ERserver
Page
ERserver
Fifth Edition September
Contents
Selecting records in Query for iSeries
Defining result fields in Query for iSeries
Selecting and sequencing fields in Query for iSeries
Selecting sort fields in Query for iSeries
Selecting a collating sequence in Query for iSeries
Specifying report column formatting in Query for iSeries
Defining Query for iSeries report breaks
Part 3. Advanced information about Query for iSeries
Specifying Query for iSeries processing options
Exiting and running a Query for iSeries query
Working with Query for iSeries query definitions
Appendix B. Practice exercise for Query for iSeries query
Viii Query for iSeries Use V5R2
About Query for iSeries Use
Who should read the Query for iSeries Use book
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Part 1. Introduction to Query for iSeries
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
What is Query for iSeries?
Query for iSeries fundamentals
Files, fields, and record formats in Query for iSeries
State
Double-byte character set Dbcs fields in Query for iSeries
UCS2 level 1 character set support in Query for iSeries
Major functions of Query for iSeries
Query for iSeries definitions
Libraries in Query for iSeries
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
General operating information for Query for iSeries
Using Query for iSeries function keys
Displaying a Query for iSeries list
Using lists in Query for iSeries
Printing what you see on your Query for iSeries display
Special Library Name Description
Selecting items in a Query for iSeries list
Special library names in Query for iSeries
Query
Using Query for iSeries commands
Using the Query Utilities menu
Using the Work with Queries display
Choosing a single Query for iSeries task
Choosing multiple Query for iSeries tasks
Specifying a Query for iSeries query and its library
=Run
Qgpl
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Positioning a list of Query for iSeries queries
Acctrecfeb
Acctpayfeb
Acctpaymar
F12=CANCEL
Displaying the format of constants in Query for iSeries
QRY1
Qgpl Ccsid
Changing your Query for iSeries queries
Handling Query for iSeries messages and errors
Query for iSeries profile information
General operating information for Query for iSeries
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Creating a Query for iSeries query definition
Selecting and sequencing fields in Query for iSeries
Selecting sort fields in Query for iSeries
Defining Query for iSeries report breaks
Working with Query for iSeries query definitions
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Creating a Query for iSeries query definition
Starting Query for iSeries query definition
Define the Query Option Create Library Qgpl
Selecting options for a Query for iSeries query definition
Selecting files, records, and fields for Query for iSeries
Moving through the Query for iSeries definition displays
Considerations for creating Query for iSeries queries
Creating a Query for iSeries query definition
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Specifying and selecting files for a Query for iSeries query
Specifying file selections for a Query for iSeries query
First
Choosing a file for a Query for iSeries query
Choosing a library for a Query for iSeries query
Selecting multiple files for a Query for iSeries query
Exampfile
Removing a option for a Query for iSeries query
Using file IDs for a Query for iSeries query
Confirming your options for a Query for iSeries query
Selecting files on the Query for iSeries Select File display
Custinv
Cust
Custinv Custrelfeb
Custinv Custreljan
Custinv Custrelmar
Specifying and selecting files for a Query for iSeries query
EXAMPMBR1 EXAMPMBR2 EXAMPMBR3
