See Appendix a for additional support information
Intel EtherExpress PRO/100 LAN+Modem56 PC Card
Page
Contents
Modem Reference
Utilities and Applications
Hardware Installation
Introduction
56K Technology
Additional Features
Model
Software Supplied
Power Management Suspend/Resume
Hardware Installation
Unpacking and Inspection
HotSwap
Other Required Equipment
Package Contents
Inserting the PRO/100 PC Card into the PC Card Slot
Installing Card and Cables
PRO/100 Modem and Ethernet Connections
Connecting the Modem Cable to the PRO/100
Connecting the Ethernet Adapter Cable to the PRO/100
Connecting the Ethernet Adapter Cable to the Network
Two Versions and Two Installation Paths
Windows 95 Installation
Which Version of Windows 95?
How Can I Tell Which Version I Have?
Additional Information in this Chapter
Windows 95 Installation Retail Version
Overview
Important Notes
Insertion, Detection, and Prompt for Disk
Recommended Installation Steps
Windows 95 OSR2 Installation OEM Version
Recommended Installation Steps
Copying Intel Files
Country Identifier Utility
Utilities
How to Install for Windows 95 and NetWare
Power-Saving Modes
Windows 95 Troubleshooting
Quick Troubleshooting Device Conflicts
Troubleshooting Checklist
Run the Intel diagnostic utility M16BTEST
Be sure that Pcmcia support is enabled in Windows
Be sure you have the latest firmware and driver
Following information may also be helpful
Contact your computer vendor for updated information
M16B.SYS Ndis 3 Settings for Microsoft Windows
Windows 95 Driver Parameters Reference
Windows 95 Support
Parameter Default Valid Values
Registry parameters are as follows
Keyword Default Valid Values
16 PRO/100 LAN+Modem PC Card User’s Guide
Which Version of Windows NT?
Windows NT Installation
How Can I Tell Which Version and Service Pack I Have?
Windows NT 4.0 Installation
Pcmcia Services Verification
Network Driver Installation
Select the Adapters tab and click Add
Modem Setup
Network Driver Installation and Modem Setup
Windows NT 3.51 Installation
\NT351
Power-Saving Modes
Files necessary for using M16B.SYS include
M16B.SYS Ndis 3 Settings for Microsoft Windows NT
Intel PRO/100 installation DLL
Windows NT Driver Parameters Reference
Parameter Default
Busnumber Bustype
Windows 3.x/DOS Installation
Installation under MS-DOS
Completing the Installation
Installation of Other Network Operating Systems
Windows 3.x Network Operating System Alphabetical Reference
Artisoft LANtastic version
AT&T StarGROUP LAN Manager version 2.1a
See Microsoft LAN Manager
Banyan Vines version
DEC Pathworks versions 5.x or
Now continue with the DEC Pathworks installation as follows
Change the line
To read
Ndis Driver File M16BNDIS.EXE Ndis Driver Name INTEL$
FTP Software LANWatch
FTP Software LANWatch Packet Driver Installation
File
FTP Software LANWatch Ndis 2.0 Driver Installation
FTP Software PC/TCP
FTP PC/TCP 3.X with OnNet 1.1 and Windows for Workgroups
