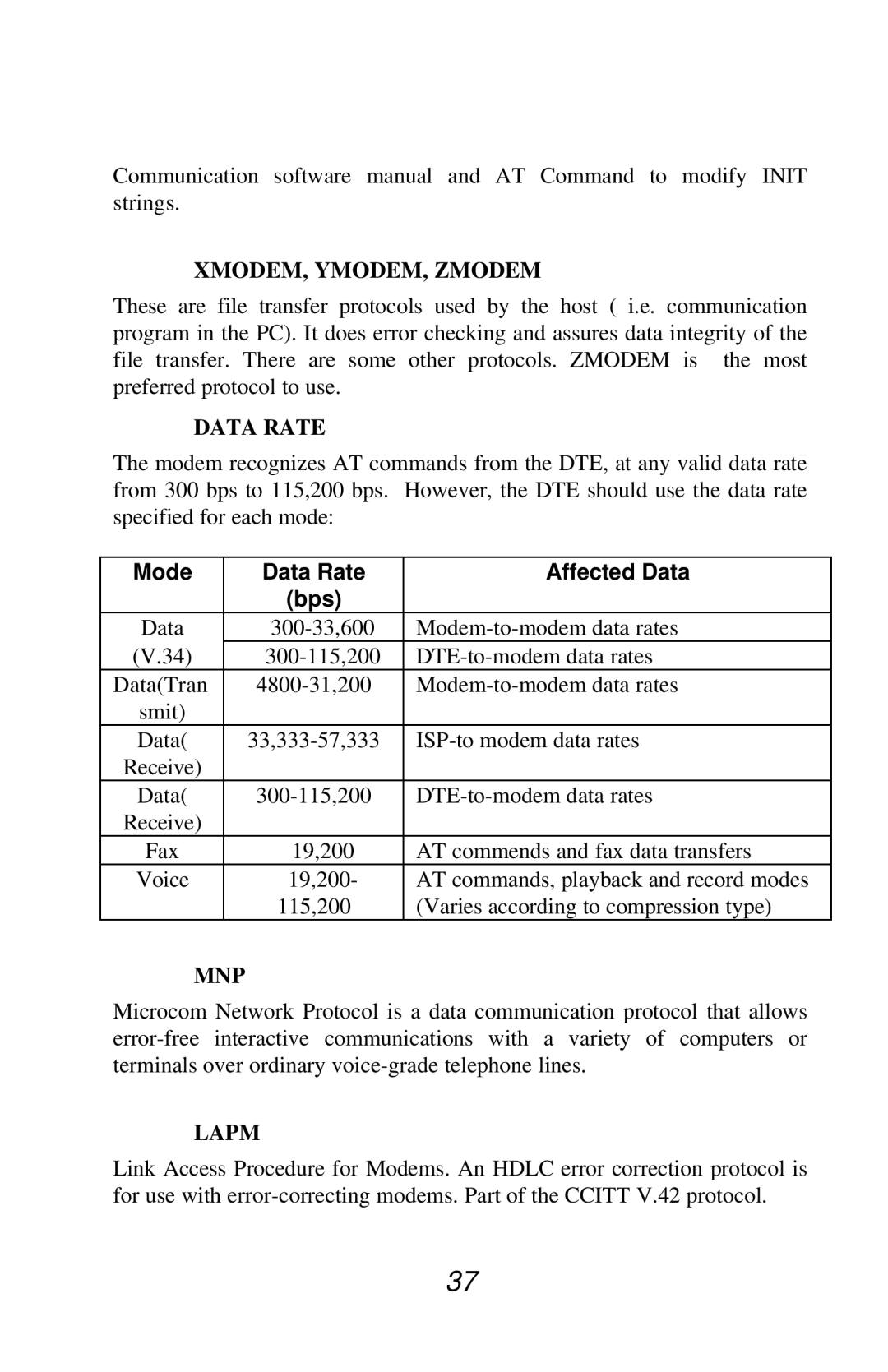
V.90 specifications
The Jaton V.90 modem is a classic example of 56K technology that revolutionized dial-up internet connections in the late 1990s. As one of the early models supporting the V.90 standard, this modem enabled users to experience faster internet speeds compared to its predecessors. The V.90 protocol allowed for a maximum download speed of 56 Kbps, offering significant improvements over the previous V.34 modem, which capped out at 33.6 Kbps.One of the standout features of the Jaton V.90 is its ability to adapt to different line conditions, ensuring optimal performance regardless of the quality of the telephone line. The V.90 standard provided a retransmission mechanism that allowed data to be resent if errors occurred during transmission, improving reliability and reducing the likelihood of dropped connections.
The modem incorporates technologies such as error correction and data compression. With built-in error correction protocols like V.42 and MNP, the Jaton V.90 can detect and correct common transmission errors, which is vital in maintaining a stable connection. The data compression technology, which uses MNP Class 5, enhances throughput by compressing data before transmission. As a result, users could effectively increase their upload speeds and minimize latency, creating a more seamless browsing experience.
The hardware features of the Jaton V.90 modem typically include a standard RJ-11 telephone connector, which makes it easy to connect to existing phone lines. The modem may come with both internal and external configurations, allowing flexibility depending on user preferences and system requirements. The external version often features indicator LEDs that provide real-time feedback on connection status, data transfer activity, and power status.
Compatibility is another crucial aspect of the Jaton V.90 modem. Operating with a variety of systems, it was designed to work with Windows, Mac OS, and other operating environments, making it accessible for a wide range of users. Additionally, the modem generally supports various software applications for easy configuration and management.
Ultimately, the Jaton V.90 modem played a pivotal role in facilitating internet access during a transformative period, laying the groundwork for future high-speed connections. While modern broadband solutions have since eclipsed dial-up speeds, the legacy of the Jaton V.90 as a reliable and innovative piece of technology remains significant in the history of internet connectivity.