Crypto-C
Cryptographic Components for C
Distribution
Trademarks
License agreement
Limit distribution of this document to trusted personnel
Contents
Quick Start
Cryptography
N t e n t s
Using Crypto-C 101
Algorithms in Crypto-C
Non-Cryptographic Operations 151
Saved State
Symmetric-Key Operations 177
Public-Key Operations 213
Secret Sharing Operations 305
Putting It All Together An X9.31 Example
Appendix a Command-Line Demos 327
Glossary 339 Index 349
List of Figures
A B S a F E C r y p t o C D e v e l o p e r ’s G u i d e
List of Tables
A B S a F E C r y p t o C D e v e l o p e r ’s G u i d e
Preface
Hardware support
What’s New in Version 5.2.2?
Improved performance
MultiPrime RSA
Organization of This Manual
Organization of This Manual
Advanced Encryption Standard AES
E f a c e
Conventions Used in This Manual
Crypto-C procedures to use with algorithm object
Conventions Used in This Manual
Terms and Abbreviations
Terms and Abbreviations
Related Documents
Related Documents
A B S a F E C r y p t o C D e v e l o p e r ’s G u i d e
Ieee Standard Specifications for Public-Key Cryptography on
Http//stdsbbs.ieee.org/groups/1363/index.html
How to Contact RSA Security
How to Contact RSA Security
RSA Security Web Site Getting Support and Service
You can get technical support as follows
Introduction
Crypto-C Toolkit
Algorithms
Elliptic Curve Public-Key Algorithms
Public-Key Algorithms
Digital Signatures
Secret Sharing
Nist Standards and Crypto-C
Cryptographic Standards and Crypto-C
Pkcs Standards and Crypto-C
Nist Approval and Windows 32-bit Platforms
Pkcs Compared with Nist
Nist Approval and Windows NT Platforms
Ansi X9 Standards and Crypto-C
Quick Start
Six-Step Sequence
Six-Step Sequence
Creating an Algorithm Object
Introductory Example
Include Files
Introductory Example
Typedef unsigned char *POINTER
Where Pointer is defined in aglobal.h
Nullptr is also defined in aglobal.h
#define Nullptr POINTER0
Balgorithmobj algorithmObject Algorithm object
Setting the Algorithm Object
Algorithm information
Init
Break
Creating a Key Object
Setting a Key Object
For our example, we use
Int BSetKeyInfo
Key information
Selecting an Algorithm Chooser
Now we can complete the call to BSetKeyInfo
Surrender Context
Update
Saving the Object State optional
We can now complete our call to BEncryptInit
Length of output data
Output data buffer
Unsigned int
Input data
For now, we declare
Unsigned int outputLenUpdate
Unsigned char *encryptedData = Nullptr
If status = BEncryptUpdate
Final
Destroy
Asurrenderctx *surrenderContext Surrender context
Balgorithmobj * algorithmObject
For our example, we use the following
Pointer to key object
Pointer block
Tfree encryptedData
Putting It All Together
For this example, call Tfree as follows
If rc4KeyItem.data != Nullptr
Init If status = BEncryptInit
Introductory Example
If encryptedData != Nullptr
EncryptedData = Nullptr End main
Decrypting the Introductory Example
Decrypting the Introductory Example
Creating the Key Object
First create the algorithm object
Setting the Key Object
Always destroy objects when you no longer need them
DecryptedData = Nullptr
Multiple Updates
Multiple Updates
Updatesize
Break End while
Multiple Updates
