Reference Manual for Cable/DSL Wireless Router WGR614
Trademarks
World Wide Web
This page intentionally left blank
Contents
Chapter Wireless Configuration
Chapter Troubleshooting
Appendix C Preparing Your Network
Glossary
Contents
Audience
Preface About This Manual
Typographical Conventions
Special Message Formats
Chapter Introduction
Key Features of the Router
Powerful, True Firewall with Content Filtering
802.11g Wireless Networking
Autosensing Ethernet Connections with Auto Uplink
Security
Extensive Protocol Support
Maintenance and Support
Easy Installation and Management
Package Contents
LED Descriptions
Router’s Front Panel
WGR614 Rear Panel
Router’s Rear Panel
Reference Manual for Cable/DSL Wireless Router WGR614
What You Will Need Before You Begin
Chapter Connecting the Router to the Internet
Cabling and Computer Hardware Requirements
Internet Configuration Requirements
Computer Network Configuration Requirements
Where Do I Get the Internet Configuration Parameters?
Record Your Internet Connection Information
Connecting the Router
Connecting the WGR614
Connect the router to your network
Which
Log in to the router
Log in to the router
Connect to the Internet
Login window
PPPoE Smart Wizard-Detected Option
Setup Smart Wizard menu for PPPoE accounts
Telstra Bigpond Cable Smart Wizard-Detected Option
Setup Smart Wizard menu for Telstra Bigpond Cable accounts
Dynamic IP Smart Wizard-Detected Option
Setup Smart Wizard menu for Dynamic IP address accounts
Fixed IP Account Smart Wizard-Detected Option
Click Apply to save the settings
ISP Does Not Require Login ISP Does Require Login
How to Manually Configure Your Internet Connection
Reference Manual for Cable/DSL Wireless Router WGR614
12 Basic Settings ISP list
Observe Performance, Placement, and Range Guidelines
Chapter Wireless Configuration
WGR614
Implement Appropriate Wireless Security
Wireless Settings menu
Understanding Wireless Settings
Reference Manual for Cable/DSL Wireless Router WGR614
Authentication Scheme Selection
Understanding WEP Authentication and Encryption
Feature Default Factory Settings
Default Factory Settings
WEP Encryption Keys
Before You Change the Ssid and WEP Settings
How to Set Up and Test Basic Wireless Connectivity
How to Restrict Wireless Access by MAC Address
Wireless Card Access List Setup
Wireless Settings encryption menu
How to Configure WEP
Reference Manual for Cable/DSL Wireless Router WGR614
Content Filtering Overview
Chapter Content Filtering
Block Sites menu
Blocking Access to Internet Sites
Block Services menu
Blocking Access to Internet Services
Add Services menu
Configuring a User Defined Service
Configuring Services Blocking by IP Address Range
Scheduling When Blocking Will Be Enforced
Logs menu
Viewing Logs of Web Access or Attempted Web Access
Email menu
Configuring E-Mail Alert and Web Access Log Notifications
Reference Manual for Cable/DSL Wireless Router WGR614
Viewing Router Status Information
Chapter Maintenance
This screen shows the following parameters
Renew Click the Renew button to renew the Dhcp lease
This screen shows the following statistics
Show Statistics action buttons are described in Table
Upgrading the Router Software
Viewing a List of Attached Devices
Router Upgrade menu
Configuration File Management
Settings Backup menu
Restoring and Backing Up the Configuration
Erasing the Configuration
Changing the Administrator Password
Configuring Port Forwarding to Local Servers
Chapter Advanced Configuration
Editing or Deleting a Port Forwarding Entry
Adding a Port Forwarding Custom Service
Multiple Computers for Half Life, Kali or Quake III Example
Local Web and FTP Server Example
Connect Automatically, as Required
Configuring WAN Setup Options
Disable SPI Firewall
Setting Up a Default DMZ Server
Respond to Ping on Internet WAN Port
Setting the MTU Size
Using a Dynamic DNS Service
LAN IP Setup Menu
Using LAN IP Setup Options
Using the Router as a Dhcp server
Using Address Reservation
Static Route Summary Table
How to Configure Static Routes
Click the Add button to open the Add/Edit Menu, shown below
Enabling Remote Management Access
Using Universal Plug and Play UPnP
Reference Manual for Cable/DSL Wireless Router WGR614
Power LED Not On
Chapter Troubleshooting
Basic Functioning
LAN or WAN Port LEDs Not On
LEDs Never Turn Off
Troubleshooting the Web Configuration Interface
Troubleshooting the ISP Connection
Testing the LAN Path to Your Router
Troubleshooting a TCP/IP Network Using a Ping Utility
Testing the Path from Your PC to a Remote Device
Problems with Date and Time
Restoring the Default Configuration and Password
Reference Manual for Cable/DSL Wireless Router WGR614
TCP/IP, RIP-1, RIP-2, Dhcp
Appendix a Technical Specifications
Wireless
Related Publications Basic Router Concepts
Appendix B Network, Routing, Firewall, and Basics
IP Addresses and the Internet
What is a Router?
