Stereo 3W Audio Power Amplifiers with Headphone Drive and Input Mux
MAX9777/MAX9778
BIAS Capacitor
BIAS is the output of the internally generated 2.5VDC bias voltage. The BIAS bypass capacitor, CBIAS, improves PSRR and THD+N by reducing power supply and other noise sources at the
Supply Bypassing Proper
Gain Select
The MAX9777/MAX9778 feature multiple gain settings on each channel, making available different gain and feed- back configurations. The
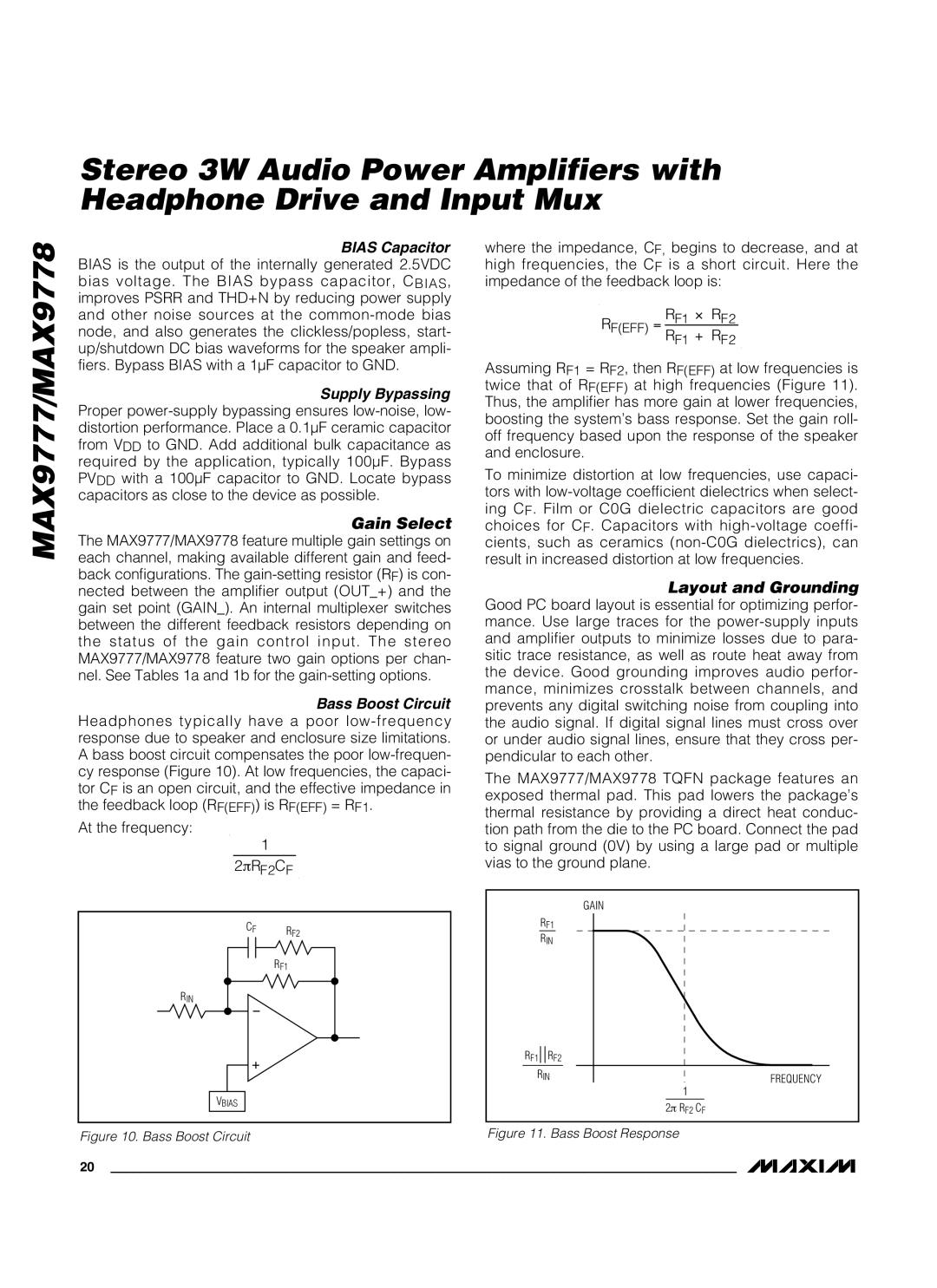
Bass Boost Circuit Headphones typically have a poor
At the frequency:
1
2πRF2CF
CF RF2
RF1
RIN
VBIAS
Figure 10. Bass Boost Circuit
where the impedance, CF, begins to decrease, and at high frequencies, the CF is a short circuit. Here the impedance of the feedback loop is:
RF(EFF) = RF1 ⋅ RF2
RF1 + RF2
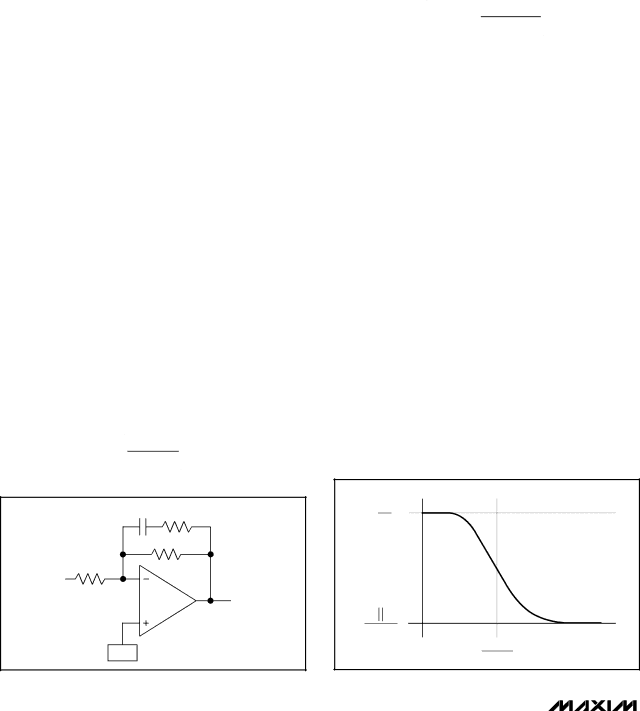
Assuming RF1 = RF2, then RF(EFF) at low frequencies is twice that of RF(EFF) at high frequencies (Figure 11). Thus, the amplifier has more gain at lower frequencies, boosting the system’s bass response. Set the gain roll- off frequency based upon the response of the speaker and enclosure.
To minimize distortion at low frequencies, use capaci- tors with
Layout and Grounding
Good PC board layout is essential for optimizing perfor- mance. Use large traces for the
The MAX9777/MAX9778 TQFN package features an exposed thermal pad. This pad lowers the package’s thermal resistance by providing a direct heat conduc- tion path from the die to the PC board. Connect the pad to signal ground (0V) by using a large pad or multiple vias to the ground plane.
|
| GAIN |
| RF1 |
|
| RIN |
|
RF1 | RF2 |
|
RIN | FREQUENCY | |
|
| 1 |
|
| 2π RF2 CF |
Figure 11. Bass Boost Response
20 ______________________________________________________________________________________