Create
Summary of the Six Steps
Include
Set
Final
Page
Cryptography
Ciphers
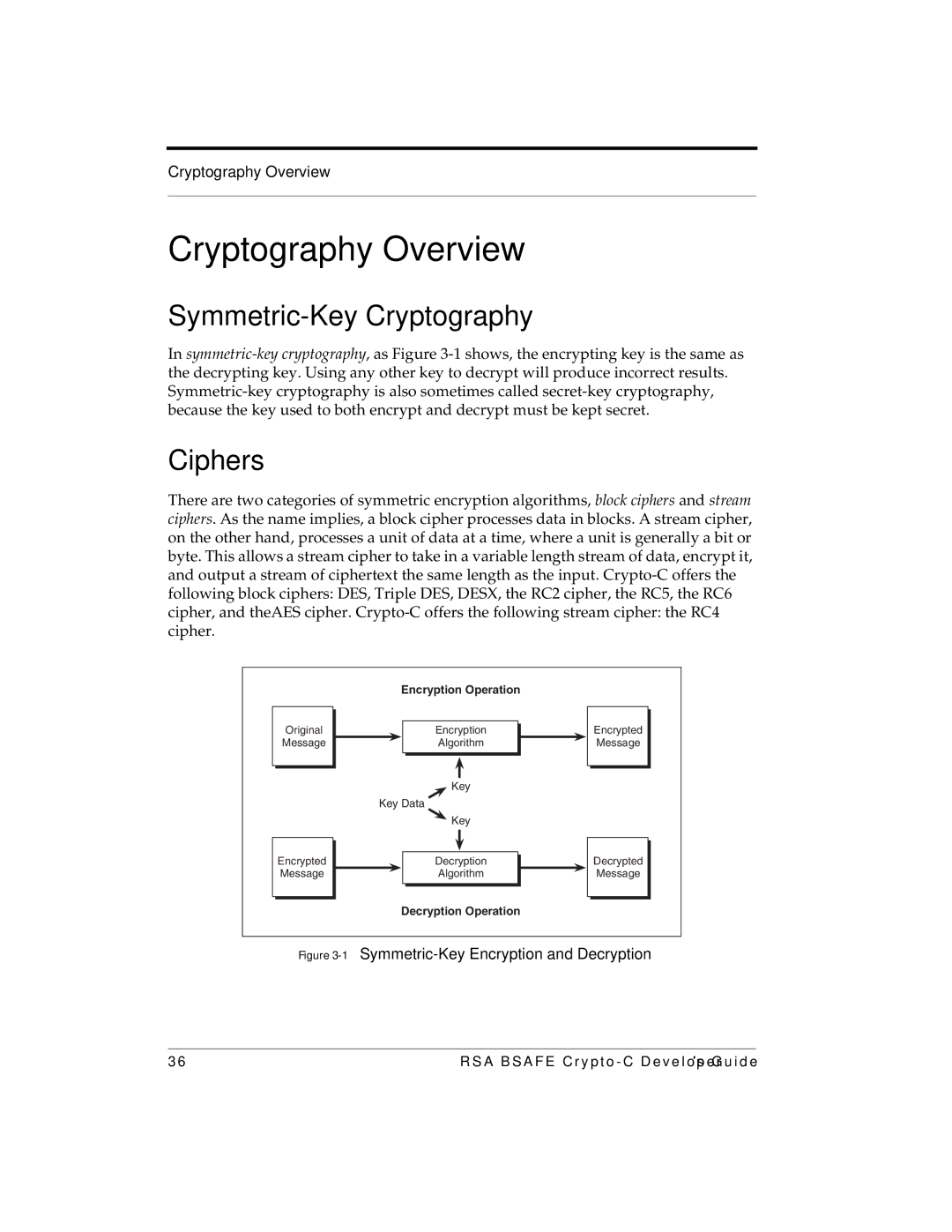
Cryptography Overview
Symmetric-Key Cryptography
Cryptography Overview
Ciphers in Crypto-C
Block Ciphers
Padding
Crypto-C implements the following block ciphers
Triple DES
2Triple DES Encryption as Implemented in Crypto-C
RC5
RC6
Modes of Operation
Four Modes
Electronic Codebook ECB Mode
3Electronic Codebook ECB Mode
Cipher Block Chaining CBC Mode
Cipher Feedback CFB Mode
5Cipher Feedback CFB Mode
Output Feedback OFB Mode
6Output Feedback Mode OFB
Stream Ciphers
Message Digests
RC4 algorithm with MAC
Message Digests and Pseudo-Random Numbers
Password-Based Encryption
Hash-Based Message Authentication Codes Hmac
8DES Key and IV Generation for Password Based Encryption
Public-Key Cryptography
RSA Algorithm
9Public-Key Cryptography
MultiPrime Numbers
Modular Math
Prime Numbers
RSA Algorithm
Cryptography Overview
Calculation is shown in Table
Summary
Security
1Calculation of 827 mod
Digital Envelopes
Optimal Asymmetric Encryption Padding Oaep
10Digital Envelope
Authentication and Digital Signatures
Cryptography Overview
11RSA Digital Signature
Digital Signature Algorithm DSA
Digital Certificates
Math
Diffie-Hellman Public Key Agreement
Algorithm
Phase
Phase
Parameter Generation
Math
Elliptic Curve Cryptography
Multiple-Party Key Agreement
Elliptic Curve Parameters
Finite Field
Fields of Even Characteristic
Odd Prime Fields
Coefficients Over an Odd Prime Field
= 0·I ≡ 2·2m-1·Imod2m
Points of an Elliptic Curve
Coefficients Over a Field of Even Characteristic
Point P and its Order
Elliptic curve parameters
Point of Prime Order
Order of an Elliptic Curve
Order of a Point
Is written EFq
Order n of P Is sometimes called the base point
Summary of Elliptic Curve Terminology
Cofactor
2Elliptic Curve Parameters
Representing Fields of Even Characteristic
Elliptic Curve Key Pair Generation
Creating the Key Pair
Ecdsa Signature Scheme
Signing a Message
Verifying a Signature
Math
Recall that Q = dP, so
Elliptic Curve Authenticated Encryption Scheme Ecaes
Now recall that s = k-1e+dr mod n, so
Encrypting a Message Using the Public Key
Decrypting a Message Using the Private Key
Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman Key Agreement
Phase
13Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman Key Agreement
Secret Sharing
First coordinate of S, xS, is their agreed-upon secret key
Working with Keys
Key Generation
Key Management
Key Escrow
Local Applications
Applications of Cryptography
Ascii Encoding and Decoding
Applications of Cryptography
Point-to-Point Applications
Client/Server Applications
Peer-to-Peer Applications
Stream vs. Block Symmetric-Key Algorithms
Choosing Algorithms
Public-Key vs. Symmetric-Key Cryptography
Choosing Algorithms
Block Symmetric-Key Algorithms
Key Agreement vs. Digital Envelopes
Secret Sharing and Key Escrow
Elliptic Curve Algorithms
Interoperability
Elliptic Curve Standards
Security Considerations
Handling Private Keys
Security Considerations
Temporary Buffers
Pseudo-Random Numbers and Seed Generation
Choosing Passwords
DES Weak Keys
Initialization Vectors and Salts
3DES Weak and Semi-Weak Keys