EXAMPFMT1 EXAMPFMT2 EXAMPFMT3
EXAMPFILE2 Custinv First
Joining files in a Query for iSeries query
EXAMPFILE1 Custinv First
How to join files in a Query for iSeries query
Types of joins in a Query for iSeries query
ZIP NBR
Rules for joining files in a Query for iSeries query
NBR Name Phone Addr
Specifying and selecting files for a Query for iSeries query
Examples of joining files in a Query for iSeries query
Specifying and selecting files for a Query for iSeries query
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Specifying and selecting files for a Query for iSeries query
Correct method
Incorrect method
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Displaying all join tests in a Query for iSeries query
Handling missing fields in a Query for iSeries query
Page
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Defining result fields in Query for iSeries
Creating results fields in Query for iSeries
Query for iSeries result field name
Query for iSeries expressions
Page
Query for iSeries character expressions
Query for iSeries concatenation operation
Query for iSeries character functions
Substr Query for iSeries function
Digits Query for iSeries function
Value Query for iSeries function
Varchar Query for iSeries function
Reschar
Vargraphic Query for iSeries function
Result Ccsid Description Character
Date, time, and timestamp expressions in Query for iSeries
Query for iSeries date
Query for iSeries time
Query for iSeries timestamp
Format Name Abbreviation Time Format Example
Displaying constants format in Query for iSeries
Date arithmetic operation in Query for iSeries
Subtracting dates in Query for iSeries
Incrementing and decrementing dates in Query for iSeries
Working with numeric dates in Query for iSeries
SUBSTRCHARDATE,5,2’/’
SUBSTRCHARDATE,1,2’/’
Mmddyy Qtemp
Yymmdd
Time arithmetic operation in Query for iSeries
Durations in Query for iSeries
Timestamp duration in Query for iSeries
Date, time, and timestamp functions in Query for iSeries
Char Query for iSeries function
Date Query for iSeries function
DAY Query for iSeries function
Days Query for iSeries function
Hour Query for iSeries function
Microsecond Query for iSeries function
Minute Query for iSeries function
Month Query for iSeries function
Second Query for iSeries function
Time Query for iSeries function
Timestamp Query for iSeries function
Year Query for iSeries function
Converting date formats in Query for iSeries
Mmddyy
Yyddd
Commands to run the query in example 4 are
Odqysd NE Omcrmm EQ Omstat EQ ’50’ Odstat NE ’99’
Column headings in Query for iSeries
Length and decimal positions in Query for iSeries
Example of defining a result field in Query for iSeries
Adding or removing result fields in Query for iSeries
Selecting and sequencing fields in Query for iSeries
Letting Query for iSeries select and sequence fields
Acctnumber Pastdue Company
Firstname
Acctnumber Pastdue Company
Company Baldue Acctnumber
Lastname Streetaddr City State Zipcode Telenumber Crlimit
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Selecting the records you want in Query for iSeries
Selecting records in Query for iSeries
Letting Query for iSeries select records
Comparison fields in Query for iSeries
Comparison values in Query for iSeries
Numeric constants as values in Query for iSeries
Fields as values in Query for iSeries
Character constants as values in Query for iSeries
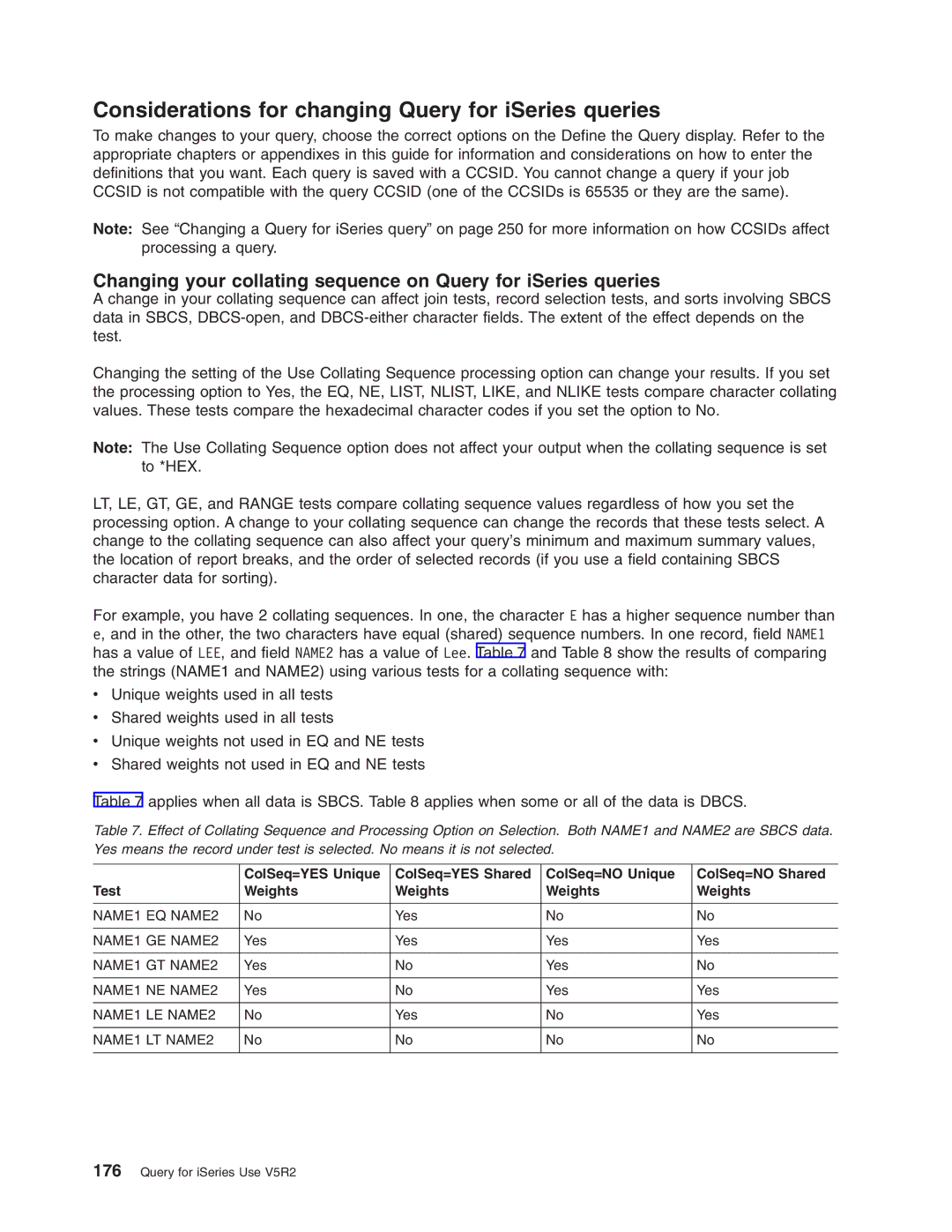
Test Description
Comparison tests in Query for iSeries
Null values in Query for iSeries
Testing for equal EQ and not equal NE in Query for iSeries
Date, time, or timestamp comparisons in Query for iSeries
Testing for values in a list List Nlist in Query for iSeries
