Glossary
Decoder
A decoder restores the coded audio signals on DVDs to normal. This is called decoding.
Dolby Digital
This is a method of coding digital signals developed by Dolby Laboratories. Apart from stereo
DTS (Digital Theater Systems)
This surround system is used in many movie theaters around the world. There is good separation between the channels, so realistic sound effects are possible.
Dynamic range
Dynamic range is the difference between the lowest level of sound that can be heard above the noise of the equipment and the highest level of sound before distortion occurs.
Film and video
Frame still and field still
Frames are the still pictures that go together to make a moving picture. There are about 30 frames shown each second.
One frame is made up of two fields. A regular television shows these fields one after the other to create frames.
A still is shown when you pause a moving picture. A frame still is made up of two alternating fields, so the picture may appear blurred, but overall quality is high.
A field still is not blurred, but it has only half the information of a frame still so picture quality is lower.
Interlace and progressive output
NTSC, the video signal standard, has 480 interlaced (I) scan lines, whereas progressive scanning uses twice the number of scan lines. This is called 480P. The video signals output from this unit’s COMPONENT VIDEO OUT terminals (Y, PB, PR) allow you to enjoy higher quality pictures than if the signals were output from the VIDEO OUT terminal or S VIDEO OUT terminal.
I/P/B
MPEG 2, the video compression standard adapted for use with DVD- Video, codes frames using these 3 picture types.
I:Intra coded picture
This picture has the best quality and is the best to use when adjusting the picture.
P:Predictive coded picture
This picture is calculated based on past I or
B:
This picture is calculated by comparing past and future I and P- pictures so it has the lowest volume of information.
Linear PCM (pulse code modulation)
These are uncompressed digital signals, similar to those found on CDs.
Playback control (PBC)
If a Video CD has playback control, you can select scenes and information with menus.
Sampling frequency
Sampling is the process of converting the heights of sound wave (analog signal) samples taken at set periods into digits (digital encoding). Sampling frequency is the number of samples taken per second, so larger numbers mean more faithful reproduction of the original sound.
Tray/disc handling procedure
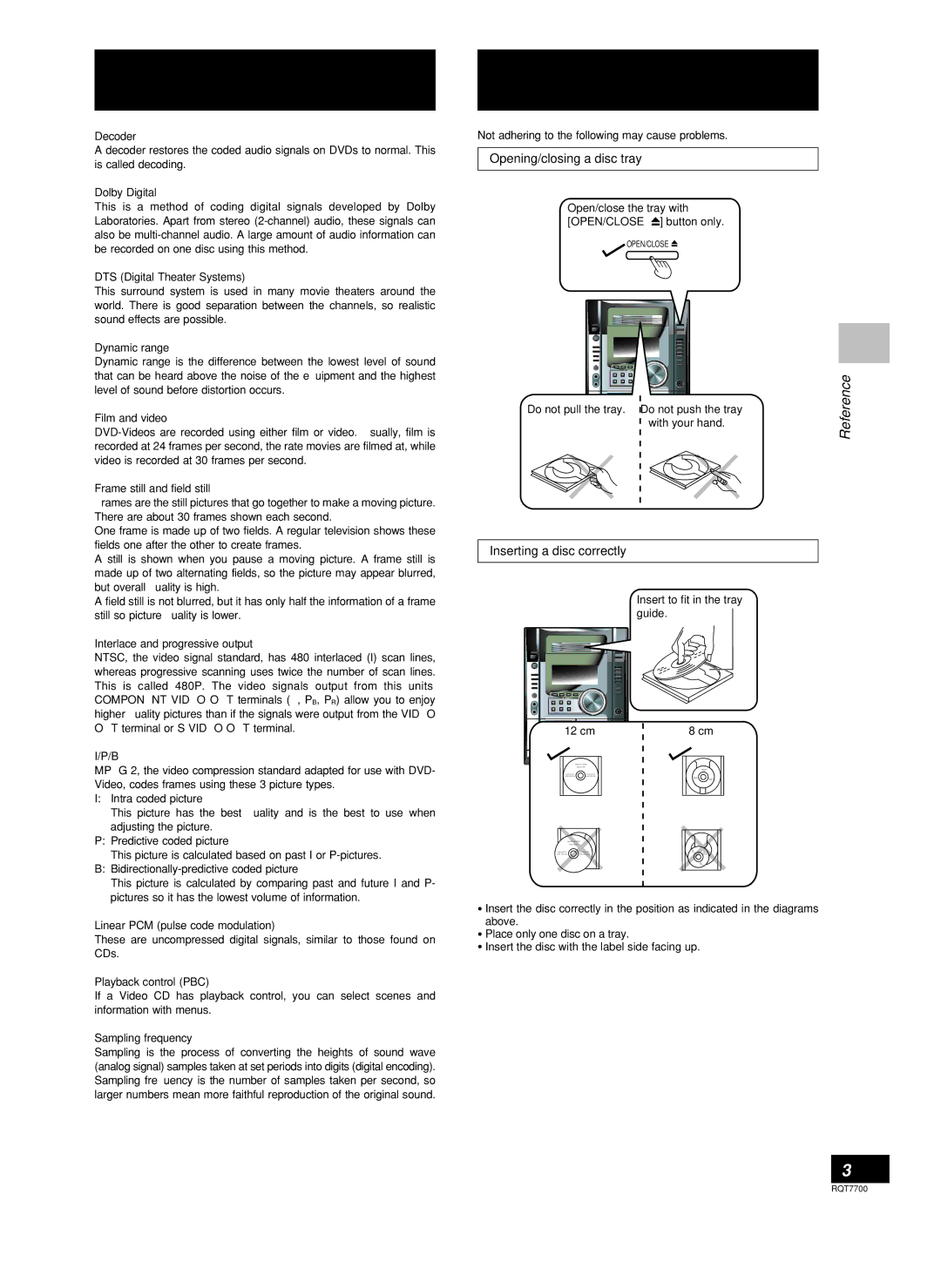
Not adhering to the following may cause problems.
Opening/closing a disc tray
Open/close the tray with [OPEN/CLOSE ![]() ] button only.
] button only.
![]() OPEN/CLOSE
OPEN/CLOSE![]()
Do not pull the tray. Do not push the tray | Reference |
| |
with your hand. |
|
Inserting a disc correctly
Insert to fit in the tray guide.
12 cm | 8 cm |
•Insert the disc correctly in the position as indicated in the diagrams above.
•Place only one disc on a tray.
•Insert the disc with the label side facing up.
35
RQT7700