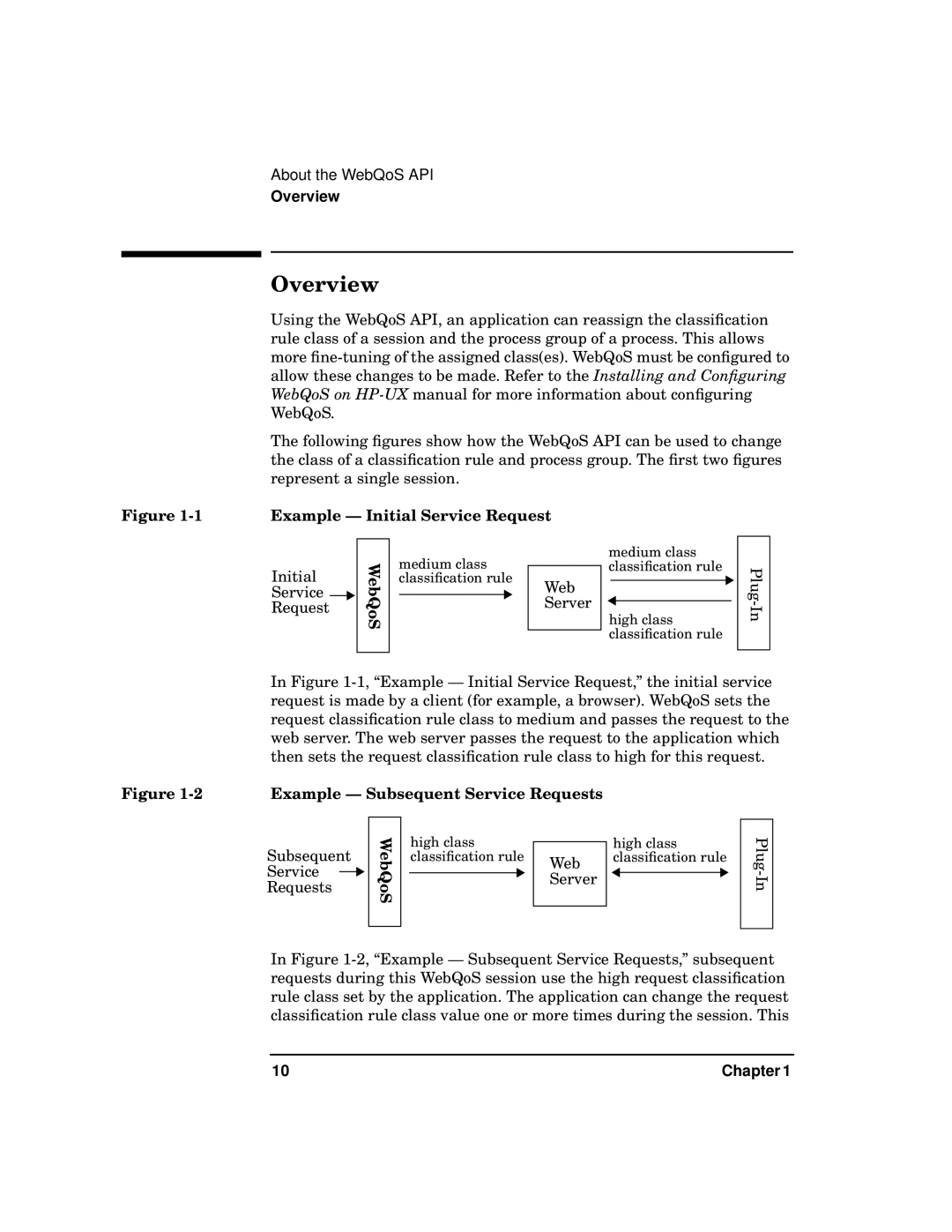
Example — Initial Service Request
Initial | WebQoS | medium class | |
classification rule | Web |
Service | | | | | | |
Request | | | | | Server |
| | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
medium class classification rule
high class classification rule
In Figure 1-1, “Example — Initial Service Request,” the initial service request is made by a client (for example, a browser). WebQoS sets the request classification rule class to medium and passes the request to the web server. The web server passes the request to the application which then sets the request classification rule class to high for this request.
Example — Subsequent Service Requests
Subsequent | WebQoS | | high class | | high class | Plug-In |
|
| classification rule | Web | classification rule |
Service | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | Server | | | | |
Requests | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
In Figure 1-2, “Example — Subsequent Service Requests,” subsequent requests during this WebQoS session use the high request classification rule class set by the application. The application can change the request classification rule class value one or more times during the session. This