Itemno List
Lastname List
Lastname Like
’ANNE EVA’
Example 1 DBCSFLD1 Like ’s/oDD%%HH%%s/i’
Using more than one comparison test in Query for iSeries
Year Baldue
AND/OR
Month List Year
Adding and removing comparisons in Query for iSeries
Year List
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Selecting sort fields in Query for iSeries
105
Lastname
Account number
Additional sort considerations in Query for iSeries
Sorted report looks like this
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Purpose of a collating sequence in Query for iSeries
Selecting a collating sequence in Query for iSeries
Letting Query for iSeries select a collating sequence
Collating sequence and CCSIDs in Query for iSeries
How a collating sequence affects Query for iSeries
Selecting a Query for iSeries collating sequence
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Defining your own collating sequence in Query for iSeries
Selecting a translation table in Query for iSeries
Selecting a system sort sequence in Query for iSeries
F12=Cancel F13=Layout F18=Files F23=Save as default
Specifying report column formatting in Query for iSeries
Formatting the columns of the Query for iSeriesquery report
Column spacing in Query for iSeries reports
Column headings in Query for iSeries reports
Starttime
Length and decimal positions in Query for iSeries reports
Lastname Init
Omitting fields from a Query for iSeries report
Editing numeric fields in Query for iSeries reports
Defining numeric field editing in Query for iSeries reports
=Numeric editing choices
=Date or time editing choice
=Edit code
=Edit word
F10=Process/previous F12=Cancel F13=Layout
Decimal point in Query for iSeries reports
Thousands separator in Query for iSeries reports
Show negative sign in Query for iSeries reports
Left negative sign in Query for iSeries reports
Show currency symbol in Query for iSeries reports
Left currency symbol in Query for iSeries reports
Right currency symbol in Query for iSeries reports
Right negative sign in Query for iSeries reports
Print zero value in Query for iSeries reports
Replace leading zeros in Query for iSeries reports
Replace with option in Query for iSeries reports
Single leading zero in Query for iSeries reports
Date/time separator in Query for iSeries reports
Specifying an edit code in Query for iSeries reports
Edit code in Query for iSeries reports
Internal
Specifying edit words
Optional edit code modifier in Query for iSeries reports
Edit word in Query for iSeries reports
=Asterisk fill
F13=Layout F16=Remove edit F18=Files
Edit word for summary total in Query for iSeries reports
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Types of summary functions in Query for iSeries reports
=Total
Total
MAX
=Average
=Minimum
=Maximum
=Count
Final Totals
Summarizing columns in Query for iSeries reports
Name Total DUE
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Defining Query for iSeries report breaks
Defining a Query for iSeries report break
Division
Region
Records in file
Field
Company Department Division Employee Region
Skip to new page in Query for iSeries reports
Suppress summaries in Query for iSeries reports
Break text in Query for iSeries reports
145
=Printer =Database file
Form of output of Query for iSeries reports
Line wrapping in Query for iSeries reports
=Detail
=Summary only
Displaying wrapping widths in Query for iSeries reports
Wrapping width in Query for iSeries reports
Record on one page in Query for iSeries reports
Decimal Numeric
Defining output to the printer in Query for iSeries reports
Integer
Printer device in Query for iSeries reports
Form size in Query for iSeries reports
Form length
Form width