Create a directory called Ndis on your hard disk, by typing
Line
Additional Steps for ODI Installation
Add the line
After the line
FTP PC/TCP 3.X with OnNet 1.1 with Windows
\PCTCP\M16BPD.COM \PCTCP\ETHDRV.EXE
FTP Software PC/TCP Packet Driver Installation with OnNet
ODI with FTP Software PC/TCP and NetWare
HP LAN Manager
Generic Installation
IBM Local Area Network Support Program
IBM Local Area Network Support Program version
Save the files and reboot the PC
IBM PC LAN and IBM DOS LAN Requester
Save the file and reboot the PC
With the line
As follows
Dcompvlm Path
Manual Installation
Microsoft LAN Manager version
Microsoft LAN Manager
Ndis 2.01 and ODI Drivers
Windows for Workgroups
22 PRO/100 LAN+Modem PC Card User’s Guide
Network Setup dialog box, choose Networks
24 PRO/100 LAN+Modem PC Card User’s Guide
Windows for Workgroups 3.11 Using the Ndis 2.0 Driver
Type
Make a directory called OEM, as follows
NetWare
Novell NetWare
With
SunSoft PC-NFS version
Ungermann-Bass Net/One for DOS
Ungermann-Bass Net/One LAN Manager version 2.1 Installation
Between the two lines
Before the line that reads
Wollongong PathWay Access for DOS
Wollongong PathWay Ndis Installation
At the end of the file, add the following fragments
Wollongong PathWay ODI Installation
Add the lines
DCOMPVLM.BAT will decompress and copy all required files
Windows 3.x Modem Configuration Notes
Installing Communications and Fax Software
Using Modem Communications Only under Windows
Automatic COM Port Detection
COM Ports, IRQs, and I/O Base Addresses
IMENABLE.COM
Changing Interrupt or I/O Address Settings
Preventing Memory Conflicts
Memory Manager Exclusions
Modem Driver Configuration Notes
Windows 3.x Modem Driver Settings
Windows and EMM386
NET.CFG MEM CC000
Modem Driver Example
Windows 3.x Network Driver Parameters
ODI Settings for driver M16BODI.COM
DOS ODI Driver Configuration Notes M16BODI.COM
NET.CFG Example
ODI Driver Example
Ndis 2.0.1 DOS Driver Configuration Notes
Ndis 2.0.1 Settings for driver
PROTOCOL.INI
M16BDOS.NIF
Packet Driver Settings for driver
Packet Driver Configuration Notes
Ndis 2.0.1 Keywords M16BNDIS.EXE
Packet Driver Example
Packet Driver Keywords
Driver Keyword Alphabetical Reference
Combase
Comirq
Frame
Linkdisable
Interrupt
Ioaddress
Memorybaseaddress
Memory
Mode
Nocheck
Noleds
Noearlytx
Port
Shareirq
Pcmcia card was not detected
Error Messages for Windows 3.x and MS-DOS drivers
Card is unreadable, possible memory conflict
Please specify either 8 or 16 for the Wordsize keyword
Driver failed the IRQ test. Try a different IRQ address
Driver failed the I/O test. Try a different I/O address
Selected COM port already exists
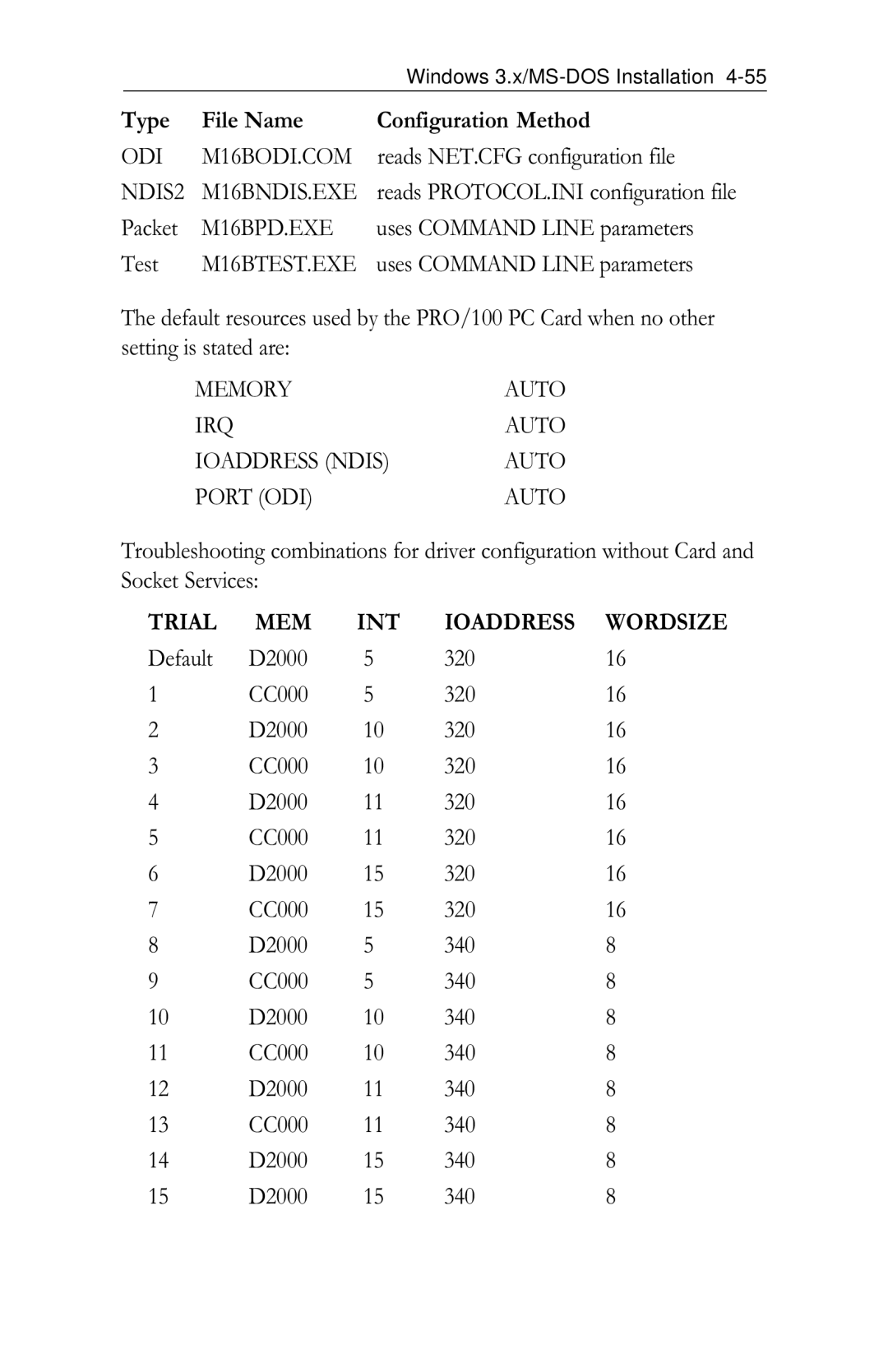
Windows 3.x Troubleshooting
ODI M16BODI.COM
NDIS2 M16BNDIS.EXE
M16BPD.EXE
SystemSoft
Phoenix
DEVICE=C\PATH\EMM386.EXE Noems X=D200-D3FF
Default D2000 320 CC000 340
Uses Command Line parameters
Ioaddress Ndis
Port ODI
