ÉÂÔ
Page
ÉÂÔ
Third Edition May 1999
Contents
SQL
With
Service Program
Chapter
Vi ILE
Exception
Working with Files and Devices
Vii
RPG
Files
Appendixes
ILE
Copy
Index
Does
Apply
Any
Law
Trademarks and Service
Programming Interface Information
Marks
Trademarks Or se Marks Others
Page
Xiv ILE RPG for AS/400 Programmers Guide
About This Guide
Guide
Who Should Use This
III
How to Send Your Comments
Prerequisite and Related Information
What New This
Release?
UCS-2
Risc
INZ*EXTDFT
INZ*USER
Element
CCSID*GRAPH
To this Guide
Changes
Since
For AS/400
Xxii ILE RPG for AS/400 Programmers Guide
ILE RPG Introduction
Program creation strategies
ILE RPG for AS/400 Programmers Guide
RPG IV Specifications
Control Specifications
Input Specifications
RPG IV Overview
The.When You Let Compiler Provide Logic For Your
Cycle Programming
Subprocedure logic
Indicators
First
Last
Operation Codes
Program
Example of an ILE RPG
Example of an ILE RPG Program
Program
File Description Specifications
Second file
Output Specifications
Bonus
Chain
Eval
Subprocedure
Heading Lines That Contain Constant String Payroll
ILE RPG
Not
Return
Entire Source Program
Fqsysprt Printer
Rate
Bonus PAY
10U 0 Value
Not *IN99 Eval
Commonly Used Control Language Commands
Interacting with the System
OS/400 System
System Library
System Offers Full Set Tools That You May find usef
Application Development Manager
AS/400 Tools
Services
ILE R
Overview of the RPG IV Programming15 Language
AS/400 Tools
RPG Programming in ILE
Program Creation
RPG Programming in ILE
ILE RPG, ILE C, ILE Cobo
CRTSRVPGM, and Crtpgm commands. They can also Specified
Language You can Create
Procedure Followed Zero Or more subprocedures
Program Management
Program Call
ILE
Bindable APIs
Source Debugging
While the progra
Accesses Are Also Threadsafe
Multithreaded Applications
AS/400 now supports multithreading. ILE
Does Not Directly
RPG Programming in ILE
Program Creation Strategies
Strategy 1 OPM-Compatible Application
Method
OPM-Compatible Application
Example of OPM-Compatible Program
Effect of ILE
Related Information
ILE Program Using Crtbndrpg
Strategy 2 ILE Program
ILE Program Using Crtbndrpg Example of ILE Program
Shows Run-time view Application in which an ILE CL pr Calls
XYZ
Although Actual Storage Not Deleted As it
Using
ILE Application Using Crtrpgmod
Strategy 3 ILE Application
Scenario
Single-Language ILE Application
Single-Language Application Using Crtrpgmod and Crtpgm
Mixed-Language ILE Application Scenario
Advanced Application Scenario
Strategy to Avoid
Strategy to Avoid
Activation Group
Creating an Application Using Multiple Procedures
Multiple Procedures Module
Procedures
Overview
Prototyped Calls
What a module might
Like with Multiple Dures
Module
Using prototyped calls you can call with the same syntax
FmtCust Name 100A Address
NumToChar
Numparm 30P 0 Value
Example of Module with
Order to format Name Address Properly
Made Expression Shows Call
Multiple
Example of Module with Multiple Procedures
DDS
ISO Move
Else
Procedures
STATE, ZIP
That
ZIP
Module
Meaning that it consists only of subprocedur
Module, by Coding
Keyword on the control specificati
Entire Arrsrpt Program
Fcustfile Disk Fcustrpt Printer
Copy QRPGLE,CVTPROCP
Icustrec
Callp
Endsr
Following About
Arrsrpt
ISO Move Duedate
Return Else Endif
DDS
When Coding Module with multiple procedures You Will Want
Coding Considerations
General Considerations
Coding Considerations
Main Procedure Considerations
Subprocedure Considerations
Contain a program entry procedure and only a
Cannot Contain Bound Procedure Calls
Main Procedures
Subprocedures