Stream Ciphers
Timing Attacks and Blinding
Pick a random value r and compute
= mre mod n
Choosing Key Sizes
MD5p padP MD5q padQ m
RSA Keys
4Summary of Recommended Key Sizes
RC4 Key Bits
Diffie-Hellman Parameters and DSA Keys
RC2 Effective Key Bits
RC5 Key Bits and Rounds
Elliptic Curve Keys
Using Crypto-C
Algorithms in Crypto-C
BER-Based Algorithm Info Types
Information Formats Provided by Crypto-C
Basic Algorithm Info Types
Algorithms in Crypto-C
BSAFE1 Algorithm Info Types
Summary of AIs
PEM-Based Algorithm Info Types
1Message Digests
4Pseudo-Random Number Generation
Algorithms in Crypto-C 2Message Authentication
3ASCII Encoding
5Symmetric Stream Ciphers
Algorithms in Crypto-C 5Symmetric Stream Ciphers
6Symmetric Block Ciphers
Algorithms in Crypto-C 6Symmetric Block Ciphers
RC2
7RSA Public-Key Cryptography
Key Generation
Algorithms in Crypto-C 7RSA Public-Key Cryptography
Oaep
8DSA Public-Key Cryptography
Digital Signatures
Algorithms in Crypto-C 9Diffie-Hellman Key Agreement
10Elliptic Curve Public-Key Cryptography
11Bloom-Shamir Secret Sharing
10 Elliptic Curve Public-Key Cryptography
12Hardware Interface
Algorithms in Crypto-C 13Advanced Encryption Standard AES
Algorithm Info Type
Keys In Crypto-C
Keys In Crypto-C
Summary of KIs
15Block Cipher Keys
16RSA Public and Private Keys
Keys In Crypto-C 15Block Cipher Keys
17DSA Public and Private Keys
Keys In Crypto-C 18Elliptic Curve Keys
An Encryption Algorithm Chooser
System Considerations In Crypto-C
Algorithm Choosers
System Considerations In Crypto-C
An RSA Algorithm Chooser
Surrender Context
Description of AIX962RandomV0 instead of AISHA1Random
Reserved for future use
Sample Surrender Function
Also gives the form that a surrender function must have
Int *Surrender Pointer handle
Saving State
When to Allocate Memory
Crypto-C uses the following memory-management routines
Memory-Management Routines
Memory-Management Routines and Standard C Libraries
Tmalloc Trealloc Tfree Tmemset Tmemcpy Tmemmove Tmemcmp
Memory Allocation
BER/DER Encoding
Binary Data
Typedef struct unsigned char *data unsigned int len
System Considerations In Crypto-C
Input constraints
Input and Output
Symmetric Block Algorithms
Output considerations
20Input Limits for RSA Pkcs Encryption
General Considerations
DES Keys
Key Size
Public Key Size
Private Key Size
C2 58 60 B1
00 C2 58 60 B1
Using Cryptographic Hardware
Using Cryptographic Hardware
Interfacing with a Bhapi Implementation
2Algorithm Object in a Hardware Implementation
Pkcs #11 Support
Using a Pkcs #11 Device with Crypto-C
Using Cryptographic Hardware
Balgorithmmethod *RSASIGNHWCHOOSER = &AMMD5
Using Cryptographic Hardware
KeypairGenParams.privateKeyAttributes.tokenFlag =
Tfprivate
Now generate
Using Cryptographic Hardware
Using Cryptographic Hardware
Return Behardware
Pkcs #11 Support for DSA Key Pair Generation
Balgorithmmethod *DSAKEYGENCHOOSER = &AMDSAKEYGEN
P11KeyGenParams.privateKeyAttributes.keyUsage =
POINTER&pubKeyData-params
Digest
Advanced Pkcs #11
For an RSA private key, it would be this
00 00 00 66 a9 47 2d 80 5a
Ckrv rv Rv =
Hardware Issues
Random Numbers
CKBYTEPTRseedBuffer, CKULONGseedLen
Using Cryptographic Hardware
Page