Driver loaded successfully, but I can’t get on the network
Driver loaded, but my DOS modem software won’t work
Modem works in DOS, but not in Windows
If the COM port does not show up after running MSD, try
Adding the following section to the SYSTEM.INI file
Exit Windows and turn computer off and on again cold boot
Turn computer power off and then on again cold boot
Cant hear the modem
Or as a standalone command preceded by the letters AT
Computer-Specific Application Notes Windows
Ambra
AST Power Exec
Austin Notebooks series
Compaq Contura Aero
Dell Latitude XP series
Compaq LTE Elite models
Gateway ColorBook series
IBM ThinkPad 350, 755CS
IBM ThinkPad 360CS
IBM ThinkPad 750CS
NEC Versa models
Sharp
Toshiba 19xx, 47xx, 48xx series
66 PRO/100 LAN+Modem PC Card User’s Guide
Country Identifier Utility
Utilities and Applications
Click on Exit to close the program
Modem Test Utility
Executing the Self Test
Diagnostic Test Utility M16BTEST.EXE
Test
Main Screen
COM port monitor Windows 3.x only
This function displays the help screen
This function exits the application
Communications Application Notes and Modem Script Files
How to Use the COM port monitor
CTS
Clear to Send
Introduction
Modem Setup with a Communications Program
Modem Setup After Windows 95 Installation
Verify modem settings as follows a Go to Control Panel
America Online version
C\AOL30\MPM sub-directory
America Online version 3.0 with Windows
CompuServe Wincim version 3.02 with Windows
Click OK, to update configuration and close menus
LapLink version
Click OK to save configuration and exit
LapLink version 6.0 with Windows
Lotus ccMail Mobile version 2.22 with Windows
Lotus Notes Desktop screen, click File Click Tools
Lotus Notes version 4.11A with Windows
Click OK to save changes and exit
Lotus Notes version 4.11A with Windows 95 and NT
Microsoft Dial-Up Adapter Network Setup for Windows
Restart the computer when prompted
Click OK to save changes and exit
Modify the Dial-Up Adapter properties
Microsoft Remote Access Server RAS
MAXCARRIERBPS= MAXCONNECTBPS=
Prodigy Internet version 1.1.6 with Windows
20PRO/100 LAN+Modem PC Card User’s Guide
Result Codes
Modem Reference
+FCERROR
Delayed
Blacklisted
Blacklist Full
Carrier
AT Command Reference
Special Commands +++ Online Escape Sequence
Repeat Last Command
AT Command Reference Answer
Break Escape command
Bn Select Communications Standard
Dn Dial a Telephone Number
Cn Carrier Control
Dial Modifiers
Redial Last Number
=n Dial a Stored Telephone Number
Tone Dialing Method
Wait for Second Dial Tone
Disable echo to the computer
En Echo Command
Return to Command Mode after Dialing
@ Wait for Quiet Answer
Switch Hook Options
Fn Online Data Character Echo command
Request ID Information
ATH0
On Online Command
Ln Monitor Speaker Volume
Mn Speaker On/Off Selection
Nn Negotiation of Handshaking Options
Select Pulse Dialing
Repeat command
Qn Result Code Display Options
Select Tone Dialing