For Further Information
For
Prototyped Call
For Further Information
Application
Running an
ILE RPG for AS/400 Programmers Guide
Statements
File
Source
Creating a Library
Using SEU
Using the Source Entry Utility
Entry Utility
IPC
Ipcx
IPP
Ippr
Press F3 Exit To the Exit display. Type Y Yes to save
Saved
Using SQL Statements
Using SQL Statements
Statements Calculation specification Start Your
DB2 UDB
Reference for more
Refer toADTS thefor AS/400 Source Entry
Utilitymanual for Information about How SEU handles
Statement Syntax Checking
Using the Crtbndrpg Command
Command
With
You can use the Crtbndrpg Command interactively Batch From
Shows Their Default Values
Debugged Using a Source View Program Type
Creating a Program for Source Debugging
List
Creates View similar Compiler listing
Binding
Creating a Program with Static
This example you create Program
Display Module Source
Command
Bnddir
¹ Wrkjob
¹ Wrkoutq queue-name
Disk Fqsysprt Printer
Chain Emprec Not *IN99
Payroll Register Date
Empname Emprate
Using a Compiler Listing
Using a Compiler Listing
Listing
Obtaining a Compiler
Customizing a Compiler Listing
Customizing a Page Heading
Compiler Listing
Xref
Last Update
Customizing the Spacing
Indenting Structured Operations
PAGE/LINE
Errors
Listing
Either Create
This Will Add Sec Level text to the messages listed Message
Using In-Line Diagnostic Messages
FLD2
FLD1
SEU
Correcting Run-time Errors
Using Additional-Diagnostic Messages
Browsing a Compiler Listing Using SEU
Source Entry Utility
Using a Compiler Listing for Maintenance
Expdds these are the defaults
Coordinating Listing Options with Debug View Options
Specified, and in the column labeled as Sta Ment
Area
Data
Accessing the Returncode Data Area
Accessing the Returncode Data Area
Commands
Creating
Module Object
Chapter
Using the Crtrpgmod
Command
You Create a Module using the Create
Creating a Nomain Module
Requested
Creates a compiler listing which
Crtrpgmod MODULEMYLIB/TRANSSVC SRCFILEMYLIB/QRPGLESRC
¹ Dspjob
Then Select option Display4 spooled
Files
Related Files N/A Related Source Transrpt
Endsl Return
Other
Endsl
Creating a Module for
Prototype for TransInc
Prod
Prototype for ProdName
Itrnsrec
Ftrnsdta Disk Fqsysprt Printer
QTY
Related CL Commands
RPG, mainthe procedureis
Additional Examples
Modules
Binding Modules into a Program
Binding Modules into a Program
Binder
Using
Command
Into a
Crtclmod
Group
Export
Concepts for
Modules
Trpt
Using a Binder Listing
Using a Binder Listing
Changing a Module or Program
Changing a Module or
Using the Updpgm Command
Level
Size
Removing Observability
Reducing an Objects
Changing a
Changing a Module or Program
Creating a Service Program
Service Program Overview
Service Program Overview
Dspsrvpgm Payroll DETAIL*PROCEXP *DATAEXP
Strategies for Creating Service Programs
Creating a Service Program Using Crtsrvpgm
Creating a Service Program
Using Crtsrvpgm
Changing a Service Program
Service Program Using Crtsrvpgm
Sample Service Program
Sample Service Program
API
Opdesc
Const OPTIONS*VARSIZE
OPTIONS*VARSIZE
Ceedod
Exsr
Enddo
Begsr Eval
DIV MVR
Creating the Service Program
Parameters Crtsrvpgm command
Strpgmexp Signaturecvthex Export Symbolcvttohex Endpgmexp
Input String Charactern Output Hex string Character2 * n
Binding to a Program
Create the program by typing
Crtrpgmod MODULEMYLIB/CVTHEXPGM SRCFILEMYLIB/QRPGLESRC
Call Cvthexpgm
Copy RPGGUIDE/QRPGLE,CVTHEXPR
Clear Callp
Except
Clear
Updating the Service
Sample Binder Listing
Basic Binder listing for Cvthexpgm
Sample Service Program
Running a Program Using the CL Call Command
Running a Program Using