Non-Cryptographic Operations
Message Digests
Message Digests
Creating a Digest
Example in this section corresponds to the file mdigest.c
If status = BDigestInit
Your call will be the following
If status = BDigestUpdate
#define Digestlen
Remember to destroy all objects when you are done with them
BER-Encoding the Digest
Saved State
Saving the State of a Digest Algorithm Object
Following example BER-encodes the preceeding sample digest
Item stateInfo = Null
Message Digests
1Code Sample DigestDataSavedState
Status = Rsademoealloc break
Message Digests
Hash-Based Message Authentication Code Hmac
Hash-Based Message Authentication Code
Generate a random 24-byte key using KI24Byte
Hash-Based Message Authentication Code Hmac
Create the key object
RandomAlgorithm, keyData, KEYSIZE, Asurrenderctx *NULLPTR !=
Unsigned char *digestedData unsigned int digestedDataLen
Generating Random Numbers with SHA1
Generating Random Numbers
Generating Random Numbers
Setting The Algorithm Object
Random Seed
Puts Enter a random seed if status =
Unsigned char *gets char *randomSeed != 0 break
Generate
If status = BGenerateRandomBytes
Typedef struct
Generating Independent Streams of Randomness
This step is identical to the previous example
Additional seeding
These steps are identical to the previous example
Steps 4, 5
Item randomSeed AX931RANDOMPARAMS x931Params
Encoding Binary Data To Ascii
Converting Data Between Binary
Converting Data Between Binary and Ascii
If status = BEncodeInit asciiEncoder != 0 break
Decoding ASCII-Encoded Data
BDestroyAlgorithmObject &asciiEncoder Tfree asciiEncoding
If status = BDecodeInit asciiDecoder != 0 break
If status = binaryDecoding == Nullptr != 0 break
BDestroyAlgorithmObject &asciiDecoder Tfree binaryDecoding
Symmetric-Key Operations
Block Ciphers
Block Ciphers
DES with CBC
Example in this section corresponds to the file descbc.c
Points at init vector Item
Examples include des, rc5
RC5 parameters
For new padding schemes
Now set up the Bblkcipherwfeedbackparams structure
Call BGenerateRandomBytes
Depends on cipher type, as follows
Format of info supplied to BSetKeyInfo
Unsigned int outputBufferSize
Decrypting
RC2 Cipher
Now you can set your algorithm object as follows
Init
Use a random number generator to come up with 24 bytes
If rc2KeyItem.data != Nullptr
Update
EncryptedData = Nullptr If rc2KeyItem.data != Nullptr
RC5 Cipher
255 Unsigned int
0x10 Unsigned int
Initialization vector
Unsigned char initVector8 ARC5CBCPARAMS rc5Params
Item rc5KeyItem
Use a random number generator to create 10 bytes
If rc5KeyItem.data != Nullptr
Update
Final
RC6 Cipher
EncryptedData = Nullptr
#define Blocksize Unsigned char initVectorBLOCKSIZE
Setting the Key Data
If rc6KeyItem.data != Nullptr
Break OutputLenTotal = outputLenUpdate + outputLenFinal
AES Cipher
Been allocated
Unsigned char *aesParams
Creating a Key Object
If aesKeyItem.data != Nullptr
Final
Password-Based Encryption
Unsigned char * salt
Iteration count
Init
Tmemset pbeKeyItem.data, 0, Maxpwlen
Update
Final
Page
Public-Key Operations
Generating a Key Pair
Performing RSA Operations
Performing RSA Operations
Where Item is
There is no in generating a key pair
Destroy
MultiPrime
What is MultiPrime?
