AMPLIFIER OWNER’S MANUAL
Adjusting the Gain
1.Turn the gain control on the amplifier all the way down.
2.Turn up the volume control on the source unit to approximately 3⁄4 of maximum.
3.Adjust the gain control on the amplifier until audible distortion occurs.
4.Adjust the gain control down until audible distortion disappears.
5.The amplifier is now calibrated to the output of the source unit.
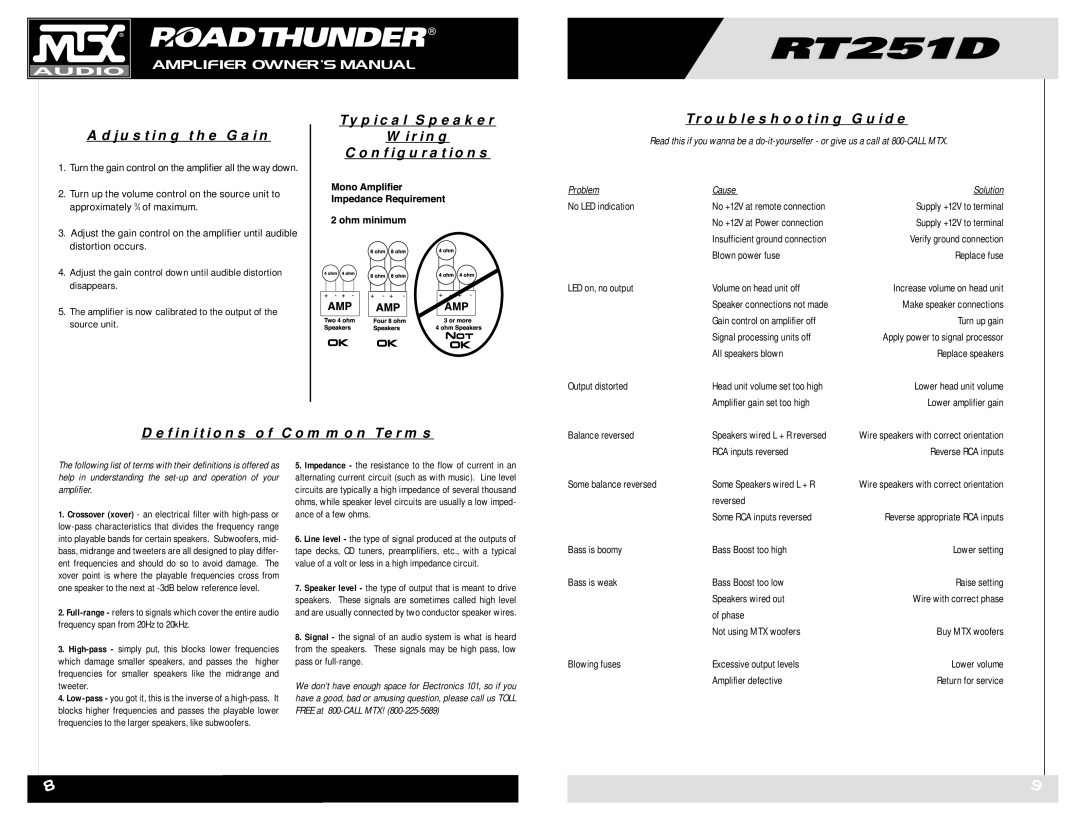
Typical Speaker
Wiring
Configurations
Troubleshooting Guide
Read this if you wanna be a
Problem | Cause | Solution |
No LED indication | No +12V at remote connection | Supply +12V to terminal |
| No +12V at Power connection | Supply +12V to terminal |
| Insufficient ground connection | Verify ground connection |
| Blown power fuse | Replace fuse |
LED on, no output | Volume on head unit off | Increase volume on head unit |
| Speaker connections not made | Make speaker connections |
| Gain control on amplifier off | Turn up gain |
| Signal processing units off | Apply power to signal processor |
| All speakers blown | Replace speakers |
Output distorted | Head unit volume set too high | Lower head unit volume |
| Amplifier gain set too high | Lower amplifier gain |
Definitions of Common Terms
Balance reversed | Speakers wired L + R reversed | Wire speakers with correct orientation |
| RCA inputs reversed | Reverse RCA inputs |
The following list of terms with their definitions is offered as help in understanding the
1.Crossover (xover) - an electrical filter with
2.
3.
4.
5.Impedance - the resistance to the flow of current in an alternating current circuit (such as with music). Line level circuits are typically a high impedance of several thousand ohms, while speaker level circuits are usually a low imped- ance of a few ohms.
6.Line level - the type of signal produced at the outputs of tape decks, CD tuners, preamplifiers, etc., with a typical value of a volt or less in a high impedance circuit.
7.Speaker level - the type of output that is meant to drive speakers. These signals are sometimes called high level and are usually connected by two conductor speaker wires.
8.Signal - the signal of an audio system is what is heard from the speakers. These signals may be high pass, low pass or
We don’t have enough space for Electronics 101, so if you have a good, bad or amusing question, please call us TOLL FREE at
Some balance reversed | Some Speakers wired L + R | Wire speakers with correct orientation |
| reversed |
|
| Some RCA inputs reversed | Reverse appropriate RCA inputs |
Bass is boomy | Bass Boost too high | Lower setting |
Bass is weak | Bass Boost too low | Raise setting |
| Speakers wired out | Wire with correct phase |
| of phase |
|
| Not using MTX woofers | Buy MTX woofers |
Blowing fuses | Excessive output levels | Lower volume |
| Amplifier defective | Return for service |
8
9