Running a Program
103
Passing Parameters using
106 shows DDS That is Referenced by the EMPRPT2 Source
Application
Running a Program From a Menu-Driven Application
Running a Program From a
Selecting Option Design menus
Rpginq
You Run Menu by Entering
RPGCHG, or Rpgadd respectively
Command
Running a Program Using User-Created
Replying to Run-Time Inquiry Messages
Replying to Run-Time Inquiry
Ending an ILE Program
Groups
Managing Activation
Wheresequence-no
Managing Activation Groups
Specifying an Activation
Group
OFF
Default
Compatibility
Running in the OPM
Activation
Reclaim Resources Command
Deleting an Activation
Group
Activation Groups Such
Managing the Default Heap Using RPG Operations
Referenceto Abridged
INZ*NULL
Managing Dynamically-Allocated Storage
Dsply
Alloc
AddName 40A
Elem@ = next@
= *NULL
Namelen = %len%trimrname
Null DOW
Heap Storage Problems
Dealloc
RPG procedure This
Managing Your Own Heap
Bindable APIs
Call Somepgm
SeeAPI theReference
Dynarray
Ceegtst
Copy Dynarri
Ceecrhp
Initalloc
Subsalloc
Reset
Dynainit
ADD Initalloc
Enddo Dynainit
Dynaset Export
Ifgt
Exsr Realloc Endif Eval
Realloc Begsr
Else ADD Subsalloc
Enddo Endsr Dynaset
Dynaget Export
Ifle
Get Heap Storage
Crtsrvpgm
Calling Programs and Procedures
Program/Procedure Call Overview
Program/Procedure Call Overview
127
Calling Programs
Calling Procedures
Static
Call stack
Call Stack
Stack
Recursive calls are only allowed For
Recursive Calls
That Most r Stack Entry is Bottom
Parameter-Passing Considerations
Recent Caller
Program/Procedure Call Overview
Using the Callp Operation
¹ Subprocedures in the same module
RPG Prototyped calls Are also Known
Callp
Using a Prototyped Call
Calling within an Expression
31A
30P
Examples of Free-Form Call
Passing Prototyped Parameters
Parameter Passing Styles
Passing by Reference
Passing by Value
Figures below
Passing
Extprocdocalc
Docalc Export
Docalc
ILE CEE API
Using Operational Descriptors
Ceetsta Extprocceetsta
When Calling Procedure You may sometimes want Leave Out Par
Omitting Parameters
OPTIONS*OMIT
Omit
Passing *OMIT
Leaving Out Parameters
OPTIONS*OMIT*NOPASS
API Qcmdexc
Passing Prototyped Parameters Checking for the Number
Psds
Copy Fmtaddrp
OPTIONS*NOPASS Const
Eval Address = %TRIMRCSTREET# + +
Trimrprovince Return
Check
Begsr Movel
Endif Endsr
144
OPTIONS*NOPASS
Ctdata
5P 0 DIM2 Ctdata
To create PRTADDR, using the source in on page 144, typ
Passing Less Data Than Required
Parameters
To create the program, PRTADDR, type
Interlanguage Calls
Order of Evaluation
Effect
Interlanguage
Calling Considerations
To obtain Actual Returned value
DCL &RET2 TYPE*CHAR LEN2 DCL &RET1 TYPE*CHAR LEN1
Call Operations
Fixed-Form
For Callb only
Using the Fixed-Form Call Operations
Operation Operation extender is Used With
Passing Parameters Using Parm
Examples of Call and Callb
Operations
Operation
Fixed-Form Call Operations
Using the Plist Operation
Plist
Returning from a Main Procedure
Procedure
Normal End
Returning from a Called
Abnormal End
Returning from a Called Program or Procedure
Entry Parm operation is perfor
Returning from a Subprocedure
Without
For the AS/400 Reference
Retu
Using Bindable APIs
Returning using ILE Bindable
Subprocedure ends abnormally
APIs
Examples of Using Bindable APIs
Calling a Graphics Routine
Calling a Graphics Routine
Ceeutx
Calling Special Routines
Multithreading Considerations
Multithreading Considerations
TheGDDM Programming Guide
Across
How to
Share Data
Example, consider the situation where two procedures Called
Will Wait For MOD1 Unlock. Procedures Not
How
To Avoid Deadlock
Considerations
PROC1