Start line in Query for iSeries reports
End line in Query for iSeries reports
Line spacing in Query for iSeries reports
Print definition in Query for iSeries reports
Define Spooled Output
Specify Cover
Heading Footing F3=Exit F5=Report
=Yes
Libcrtaut LIBCRTAUT, *CHANGE, *ALL EXCLUDE, *USE
Qqryout
File
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Page
=New file
=Replace file
=New member
=Replace member
Authorization list name
Exclude
Los Angeles Arcadia
Using an output database file created by Query for iSeries
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Specifying Query for iSeries processing options
Purpose of Query for iSeries processing options
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Specifying Query for iSeries processing options
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Exiting and running a Query for iSeries query
Ending a Query for iSeries query definition
Saving a Query for iSeries query definition
Storing the Query for iSeries query definition
Describing the Query for iSeries query definition
Giving authority to others to your Query for iSeries query
Running a Query for iSeries query
Libcrtaut
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Running a Query for iSeries query using the Runqry command
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Changes you can make to a Query for iSeries query
Working with Query for iSeries query definitions
Changing a Query for iSeries query definition
Define the Query
Prompt Changed Effect
Considerations for changing Query for iSeries queries
Copying a Query for iSeries query definition
Acctrecfeb Inventfeb Mailaddr
Renaming a Query for iSeries query definition
Deleting a Query for iSeries query definition
Displaying a Query for iSeries query definition
Printing a Query for iSeries query definition
Information printed for a Query for iSeries query definition
Breaklvl
Working with Query for iSeries query definitions
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Part 3. Advanced information about Query for iSeries
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Overriding database files in Query for iSeries
Files with different record formats in Query for iSeries
File sharing considerations in Query for iSeries
Using *ALL in Query for iSeries
Joining files in Query for iSeries
Division in Query for iSeries
Addition and subtraction in Query for iSeries
Multiplication in Query for iSeries
PRN299A
PRN299B
Selecting records ignoring field case in Query for iSeries
Changing Decimal Precision
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Part 4. Appendixes
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Conceptual Differences
Operational Differences
Library default
Character fields
Sort sequence Result fields
Calculation results
System/36 OS/400 System
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Appendix B. Practice exercise for Query for iSeries query
Iddu
Sysdic
Nameaddr
ADDRESS1
ADDRESS2
ZIP
Amount
ADDRESS1 ADDRESS2 City State ZIP Amount
Query for iSeries query exercise Creating a database file
Query for iSeries query exercise Entering data
LIBCRTAUT, *ALL, *CHANGE
USE, *EXCLUDE
Lastname Firstname ADDRESS1 ADDRESS2 City State ZIP Amount
Work with Data in a File
Entry
Lastname Firstname ADDRESS1 ADDRESS2 City State ZIP Amount
=Yes, N=No
Yourlib
Query for iSeries query exercise Creating a query
Kjoqry
Bottom
Nameaddrr
Create
Yourlib Ccsid
Change LIBCRTAUT, *ALL, *CHANGE EXCLUDE, *USE
Simpson Frank
Daye BEN
APT C
Query for iSeries query exercise Changing a query
Press the Enter key. The Select Records display is shown
Change
Press F20 to display the right portion of the report
Change LIBCRTAUT, *CHANGE, *ALL EXCLUDE, *USE
ADDRESS2 City