Xn Result Code Set/Call Progress Option
Wn Negotiation Progress Message Selection
Yn Long Space Disconnect Option
Recall Stored Profile
Automatic Retrain Options
Dn Data Terminal Ready DTR Options
Cn Data Carrier Detect DCD
Local Factory Settings
Fn Load Factory Settings
Gn V.22bis Guard Tone Selection
Jn Auxiliary Relay Option
Mn Asynchronous Communications Mode
Kn Local Flow Control Options
Pn Pulse Dial Make-to-Break Ratio Selec- tion Japan only
Qn Asynchronous Communications Mode
Tn Self-Test Commands
Sn Data Set Ready DSR Options
Yn Select Stored Profile for Hard Reset
View Configuration Profile
\Jn Adjust BPS Rate Control
Wn Write Active Profile to Memory
\Nn Error Mode Control Selection
\Kn Break Control
\Qn Local Flow Control Selection
\Xn XON/XOFF Pass Through
\Tn Inactivity Timer Limit
View Numbers in Blacklist
Cn Data Compression Control
+GCAPRequest Complete Capabilities List
+GCI Country of Installation
22PRO/100 LAN+Modem PC Card User’s Guide
Code
+GMIRequest Manufacturer Identification
+GMM Request Model Identification
+MS Modulation Selection
Subparameter
+MS=?
Carrier
Values for example, AT+MS=,0 or
Introduction to S-Registers
Register Reference
Register Reference S0 Ring to Answer After
S3 Command Line Termination Character
S1 Ring Counter
S2 AT Escape Character
S4 Response Formatting Character
S5 Command Line Editing Character
S6 Wait Before Blind Dialing
S7 Connection Completion Time-Out
S28 V.34 Modulation Enable/Disable
S10 Delay Between Lost Carrier/Hang Up
S30 Inactivity Timer
S8 Duration of Pause for Comma Dial Modi- fier
S35 Data Calling Tone
S34 DTE Throughput Limit
S36 Negotiation Fallback
S37 Dial Line Rate
S42=0 Auto rate disabled S42=1 Auto rate enabled default
S43 Auto Mode
S40 ETC Startup Autorating
S42 Auto Rate
S89 Timer to Control Sleep Mode
S48 Lapm Error Control and Feature Nego- tiation
S46 Data Compression Selection
LAPM, MNP, or hangup MNP or hangup
S92 Direct Connect Transmit Level
S91 Line Transmit Level
S95 Negotiation Message Options
S98 Cable Detection Options
World Wide Web Internet FTP
Automated Customer Support
Intel Web and Internet Sites
General Specifications
Specifications
Modem Specifications
From North America
Limited Lifetime Warranty
All other locations
Intel Adapter MONEY-BACK Guarantee North America Only
FCC Compliance Statement
Agency Notices
FCC Rules and Regulations Part
Canadian compliance Industry Canada
When tested in at least one intended host
Manufacturer declaration
Restrictions
Software License Agreement
2PRO/100 LAN+Modem PC Card User’s Guide
Software License Agreement E-3
4PRO/100 LAN+Modem PC Card User’s Guide
Index
Symbols
DEC Pathworks
DCOMPVLM.BAT
IBM PC LAN
Installation IBM Local Area Support Program
Generic Manual
Novell NetWare
LANtastic, Artisoft
LapLink LEDs
Ungermann-Bass Net/One
MODEMLOG.TXT
PATHWORKS, DEC
FTP PC/TCP
TELSEL.EXE
PC/TCP, FTP Pcmcia
Wollongong PathWay Access
NetWare installation
WinCim
Retail version