MOD2
MOD1
Debugging and Exception Handling
161
ILE RPG for AS/400 Programmers Guide
Debugging Programs
ILE Source Debugger
ILE Source Debugger
163
Debug Commands
Attr
Equate
Eval
Tbreak
Thread
Watch
Find
Order Debug it using
Preparing a Program for Debugging
Preparing a Program for
Source
Creating a Root Source View
Options On the Dbgview parameter for Either
Crtbndrpg PGMMYLIB/DEBUGEX SRCFILEMYLIB/QRPGLESRC
Crtrpgmod MODULEMYLIB/DBGEX SRCFILEMYLIB/QRPGLESRC
Listing View
View
Dbgview
Module
View
Program for Debugging
Starting the ILE Source Debugger
Starting the ILE Source
OPMSRC*NO
Setting Debug Options
Strdbg Example
Start a Debug Session for the sample debug program Debugex
Into
SET
OPM source debug support field,
Example of Adding a Service
Example of Removing ILE Programs from a Debug Session
Adding/Removing Programs from a Debug Session
Debug Session
Viewing the Program Source
Viewing the Program Source
Cobol
Lstdbg ILE
Dbgex
Viewing a Different
Libl PGM
Changing the View of a
Module
Several Different views
Cproc
Setting and Removing Breakpoints
Setting and Removing Breakpoints
Specified You Not Erate Breakpoints Specify
OPTION*NODEBUGIO
Setting and Removing
With the source positioned at the line where the breakpoint
Debug Command to set a job breakpoint
Breakpoints
Job
Setting an
Breakpoint
Setting and Removing Unconditional Thread Breakpoints
Debug Command Sets a Thread breakpo Single Current
Debug
Greater Than Equal To one
Job
Breakpoints
Example of Setting a Conditional Job Breakpoint Using F13
Line
Conditional Breakpoint
Work with Module Breakpoints
Command
Setting a Conditional Job Breakpoint Using
Break 128 when BigDate=1994-09-30
National Language Sort Sequence Nlss
Control Spec Tion Is not available
Sort Sequence
On the debug command line
One procedure per module,procedurethe -namecan Either
Main procedure or one of the subprocedures
Varia
This Example Statement View Is used to Set Breakpoint For
Set a breakpoint for Module With
Set Breakpoint For Module with
Listing, type
Setting and Removing Conditional Thread Breakpoints
Using the Work with Module Breakpoints Display
Procedurevariables-name and statement-number
Main Procedure Exit
Debug Commands
Setting and Removing Watch Conditions
Removing All Job
Conditions
Characteristics of Watches
Display
Program statemen
You Debug One Job From Another
Setting Watch Conditions
On the debug command line, without any parameters
Watch
Salary
Payroll ABC PGM
¹ To specify a variable or expression to be watched, type
Payroll
Displaying Active Watches
Removing Watch Conditions
Enddbg
IPL
Example of Setting a Watch Condition
Example of Setting a Watch Condition
BlankDisplay Module Source
Display as shown below. Instead
Stepping Through the Program Object
Object
Stepping Through
Stepping Over Call Statements
Over Into Subprocedures
Subroutines You Can
Step Into
Stepping Into Call Statements
TIP
F22
This example, you use F22 Step Into to step Into the OPM
From Program
Debugex
InputParm
This example, you use F22 Step Into to Subpr Which Module
Step completed at line
Displaying Data and Expressions
Switch
Else
On page 201 shows Use
Const
Unexpected Results when Evaluating Variables
Scalar Fields RPG Definition
Based Fields
Date, Time, Timestamp Fields
Displaying the Contents of an Array
Displaying the Contents of a Table
Displaying Data Structures
Eval DS12
Displaying Indicators
Which is discussed Below
Displaying Fields as Hexadecimal Values
Character Format
Data
Displaying Variable-Length Fields
By Pointers
Displaying Null-Capable Fields
STRING=%SUBSTRBIGDATE 1 4 =
String = 1ABCD6