MultiPrime
Milliseconds Private non-CRT
How Many Primes?
Two-Prime RSA 48.8 17.5 Three-Prime RSA 10.9
Sample
BGenerateKeypair
BGenerateInit
RsaGen
BGetKeyInfo
Generating an RSA MultiPrime Key
Set the Algorithm Object
Distributing an RSA Public Key
If status = BGenerateInit keypairGenerator
BER/DER Encoding
Crypto-C Format
If you looked at the elements of the struct
Format of info returned by BGetKeyInfo
If status = myPublicKeyBER.data == Nullptr !=
Send it off Remember to free any memory you allocated
RSA Public-Key Encryption
Tfree myPublicKeyBER.data
Reference Manual entry on AIPKCSRSAPublic states
Input constraints
#define Blocksize
RSA Private-Key Decryption
If status = BDecryptInit
Optimal Asymetric Encryption Padding Oaep
Raw RSA Encryption and Decryption
MultiPrime
RSA Digital Signatures
Computing a Digital Signature
Setting The Algorithm Object
Entry for the AI in use
Verifying a Digital Signature
Surrender context outlined in The Surrender Context on
If status = BVerifyInit
Update
Generating DSA Parameters
Performing DSA Operations
Performing DSA Operations
There is no in generating DSA parameters
Bdsaparamgenparams dsaParams DsaParams.primeBits =
Generate
Generating a DSA Key Pair
DSA Signatures
Computing a Digital Signature Creating An Algorithm Object
Properly cast Nullptr for the surrender context
#define Maxsiglen
To verify the signature created here, use the same AI
Data and you know its length, your call is the following
Generating Diffie-Hellman Parameters
Performing Diffie-Hellman Key Agreement
Adhparamgenparams
There is no in generating Diffie-Hellman parameters
Adhparamgenparams dhParams
Destroy
Distributing Diffie-Hellman Parameters
Base generator
BER Format
If you look at the elements of the struct
A p t e r 7 P u b l i c K e y O p e r a t i o n s
Diffie-Hellman Key Agreement
Item dhParametersBER
If status = BKeyAgreeInit
Phase
Saving the Object State
Other party should send their public value and its length
Generating Elliptic Curve Parameters
Performing Elliptic Curve Operations
Performing Elliptic Curve Operations
Format of info supplied to BSetAlgorithmInfo
Input of 0 defaults to fieldElementBits
Input of 0 defaults to
Implementation version
Performing Elliptic Curve Operations
No Update step is necessary for parameter generation
Retrieving Elliptic Curve Parameters
GeneralFlag =
Case that fieldType = Ftfp
Indicates type of base field
It is the prime number
Elliptic curve coefficient
If status = output-base.data == Nullptr != 0 break
Aecparams ecParamInfo
If status = output-order.data == Nullptr != 0 break
FreeECParamInfo&ecParamInfo
Generating an Elliptic Curve Key Pair
Sample code, FreeECParamInfo is implemented as follows
Becparams paramInfo
There is no Update step for key generation
Initialize
Public component
Retrieving an Elliptic Curve Key
KIECPublic gives a pointer to an Aecpublickey structure
Aecparams curveParams
Performing Elliptic Curve Operations
Generating a Generic Acceleration Table
Generating Acceleration Tables
End FreeECPubKeyInfo
Format the information
Retrieve the elliptic curve parameters
Aecparams *cryptocECParamInfo Aecparams ecParamInfo
There is no Update step for building acceleration tables
For odd prime field
Build the acceleration table
Allocate memory
Item accelTableItem
Generating a Public-Key Acceleration Table
Retrieve the public key information
Put the information retrieved in the proper format
FreeECPubKeyInfo&publicKeyInfo
Item pubKeyAccelTableItem unsigned int maxTableLen
Item pubKeyAccelTableItem
Performing EC Diffie-Hellman Key Agreement
Build the public-key acceleration table
GeneralFlag = If status = BBuildTableFinal
Create
Optional Set Acceleration Table Info
If status = alicePublicValue == Nullptr != 0 break
Performing Ecdsa in Compliance with Ansi
If status = aliceSecretValue == Nullptr != 0 break
Generating EC Parameters