Routing Information Protocol
Three Main Address Classes
Equals
Netmask
Example of Subnetting a Class B Address
Subnet Addressing
Netmask Notation Translation Table for One Octet
Private IP Addresses
Single IP Address Operation Using NAT
Single IP Address Operation Using NAT
Related Documents
MAC Addresses and Address Resolution Protocol
Internet Security and Firewalls
IP Configuration by Dhcp
Domain Name Server
Stateful Packet Inspection
What is a Firewall?
Ethernet Cabling
Uplink Switches, Crossover Cables, and MDI/MDIX Switching
Cable Quality
Reference Manual for Cable/DSL Wireless Router WGR614
Preparing Your Computers for TCP/IP Networking
Appendix C Preparing Your Network
Install or Verify Windows Networking Components
Configuring Windows 95, 98, and Me for TCP/IP Networking
Reference Manual for Cable/DSL Wireless Router WGR614
Choose Settings, and then Control Panel
Enabling Dhcp to Automatically Configure TCP/IP Settings
Primary Network Logon is set to Windows logon
Verifying TCP/IP Properties
Selecting Windows’ Internet Access Method
Configuring Windows NT4, 2000 or XP for IP Networking
Dhcp Configuration of TCP/IP in Windows XP
Dhcp Configuration of TCP/IP in Windows XP, 2000, or NT4
Locate your Network Neighborhood icon
Reference Manual for Cable/DSL Wireless Router WGR614
Dhcp Configuration of TCP/IP in Windows
Reference Manual for Cable/DSL Wireless Router WGR614
Obtain an IP address automatically is selected
Dhcp Configuration of TCP/IP in Windows NT4
Reference Manual for Cable/DSL Wireless Router WGR614
TCP/IP Properties dialog box now displays
Verifying TCP/IP Properties for Windows XP, 2000, and NT4
MacOS 8.6 or
Configuring the Macintosh for TCP/IP Networking
MacOS
Verifying TCP/IP Properties for Macintosh Computers
What Is Your Configuration Information?
Are Login Protocols Used?