Fields
Changing the Value of Fields
= Abcdef
Or Command
Equating a Name with a Field, Expression, or Command
Displaying Attributes of a Field
Equating a Name with
Sample Source for Debug Examples
For
Examples
Program using Source 215, type
Sample Source for Debug Examples
To create the program DEBUGEX, type
First Module
DIM3 Ctdata
DS1
Inzabcde
DS2
Plist Parm
Occur DS2 Move
Call Rpgpgm
Dump Seton
Else Eval
Entry Plist Parm
Dsply Seton
Source for C Procedure cproc. cproc is called by Dbgex
Handling Exceptions
Exception Handling Overview
Exception Handling Overview
217
Indicates That Severe error has been detected
Program Procedure P1 is Contro Boundary
Describes Status Work Being done by a program
Call st
Exception Message
Active on
ILE RPG Exception Handling
Dure will Only Handle Errors That Subprocedure
Exception Handling within
Operation For
OPM
PGM C
Using Exception Handlers
Using Exception Handlers
Exception Handler Priority
Nested Exceptions
For other Types Messages
Escape Message
PGM2
PRC1
Example of Unhandled Function Check
Operation as well
PGM1
PGM2, each Containing a procedur
Using RPG-Specific Handlers
Optimization Considerations
For More Information Optimization See Changing Level
Built-in-functions
This Section Provides Some Examples How to Use Each These R
Infsr error Subroutines, on Exsr Operation Code Infds
Extender
ILE RPG For AS/400 Reference provides
Using an Error Subroutine
Program Error
Operation. If Either
Explicitly c
Using a File Error Infsr Subroutine
INFSRPrdInfsr INFDSPrdInfds
Disk Ftrnbacklg O Fprint Printer
PrdInfds PrdStatus
Status
Infds
Using a Program Error Subroutine
Position Definition Specification Enter
After Keyword
Operation With Factor Entry
Parms
Proc Body of Code Goes Here
Pssr Begsr
Move Getin
If this is a divide-by-zero error, add 1 to the divisor
If control reaches ENDSR, the procedure will fail
TAG DIV
Try again Err =
Exceptions Order Show how to avoid looping Within
Pssr
Which is designed to ge
Subrou
Move Inlr
After the Else
Else ADD
Specifying a Return Point
OFL
Using a Condition Handler
ILE Condition Handlers
ILE Condition Handlers
Handlers
132
Printer Rpghdlr
LIKECondTok
Action 10I OutCondTok LIKECondTok
Shows Source For Procedure
Is registered Procedure Parameters Include Pointer
Condition Handler
Communication Area Which Contains Pointer
ARR1
Ceehdlu
Procptr
Noopt
SDS Noopt
Proc
Subst
Begsr Callp
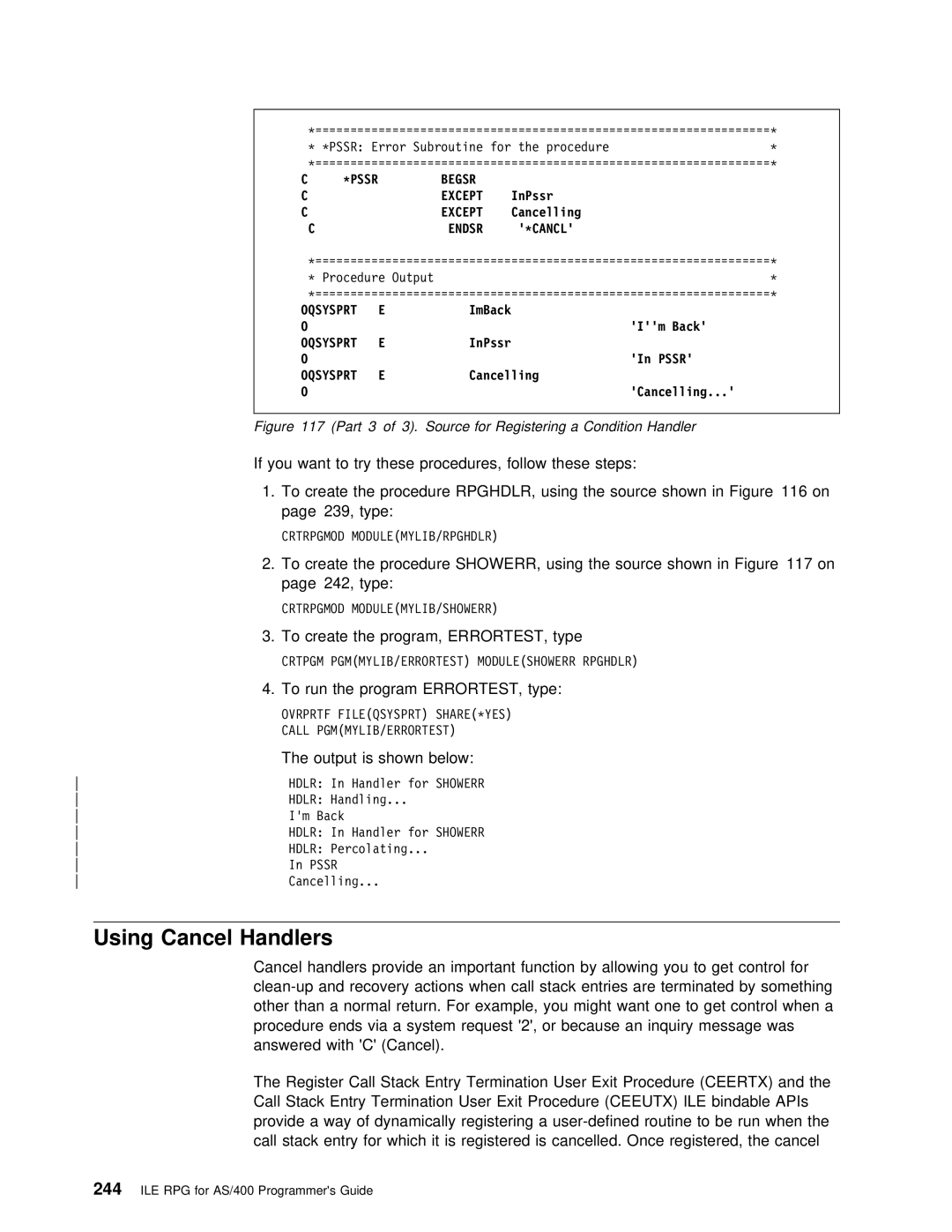
Cancel Handlers
244
Ceertx
Ceeutx ILE
Procedure to SubProc will not fail
Pssr has a Return operation, so the call from the main
Subproc Pssrdsply
Return Endsr
INZ0 Static
Callb Ceertx Parm
Parm Omit
Select When
RPG using
Condition Handlers Enabled Using
Cancel Hdlr Dsply Msg CanHdlr
Likely Occur With
Condition Handler that Ignores CPF4906
Endif Return
Handle information or warning messages, otherwise percolate
MsgSev = Warning
ILE RPG for AS/400 Programmers Guide
Using the Dump Operation Code
Using the Dump Operation Code
Obtaining a Dump
Obtaining an ILE RPG Formatted Dump
¹ If a Dump operation is bypassed By a Goto operation,
Formatted Dump
Does not Occur
Dump
Example of a Formatted Dump
Qspl
Agement
Dump
Part 1 of 2. Data section of Formatted Dump
125 Part Data section of Formatted Dump
Beginning of user variables, listed in alphabetical order,
Order Which they are defined Gaps
Working with Files and Devices
259
ILE RPG for AS/400 Programmers Guide
Defining Files
Associating Files with Input/Output Devices
Associating Files with Input/Output Devices
261
Compilation Time Certain
Operation Device Dependent Device dependency Is that
