EM78P468N/L
Elan Microelectronics Corporation
Contents
Infrared Remote Control Application/PWM Waveform Generate
Appendix
Doc. Version Revision Description Date
Contents Product Specification V1.5
General Description
Features
Bit Microcontroller
Pin Assignment
Pin QFP Pin Lqfp
Block Diagram
System Block Diagram
Pin Description
Symbol Pin No Type Function
Pin Description for Package of QFP64 and LQFP64
Pin Description for Package of QFP44 and LQFP44
SEG11~SEG14
Operational Registers
2 R1/TCC Timer Clock Counter
Function Description
1 R0/IAR Indirect Addressing Register
On-ChipProgrammemory
Bit 2 Z Zero flag
4 R3/SR Status Register
Bits 6 ~ 5 PS1 ~ 0 Page select bits
Bit 0 C Carry flag
7 R6/Port 6 Port 6 I/O Data Register
5 R4/RSR RAM Select Register
6 R5/Port 5 Port 5 I/O Data and Page of Register Select
8 R7/Port 7 Port 7 I/O Data Register
10 R9/LCDCR LCD Control Register
Bit 4 Lcden LCD enable bit
9 R8/Port 8 Port 8 I/O Data Register
Lcdtype = 0 a type waveform Lcdtype = 1 B type waveform
11 RA/LCDADDR LCD Address
RC/CNTER Counter Enable Register
RB/LCDDB LCD Data Buffer
Main clock
14 RD/SBPCR System, Booster and PLL Control Register
Address 0Dh
Example Fs=32.768K
Bit Microcontroller CPU Operation Mode
15 RE/IRCR IR and Port 5 Setting Control Register
Address 0Eh
Address 10h~3Fh R10~R3F General Purpose Register
16 RF/ISR Interrupt Status Register
Address 0Fh
Accumulator
Special Purpose Registers
Address 05h, Bit 0 of R5 =
5 IOC80/P8CR Port 8 I/O Control Register
3 IOC60/P6CR Port 6 I/O Control Register
4 IOC70/P7CR Port 7 I/O Control Register
6 IOC90/RAMADDR 128 Bytes RAM Address
IOCC0/CNT2PR Counter 2 Preset Register
IOCB0/CNT1PR Counter 1 Preset Register
IOCD0/HPWTPR High-Pulse Width Timer Preset Register
IOCF0/IMR Interrupt Mask Register
IOCE0/LPWTPR Low-Pulse Width Timer Preset Register
Bits 6, 5, 4 Not used
Bits 3~0 PSRE, TCCP2 ~ TCCP0 TCC prescaler bits
14 IOC71/TCCCR TCC Control Register
Bit 7 Intedge
TCC Rate
Bits 7 ~ 4 Not used
15 IOC81/WDTCR WDT Control Register
16 IOC91/CNT12CR Counters 1, 2 Control Register
WDT Rate
High-pulse Width Timer Scale
IOCA1/HLPWTCR High/Low Pulse Width Timer Control Register
Low-pulse Width Timer Scale
Counter 1 Scale
IOCD1/P8PH Port 8 Pull High Control Register
IOCB1/P6PH Port 6 Pull-high Control Register
IOCC1/P6OD Port 6 Open Drain Control Register
IOCE1/P6PL Port 6 Pull Low Control Register
TCC and WDT Prescaler
MUX
Bit Microcontroller WDT Setting Flowchart
TCC Setting Flowchart
Reset and Wake-up
I/O Ports
Address Name Reset Type Bit
Bit Microcontroller Summary of Registers Initialized Values
INT Psre TCCP2 TCCP1 TCCP0
Name Reset Type Bit
Wake-up Signal Sleep Mode Idle Mode Green Mode Normal Mode
Oscillator
Phase Lock Loop PLL Mode
Oscillator Modes
Main clock Example Fs=32.768KHz
Crystal Oscillator/Ceramic Resonators Crystal
