Model SP2S13H20A
Proposition 65 Warning
SILICOSIS/RESPIRATORY Warnings Silicosis Warning
Respiratory Hazards
Table of Contents
Order via Fax Dealers Only
Parts Ordering Procedures
Best Deal! Order via Internet Dealers Only
Specifications
Specifications
Dimensions
SP2S13H20A Dimensions
Safety Message Alert Symbols
If you do not follow these directions
Always wear approved respiratory protection
Always wear approved eye and hearing protection
Rules for Safe Operation
Rules for Safe Operation
General Safety
Diamond Blade Safety
Maintenance Safety
Saw Transportation Safety
Emergencies
Always know the location of the nearest first aid kit
SP2S13H20A SAW Operation and Parts Manual REV. #1 05/17/10
Major Components
SP2S13H20A Saw Major Components
Cannister to gain access to filter element
13HP Honda Engine Components
Smoothly
Flow of fuel
General Information
SP2S13H20A SAW Operation and Parts Manual REV. #1 05/17/10
Inspection
Before Starting
Engine Oil Check
Honda 13 HP engine shown
Use only distilled water
Additionally, when connecting the positive
Hydrostatic Transmission
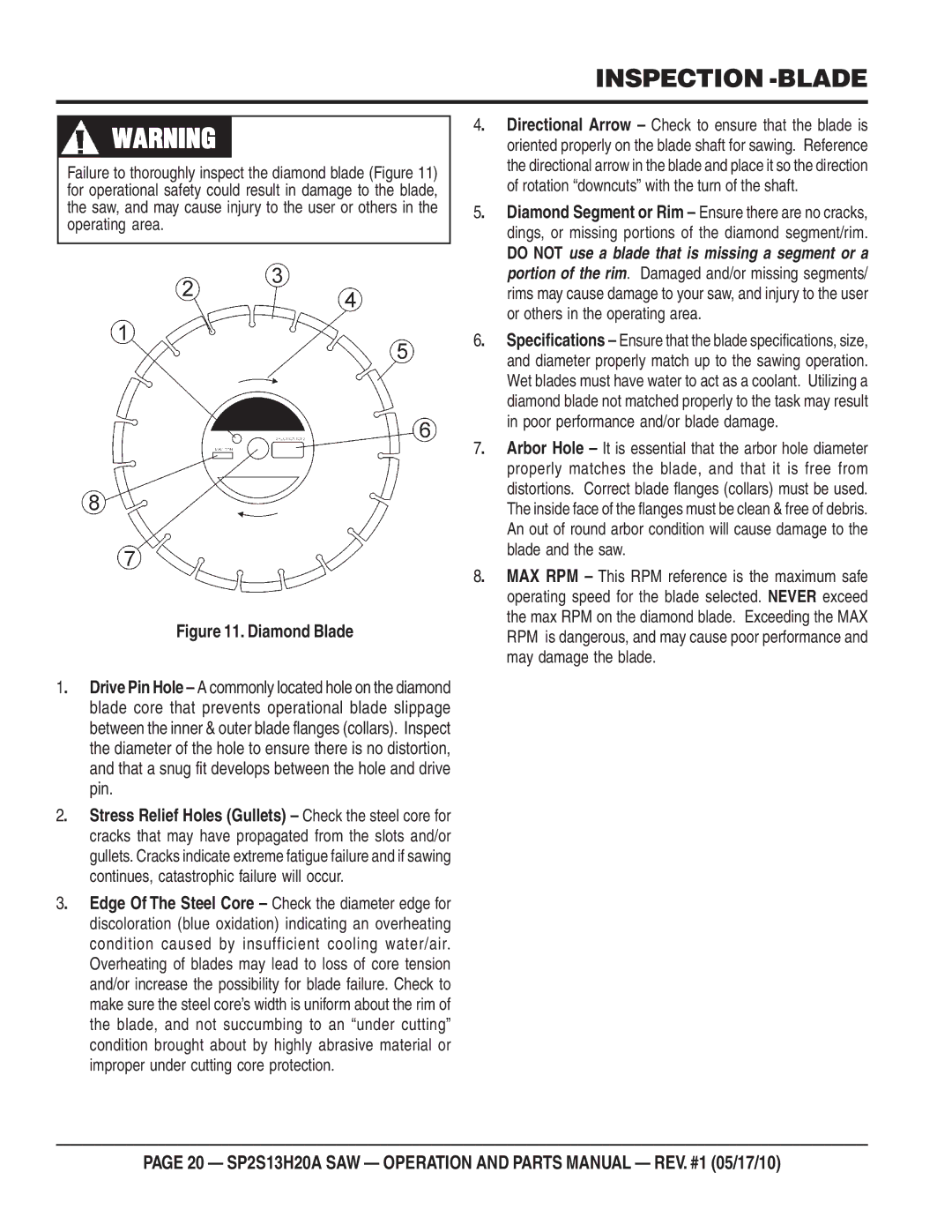
Inspection -BLADE
Rotation downcuts with the turn of the shaft
Or others in the operating area
Poor performance and/or blade damage
Inspection Blade Placement
Set the engine ON/OFF switch to the OFF position
Flange
Inner flange collar
Inspection -GUARDS, Covers & Belts
Guards and Covers Check
Institute Ansi B7.1 and B7.5
Belts Alignment and Tensioning
Water Tank
Replacement part numbers
Inspection Belts & Water Tank
Manual START-UP
Fuel Valve Lever
Started repeat steps 1 through
Blade operating speeds
Associate with a loose guard and/or covers
do not pull the starter rope all the way to the end
Place the fuel valve lever to the OFF position
SHUT-DOWN Procedures
Stopping the Engine 13 HP Honda Engine
SP2S13H20A SAW Operation and Parts Manual REV. #1 05/17/10
Adjusting the Handle Bars
Adjusting the Blade Height
When moving the saw around
Operation
Engage Position
Traveling During Cutting
Place the travel lever in the Neutral position
Cutting
Wet Cutting Operation
Turn water source on Figure
Follow steps 1-4 of the Traveling During Cutting section
Blade Speed
Finishing a Cut
Extreme heat Diamond Blades
Maintenance