Generating an EC Key Pair
Computing a Digital Signature Create
Build an algorithm chooser with the appropriate AMs
Item aTableItem
Aecparams *ecParamInfo
Now, using BSignUpdate, pass in the data to be signed
If status = signature == Nullptr != 0 break
Use the same AI and digestInfo as you did for signing
Initialized random algorithm in BSignFinal
Destroy all objects that are no longer needed
Unsigned int signatureLen
Optional Set Public Key Acceleration Table Info
Performing Ecdsa with X9.62-Compliant BER
0x52 0xd1
Item stockECParamsBER
ECParamsBER154 = 0x30 0x81
0x7a
StockECParamsBER.data = ECParamsBER stockECParamsBER.len =
0x73
DataToSign = 0x53
0x68
0x79
Aecparams *ecParamsInfo
Use the same AI as you did for signing
Using Ecaes
Tfreesignature BDestoryAlgorithmObject &ecDSAVerify
Using an EC Key Pair
Using Elliptic Curve Parameters
Ecaes Public-Key Encryption
Now, pass this information into your algorithm object
Optional Acceleration Table
Item accelerationTableItem
Break FieldElementLen = ecParamInfo-fieldElementBits + 7
Final
Steps for decryption are similar to those for encryption
Ecaes Private-Key Decryption
Create an algorithm object
MaxDecryptedDataLen = outputLenTotal
BDecryptUpdate
OutputLenUpdate
= TmallocmaxDecryptedDataLen
Page
Secret Sharing
Generating Shares
Secret Sharing
Example in this section corresponds to the file scrtshar.c
#define Secretsize 16 #define Totalshares
Unsigned int outputLenFinal If status = BEncryptFinal
If status = secretSharecount == Nullptr != 0 break
Break If status != 0 break
Tfree secretSharecount
Reconstructing the Secret
Use the same AI, AIBSSecretSharing
Asurrenderctx *NULLPTR != 0 break If status != 0 break
BDestroyAlgorithmObject &secretReconstructer
Page
Putting It All Together An X9.31 Example
X9.31 Sample Program
X9.31 Sample Program
Bkeyobj privateKey = Bkeyobjnullptr Item randomSeed
Unsigned int status
Generating Random Bytes
Static unsigned char f4Data = 0x01, 0x00
Printf ================================================\n
To create a random algorithm object and set the parameters
Providing the Seed
Generating a Key Pair
Break
Printf ============================= \n
Computing a Digital Signature
RsaVerifyX931. For signing, use rsaSignX931
AX931PARAMS
Break Init
Verifying the Signature
If status !=
Surrendering Control
Return End GeneralSurrenderFunction
Printing the Buffer Contents
Overview of the Demos
Appendix a
Input Redirection mode
Command-Line Demo User’s Guide
Command Line mode
Command-Line Demo User’s Guide
Specifying User Keys
Using Bdemo
Sign a File
Verify a Signed File
Create a File Envelope
Open a File Envelope
Generate a Key Pair
Running Bdemodsa
Using Bdemodsa
Enter any arbitrary string of printable characters
Sign a File
Using Bdemoec
Running Bdemoec
File Reference
File Reference
Table A-1Demo Program Source Files
BSLite
BSLite Table A-1Demo Program Source Files
BSLite
Page
Glossary
American National Standards Institute
Advanced Encryption Standard
Series of steps used to complete a task
Application Programming Interface
O s s a r y
See ECC
Generic security service application program interface
Electronic business Data Interchange
See XOR
Act of creating a key
Process of having a third party hold onto encryption keys
Process that creates a larger key from the original key
An algorithm that generates the subkeys in a block cipher
Data to be encrypted
Extra bits concatenated with a key, password, or plaintext
Private key in the RSA public-key cryptosystem
Number extracted from a pseudo- random sequence
Secure Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions
See secret key
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
Secure Wide Area Network
Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria
XOR
Page
Index
Ecdsa
D e
A B S a F E C r y p t o C D e v e l o p e r ’s G u i d e
D e
See also RC4 subprime