Oscillator Source Oscillator Type Frequency C1 pF C2 pF
RC Oscillator Frequencies
Power-on Considerations
RC Oscillator Mode with Internal Capacitor
Pin Rext Average Fosc 5V, 25 C Average Fosc 3V, 25 C
External Power-on Reset Circuit
Residue-Voltage Protection
Interrupt
13 Interrupt Back-up
1 R9/LCDCR LCD Control Register
LCD Driver
Bits 6 ~ 5 DS1 ~ DS0 LCD duty select
Bits 7 ~ 5 Not used, fixed to
2 RA/LCDADDR LCD Address
3 RB/LCDDB LCD Data Buffer
Bits 4 ~ 0 LCDA4 ~ LCDA0 LCD RAM address
4 RD/SBPCR System, Booster and PLL Control Registers
Bit 2 ~ 1 BF1 ~ 0 LCD booster frequency select bits
External circuit for 1/3 Bias
Boosting circuits connection for LCD voltage
External circuit for 1/2 Bias
16 LCD Waveform for 1/2 Bias, 1/2 Duty
18 LCD Waveform for 1/3 Bias, 1/3 Duty
Infrared Remote Control Application/PWM Waveform Generate
⋅ 1 + decimal C ounter Preset Value Iocc 0 ⋅ prescaler
21 LGP=0, Irout Pin Output Waveform
23 LGP=0, Irout Pin Output Waveform
Bit Microcontroller IR/PWM Function Enable Flowchart
IR application
Word
Code Options
Bits 12 ~ 10 Not used
Bits12~10 Word
Bits 2~0 PR2~PR0 Protect Bit
Instruction Set
PR1PR0Protect
Binary Instruction Hex Mnemonic Operation Status
Convention
Binary Instruction Hex Mnemonic Operation Status Affected
JZA
Timing Diagram
AC Test Input/Output Waveform
Items Symbol Condition Rating Min Max Unit
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol Parameter Condition Min Typ Max Unit
Electrical Characteristic
DC Electrical Characteristics
Ta= -40 C ~85 C, VDD= 5.0V, GND=
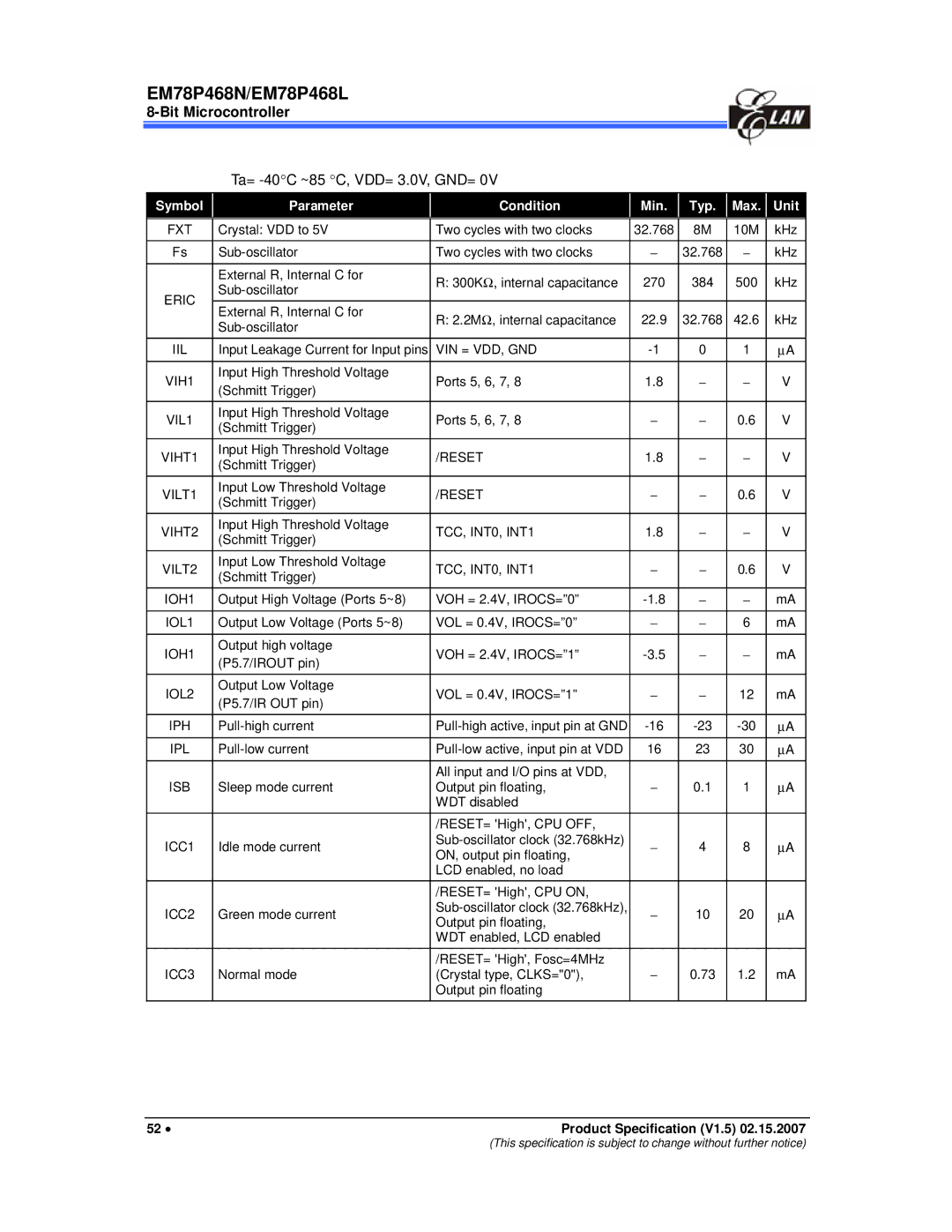
Ta= -40C ~85 C, VDD= 3.0V, GND=
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
AC Electrical Characteristics
Ta=- 40C ~ 85 C, VDD=5V±5%, GND=0V
Device Characteristic
Vih/Vil /RESET pins with schmitt inverter
Vih/Vil Port 7, Port 8 All Input pins with schmitt inverter
P5.7 Voh/Ioh VDD=5V, IROCS=1 P5.7 Voh/Ioh VDD=3V, IROCS=1
80 P5.7 Voh/Ioh VDD=5V, IROCS=0 Max Typ +25
Setup time from Power on Reset
= 51 K
13 Typical Eric OSC Frequency vs. Temperature Xin Pin
VDD=5V
Typical ICC2 vs. Temerature
Typical ICC1 vs. Temerature
Typical ISB vs. Temerature
22 Operating Voltage under Temperature Range of 0C to 70C
Application Circuit
Name Package Type Pin Count Package Size
Package Type
EM78P468NxS/xJ
Package Information
QFP
Lqfp
900 100 BSC 00 REF
Min Normal Max 30TYP 15TYP
EM78P468N/L Program Pin List
Wiring diagram is for Elan Dwtr
Program Pin Name IC Pin Name QFP-64 QFP-44
ICE 468XA Oscillator Circuit JP
Main oscillator Crystal mode, Sub oscillator Crystal mode
Main oscillator PLL mode, Sub oscillator Crystal mode
Main oscillator RC mode, Sub oscillator Crystal
Bit Microcontroller
ICE 468XA Output Pin Assignment JP
VLCD3 GND Osco
Address Trap Detect
Quality Assurance and Reliability
Test Category Test Conditions
Contents III