Operation Code is Valid Only
Write
Types of File Descriptions
Naming Files
Types of File Descriptions
Using Files with
Program-Described
Files
Example of Some Typical Relationships between
Defining Externally Described
Defining Externally Described Files
OPTION*EXPDDS
Renaming Record-Format Names
Ignoring Record Formats
Renaming Field Names
Nbrofcharreplaced. Figure
Using Input Specifications
Modify an
Description
External
You Then Fixed Name Specification Will Get Error
Indicator Record
Files
Used Program This Example Field
Using Output Specifications
Level Checking
For Character Fields zero
Is written
ALL
Defining Program-Described Files
Data Management Operations and ILE RPG I/O Operations
RPG I/O Operations
SEQ Special
Data Management Operations and ILE RPG I/O Operations
Delete
File Considerations
Overriding and Redirecting File Input and Output
Overriding and Redirecting File Input and Output
273
Input Output
Input Output
Example of Redirecting
FMT1
File Locking
File Locking
Data Management manual
Program Can Chang Allocate Object
Record Locking
Record Locking
See Using
Path
Sharing an Open Data
Control For More Information
Spooling
Spooling
Program Details System Open Options Allowed for Each
Can Specify
Output Spooling
Program Versus
SRTSEQ/ALTSEQ
Accessing
Database Files
Physical Files and Logical Files
Data Files and Source
Using Externally Described Disk Files
Record Format Specifications
Access Path
Using Externally Described Disk Files
Unique
Contained Physical file CUSMSTP, which is Identified
Unique
Dstref Distribution Application Field Reference
Basdat Edtcdey
Cust Checkmf
Addr Reffldname
Valid Keys for a Record File
Disk
City
Edtcdej
Partial Key
Arguments
Referring to
Record Blocking and Unblocking
Used,
Using Program-Described Disk Files
Using Program-Described Disk Files
Indexed File
Valid
Keyword specifies position 15 as the starting po
Logical file ORDDTLL. For the two fields
Sequential File
Record Address File
10AIDISK
Move Order KEY Chain
Methods for Processing Disk Files
Limits Records
Relative Record Numbers
Methods for Processing Disk Files
Subsequent Text Describes Each Method Processing
Consecutive Processing
ADD
Sequential-by-Key Processing
Examples of Sequential-by-Key Processing
Database Programming
Database Programming manual
Example, the employee master record
Weekly hours worked
YTDRPT1 Related Files EMPL1
Fprint
FEMPL1 Disk
Iemprec Ircweek
YTDRPT2 Related Files EMPL1
Setoff Read EMPL1 Goto Eofend Move Enum Empno
Seton Endif
Eofend TAG Seton
For Processing Disk Files
Records Are Processed as Matching records With
ADD Tothrs Totovt Setoff
ADD Ehwrk Tothrs
SUB Enhrs Ovthrs
ADD Ovthrs Totovt Seton Endif Oprint
Random-by-Key Processing
Example of Random-by-Key Processing
Emstupd Descriptions
Nnhrs
Change
Sequential-within-Limits Processing
Fchange
Examples of Sequential-within-Limits Processing
Disk Files
ESWLIM1 Related Files Empmst
Limits
Flimits Disk
3PIDISK KEYLOC1 Fprint
ESWLIM2 Related Files Empmst
Relative-Record-Number Processing
Fempmst Disk Fprint
Valid File Operations
Valid File Operations
Z/F
Recno
Using Commitment Control
Using Commitment Control
Starting and Ending Commitment
Commitment Control Locks
See theBackup and Recovery manual
Abridged for
Using
Files For
Specifying
Concepts,
Receiver
Example of Using Commitment Control
Journal
This command calls the program Revise
Update Mastrec Tranrec
Control
Disk Commit Ftrans
DDM Files
Cycle
DDM Files
Pre-V3R1 DDM
ReferDistributedto the Data
DDM Files
Accessing
Types of Device Files Chapter
Attached
315
Accessing Printer Devices
Accessing Printer Devices