Retighten the adjustment nut
General Transmission Care
Transmission Reservoir Cup
Spline GearWheels
Loosen the 4 1-1/2 HHC screws Engine Mount Assy., item
AdjustV-Belt Alignment/Replacement Pulleys
DriveV-Belt Check
Blade Shaft Bearing Replacement
Reference & for steps
Battery Maintenance
Battery Electrolyte Levels
13HP Engine Wiring Diagram Recoil Start
HP Honda Engine Wiring Diagram
Troubleshooting Engine
Engine Troubleshooting
Engine Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Blade
Blade Troubleshooting
SP2S13H20A SAW Operation and Parts Manual REV. #1 05/17/10
Explanation of Code in Remarks Column
Xxxxx only Not Used on
Suggested Spare Parts
Description
Name Plate and Decals
Name Plate and Decals
DECAL, Recommended Maintenance
DECAL, Multiquip
DECAL, SP2S13H20A
DECAL, FORWARD/REVERSE Lever
Under Carriage Assy
Under Carriage Assy
AXLE, Rear & Front
FRAME, Undercarriagee Assy
WASHER, Flat SAE 3/4
Bearing Plain
Blade Shaft Assy
Blade Shaft Assy
SPINDLE, Blade
FLANGE, Blade Inside 4.0OD X 1.0ID
KEY, Woodruff #15
NUT, HEX JAM LH 1-14 Plated
Lifting Bale Assy
Lifting Bale Assy
13HP, Lift Bale Assy
20HP, Lift Bail Assy
BRACE, 13HP Bail
BRACE, 20HP Bail
Console Assy
Console Assy
Housing ASSY. RED
Handle Assy
GRIP, 1 ID
WASHER, Lock 3/8 MED
13HP Honda Engine Mount Assy
13HP Honda Engine Mount Assy
NUT, HEX Finish 1/2-13
Engine Base Assy
Engine Assy
Engine Assy See Blade Shaft Assy See Hydrostatic Drive Assy
Engine Assy
Part Name QTY. Remarks
Pointers and Covers Assy
Pointers and Covers Assy
Pointer and Covers Assy
Blade Guide Weldment
Spanner Bushing CSI
Pointer
Water System Assy
Water System Assy
FITTING, Plastic 90 1/2MP X 1/2BARB
FITTING, Nipple 1/2MP X 2 Galv
Bolt W/NUTS
FITTING, Brass 1/2 Barb X 3/4 Grdn
Blade Guard Assy
Blade Guard Assy
Connector 3/8
Blade Guard W/A RED
GUARD, Splash Blade
Spring TENSION, Guard Blade
Manual Raise and Lower Assy
Manual Raise and Lower Assy
Jack Screw Assy Blade
Jackpost Assy
Jackscrew
BEARING, Flange
Battery Assy
Battery Assy
Bracket Battery
Battery Hold Down KIT
STRAP, Ground
NUT, HEX Finish 5/16-18
Transmission Engage Lever Assy
Transmission Engage Lever Assy
HYD. Transmission Engage Lever Assy
WASHER, Flat SAE 3/8
Hydrostatic Transmission Assy
Hydrostatic Transmission