APT
Query for iSeries query exercise Creating an advanced query
Cebqry
Main
=== Wrkqry
Qname
Qryfile
Qlidobjd
Oddcen Odccen
Odddat Odcdat
Oddtim Odctim
Odlbnm Odobow
Oddtim Display Time Odobnm Object Odobfr
Odobtp List
Library Object
Attribute Size
CLP
Odlbnm Library Odobtp Object Type Odobat
Odobsz Object Size Odobtx
Odlbnm Library Odobtp Object Type Odobat Attribute
Odlbnm Name Library Odobtp Object Type Odobat Attribute
Odobsz Object Size Odobtx Text Description
3 4
Break text
Qname
Qgpl File Tapf
Name Object
Qgpl File Dspf
Qgpl
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Keyed sequence access paths in Query for iSeries
Introduction to Query for iSeries query processing
Select/omit access paths in Query for iSeries
Access plans in Query for iSeries
File definitions in Query for iSeries
Updating access plans in Query for iSeries
File definitions and data in Query for iSeries
File data considerations for Query for iSeries
Defining queries for Query for iSeries
Select records in Query for iSeries
Define result fields in Query for iSeries
Select and sequence fields in Query for iSeries
Select sort fields in Query for iSeries
Select output type and output form in Query for iSeries
Select collating sequence in Query for iSeries
Specify report summary functions in Query for iSeries
Option 1-Matched records
Using join operations in Query for iSeries
Specify processing options in Query for iSeries
Option 3-Unmatched records with primary file
Performance tips for join operations in Query for iSeries
Option 2-Matched records with primary file
Miscellaneous tips and techniques for Query for iSeries
Batch processing for Query for iSeries
Query for iSeries performance tuning
Query running. Building access path for file X in Y
Query for iSeries migration considerations N to N-1
Query for iSeries status messages
Query for iSeries debug mode messages
Query running. Building access path from file X in Y
Query running. Creating copy of file X in Y
Query running. Sorting copy of file *N in *N
243
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
245
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Ccsid marking in Query for iSeries
CCSIDs and collating sequences in Query for iSeries
Query for iSeries language sequences
Displaying a Query for iSeries query
Changing a Query for iSeries query
Getting a list of objects with text in Query for iSeries
Defining a Query for iSeries query
Defining a collating sequence in Query for iSeries
Running a default query in Query for iSeries
Selecting records at run time in Query for iSeries
CCSIDs and Query for iSeries query definition items
Ccsid and file selections in Query for iSeries
Ccsid and join tests in Query for iSeries
Ccsid and result field expressions in Query for iSeries
Ccsid and result field column headings in Query for iSeries
Ccsid and sort fields in Query for iSeries
Ccsid and record selection tests in Query for iSeries
Ccsid and summary functions in Query for iSeries
Ccsid compatibility considerations in Query for iSeries
Consequence
CCSIDs Conversion Problems-Run-Time Consequences
For displayed output, the run request continues, but all
How CCSIDs Affect Query Use
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Bibliography
259
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
261
Trademarks
DB2
Index Special Characters
Date
Character substitution warning
Command
Currentdate ISO JIS Local
Dec column data type
Definition Display
Example
Field
Function
189
List
Heading Ccsid coded character set identifier 253 Defining
Dbcs Like
Report
Sort Field
Currenttime Currenttimezone ISO JIS Local
Work with File Definitions display Iddu 202
Query for iSeries Use V5R2
Page
SC41-5210-04