Specifying Printer Files
Handling Page Overflow
Overflow
On an and notline,anoverflowthe linelineis
Example of Printing Headings on Every
Example of Printing a Field on Every
OANL2
Account
Routine in Program-Described Files
Using the Fetch-Overflow
Overf
Overflow Printing Setting of the Overflow Indicator
Fetch Overflow
Example of Specifying Fetch Overflow
File
Changing Forms Control
OPM Prtctl data structure
Dat
Values Contained First four subfields
Forms
Accessing Tape Devices
Accessing Tape Devices
Print
File Name Associated Data Structure is
Accessing Display Devices
Using Sequential Files
Using Sequential Files
Ovrdbf
Using Special Files
Using Special Files
File
Program name
Status
Error
Description
Example of Using a Special File
Special Pgmnameuserio
FLD
Spcl Plist Parm FLD1 Movel Hello Write Excptn Outbuf Seton
Program User-written routine
Are Added To the end of the RPG-created Parameter list
Userio
Using Externally Described Workstn Files
Using Workstn Files
Function
¹ Output
On page 333 shows an example of the DDS for a display-devic
Refdstref
Prompt
Overlay
Descrp
Specifying Command Keys Display
Specifying Function Key Indicators on Display Device Files
Device
Using Subfiles
Processing an Externally Described Workstn File
Field
Sfile
Use of Subfiles
You press Specified Function key During Read
Name Search
SFL TEXTSubfile Record
Using Program-Described Workstn Files
Using Program-Described Workstn Files
Subfil
Using a Program-Described
With
Input Specifications
Calculation Specifications
Name
Format
Valid Workstn File Operations
Input File
Output File
Combined File
Exfmt Operation
Read Operation
Write Operation
Multiple-Device Files
Devid
Is updated
Keyword. This field Initialized
Multiple-Device Files
Example of an Interactive Application
Database Physical File
Database Physical File
345
Inquiry
DDS for a
Display Device
Main Menu Inquiry
Cusmain RPG Source
First option specifies that the first module in the list
Using Crtrpgmod Create Program By entering
Main menu will appear as in on
File Maintenance
File Maintenance
CUSMSTL1 DDS for a
Logical
Display
Device
70DATE Edtcdey
Mode
Edtcdez
Record Format contains Constant Customer File Maintenance
Cusmnt RPG Source
Addsub Begsr Cstkey Chain CMLREC1 Not *IN50 Move
Subroutine Addsub Purpose
Else Move OFF
Move ADD Mode When
Move Update Mode When
Move Delete Mode When
Move Display Mode Endsl MODE1 Endsr
Display Mode
Customer File Maintenance
Cstinq
223021
On page 357 a new customer is added to the Customer Mast
223106
30/94 Customer 00007
223143
Delete Mode
ADD Mode
Bathurst Avenue
Zip
Search by
Search by Zip Code
Code
Szipmenu
Related Files CUSMSTL2
File SZIPMENU. IT has
REFCUSMSTL2 Printqsysprt Indara
Indicates when to display Subfile When Indicator 55 is
Schzip RPG Source
Move OFF
Write Subctl Move OFF
ADD Zero Recnum Endsr
File indicator 71 on th
Zip
Routine Fills Subfile Record Read From
Subfile Is written to the screen as shown in on
Search and Inquiry by Name
Search and Inquiry by Name
For Database File Used This Program Defines one reco
Identifies Name field Key Fields
Device File
Snammenu DDS for a Display
FOOT2
Subfile
Records Using Subfiles
Schnam RPG Source
This Program Prompts the User for the Customer
File by the Setll OPERATION. then IT Displays
Example of an Interactive 367Application
File Indicator On the Read operation
File Record Count
Recnum
Inc
Judah Gould
Inquiry by Name
233948 30/94 Customer 00012 Name
Gould
Yorktown
Appendixes
371
ILE RPG for AS/400 Programmers Guide
RPG/400 ILE
For AS/400
Appendix
Differences
Running
Debugging and Exception
RPG III