Hydrostatic Transmission Assy
Hydrostatic Drive Assy
Hydrostatic Drive Assy
CHAIN, Roller .375 Pitch X
Honda GX390K1QWT2 Engine AIR Cleaner Assy
AIR Cleaner Assy
SEAL, AIR Cleaner Cover
GROMMET, AIR Cleaner
COLLAR, AIR Cleaner
Collar B, AIR Cleaner
Honda GX390K1QWT2 Engine Camshaft Assy
Camshaft Assy
SPRING, Weight Return
ROD, Push
ARM, Valve Rocker
LIFTER, Valve
Honda GX390K1QWT2 Engine Carburetor Assy
Carburetor Assy
PLATE, Lever Setting
Gasket SET
Valve SET, Float
Float SET
Honda GX390K1QWT2 Engine Control Assy
Control Assy
ARM, Governor
ROD, Governor
SPRING, Governor
SPRING, Throttle Return
Honda GX390K1QWT2 Engine Crankcase Assy
Crankcase Cover Assy
WEIGHT, Governor
HOLDER, Governor Weight
PIN, Governor Weight
GASKET, Case Cover
Honda GX390K1QWT2 Engine Crankshaft Assy
Crankshaft Assy
WEIGHT, Balancer
Honda GX390K1QWT2 Engine Cylinder Barrel Assy
Cylinder Barrel Assy
Switch ASSY., OIL Level
SHAFT, Governor ARM
BOLT, Drain Plug
OIL Seal
Honda GX390K1QWT2 Engine Cylinder Head Assy
Cylinder Head Assy
GUIDE, Valve OS Optional
CLIP, Valve Guide
GASKET, Cylinder Head
COVER, Head
Honda GX390K1QWT2 Engine FAN Cover Assy
FAN Cover Assy
Switch ASSY., Engine Stop
CLIP, Tube
COVER, FAN *NH1* Black
Shroud
Honda GX390K1QWT2 Engine Flywheel Assy
Flywheel Assy
NUT, Special 16MM
FAN, Cooling
Flywheel
Honda GX390K1QWT2 Engine Fuel Tank Assy
Fuel Tank Assy
RUBBER, Supporter 107MM
JOINT, Fuel Tank
TANK, Fuel *NH1* Black
GASKET, Fuel Filler CAP
Honda GX390K1QWT2 Engine Ignition Coil Assy
Ignition Coil Assy
GROMMET, Wire
WIRE, Stop Switch 430MM
CLIP, Wire Harness
Coil ASSY., Ignition
Honda GX390K1QWT2 Engine Muffler Assy
Muffler 1 Assy
Muffler
PROTECTOR, Muffler
PIPE, EX
CAP, Muffler
Honda GX390K1QWT2 Engine Piston Assy
Piston Assy
BOLT, Connecting ROD
Ring SET, Piston STD
Ring SET, Piston 0.75 Nippon
Piston STD
Honda GX390K1QWT2 Engine Recoil Stater Assy
Recoil Starter Assy
PULLEY, Recoil Starter
RATCHET, Starter
SPRING, Friction
SPRING, Starter Return
Honda GX390K1QWT2 Engine Labels Assy
Labels Assy
LABEL, AIR Cleaner Caution
MARK, AIR Cleaner Sales Point
Emblem
LABEL, Caution
Terms and Conditions of Sale Parts
Freight Policy
SP2S13H20A SAW Operation and Parts Manual REV. #1 05/17/10
HERE’S HOW to GET Help

![]() WARNING
WARNING