Verifying the Readiness of Your Internet Account
Select the Gateway tab
Reference Manual for Cable/DSL Wireless Router WGR614
Restarting the Network
This page intentionally left blank
Wireless Networking Overview
Appendix D Wireless Networking Basics
Infrastructure Mode
Network Name Extended Service Set Identification Essid
Ad Hoc Mode Peer-to-Peer Workgroup
Authentication
Authentication and WEP
Open System Authentication Steps
Overview of WEP Parameters
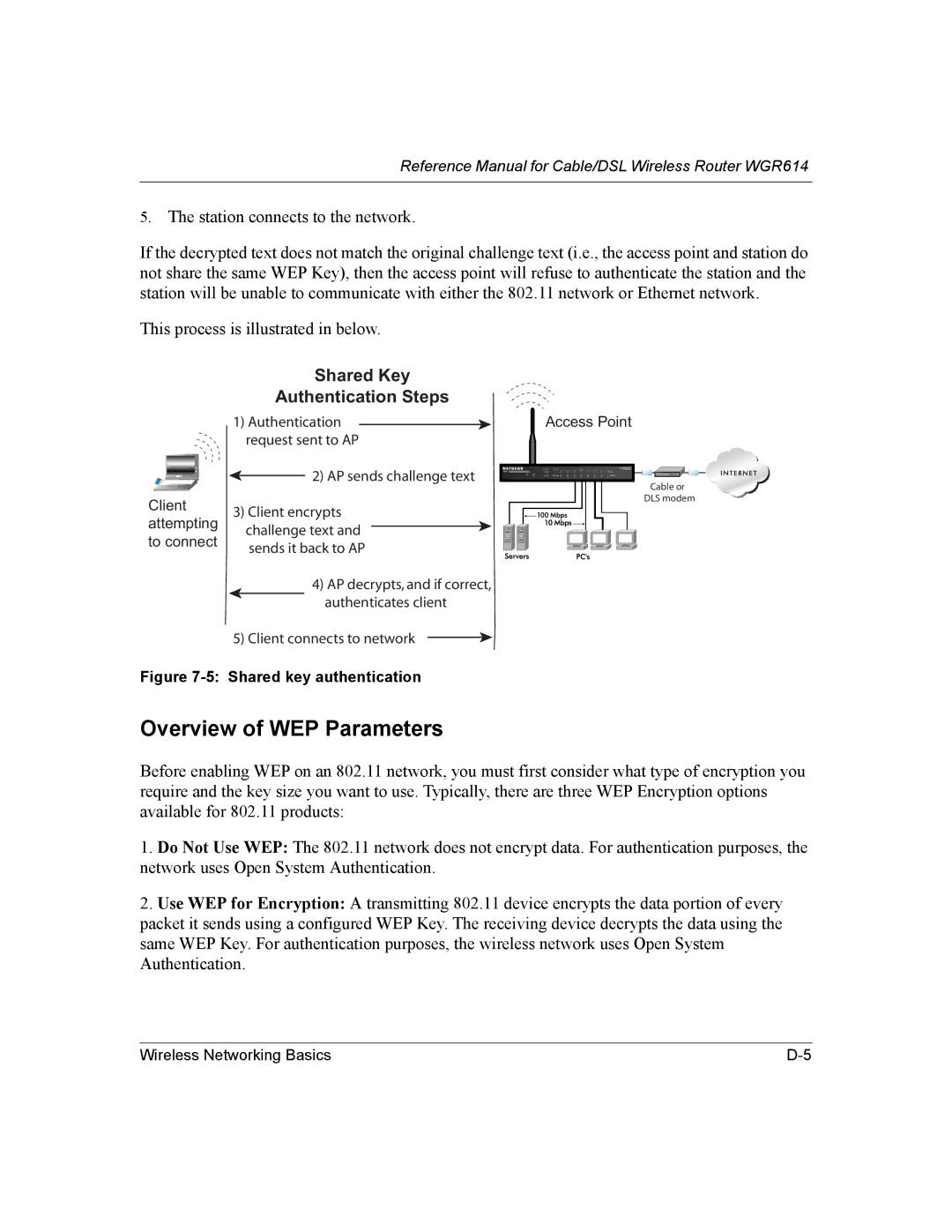
Shared Key Authentication Steps
Key Size
WEP Configuration Options
Wireless Channels
Radio frequency channels used are listed in Table
List of Glossary Terms
Glossary
Adsl
CRL
Encapsulating Security Payload
Internet service provider
Megabits per second
NAT
Public Switched Telephone Network
Ssid
UTP
Wins
Reference Manual for Cable/DSL Wireless Router WGR614
Numerics
Index
Ietf B-1
RFC
Index