Will issue the RNQ1222 inquiry Message
RPG/400 Will Issue
Will issue the RNQ1022 inquiry Message
Will Issue
Compiler Such Programs Will Get Compilation errors
Dbcs Data in Character Fields
Differences Between OPM RPG/400
Appendix B. Using
Conversion Overview
379
Hurry
File Considerations
File Record Length
Conversion Aid Tool Requirements
Log File
USE
Wont Do
Converting Your Source
Converting Your Source
Aid
Cvtrpgsrc Command
Fromfile
Libl
Curlib
Frommbr
Tofile
Qrpglesrc
None
Tombr
Expcpy
YES
Cvtrpt
Seclvl YES Insrtpl
Converting a Member Using
Defaults
Source
Converting All Members in a File
Performing a Trial Conversion
Converting Some Members
Cvtrpgsrc FROMFILEOLDRPG/QRPGSRC Frommbrpayroll TOFILE*NONE
Obtaining Conversion Reports
Converting Auto Report
Source Members
CVTRPT*NO
Inserting Specification Templates
Data
Example of Source Conversion
Example of Source Conversion
To convert this source, enter
Example Source Conversion
Converted source is shown in on
ARR2
III specifications for ARR2. The Conversion Aid
Analyzing Your Conversion
Analyzing Your Conversion
DS1
Using the Conversion
Shows Command summary for a sample Conversion
Report
Conversion Aid generates a conversion report if you specify
Your
Call PROG1
Using the Log File
Qrncvtfm Lgcent Colhdgcvt Cent
Lgdate Colhdgcvt Date
Ymmdd
Lgtime Colhdgcvt Time
Resolving Conversion Problems
Compilation Errors in Existing RPG III Code
Unsupported RPG III Features
Use of the /COPY
TEST1
Context-Sensitive Problems
Records Using
Members in the converted RPG IV source member
Comp
Command Or manually Correct Code After Conversion
Use of Externally
Structures
Char
When converted
Merging an Array with an Externally Described DS Subfield
Initializing
Extrec
Run-time Differences
Behavior With
XYZ
Dsone Extnameextrec Char
Resolving Conversion Problems
Appendix C. The Create Commands
Using CL Commands
How to Interpret Syntax Diagrams
Reading Syntax Diagrams
Crtbndrpg Command
Crtbndrpg Command
Values
KEYWORDREQUIRED-VALUE
Appendix C. The Create Commands407
Description of the Crtbndrpg Command
PGM
Program-name
Srcfile
Srcmbr
Genlvl
Text
Srcmbrtxt
Option
Noxref
GEN
Nogen
Noext
Elseif
Eventf
Dbgview
Stmt
List
ALL
Output
Print
Optimize
Cvtopt
Datetime
Graphic
Varchar
Langid
Replace
Usrprf
User
Issued
Change
USE
Exclude
Fixnbr
Zoned
Tgtrls
PRV
Alwnull
Inputonly
Bnddir
Binding-directory-name
Usrlibl
Actgrp
Qile
NEW
Crtrpgmod Command
Crtrpgmod Command
Prfdta
Nocol
Appendix C. The Create Commands421
Description of the Crtrpgmod command
Usrprf
PF4
PF1
Compiler Listings
Appendix D. Compiler Listings
423
Which was Compiled Using
Compiler Listing
Reading a
Crtb
Module or Program
Source member
Compiler options
Indentation Mark
Endif
Section
Eject
Listings
Sequence Numbers Root
Part 1 of 3. Sample Source Part of the Listing
Part 2 of 3. Sample Source Part of the Listing
1a/ *NOSRCSTMT Source Heading
Line Number
Ruler Line
Do Number
Diagnostic
Additional
Output Buffer Positions
Copy Member Table
Compile-Time Data
Total Number of Characters Altered
Character to be Altered
Alternate Sequence
Key Field Information
Cross-Reference Table
External References List
Duedate
Message Summary
Final Summary
Code Generation and Binding Errors
N a L M M a R Y
Compiler Listings
Bibliography
439
Iddu
ILE RPG
ILE RPG for AS/400 Programmers Guide
443
Special
Characters
See
Ceeutx
See AlsoILE
Control-record format, subfile Create Program
Dbcs
Describing
Dsppgmref
Binder Listing 100 Exception Service
Find
See halt
See file
See last
See long
Plist
Methods
Qual
OA-OG, OV
SEU
See DB2
Totc
ILE RPG for AS/400 Programmers Guide
Éâôù