Achieving Low Power and Superb Viewability
Amorphous Optical Sensors
Amorphous Silicon Solar Cells
Amorphous Optical Sensors 
These devices are a type of photodiode that can detect light with about the same sensitivity as the human eye. Since these devices flexibly support a wide range of end product designs and sizes, they can be used to control the LCD backlight and button lamps in cell phones to implement power saving automatic brightness adjustment
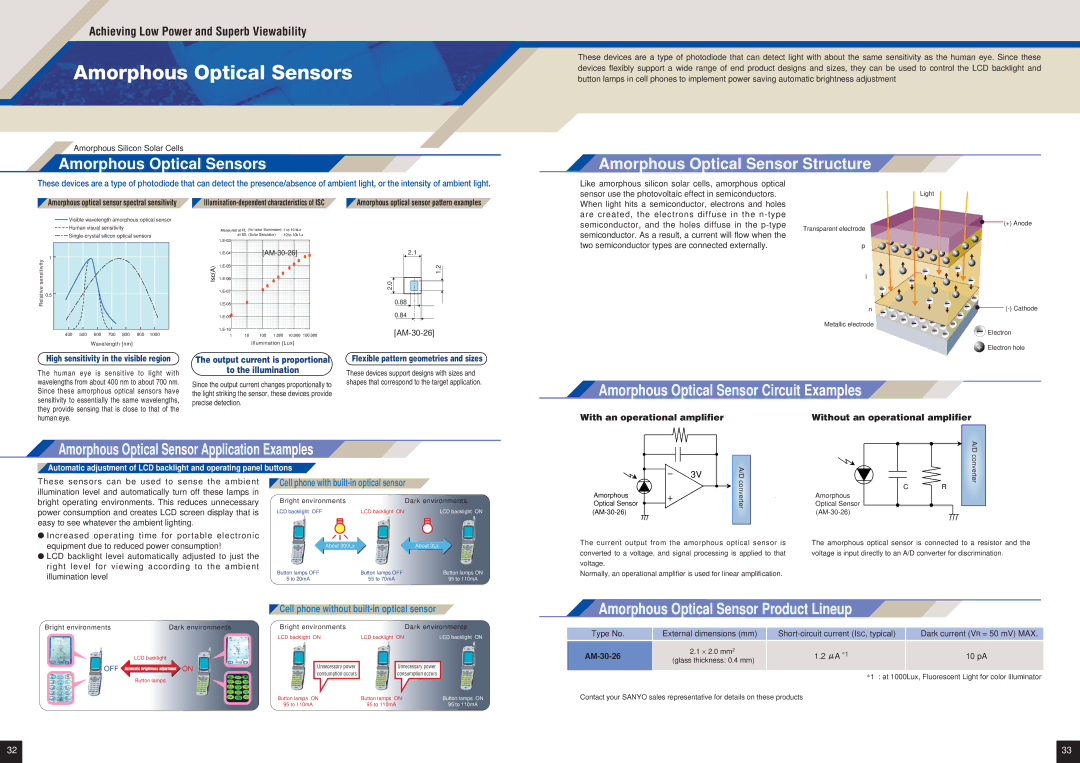
Amorphous Optical Sensor Structure
These devices are a type of photodiode that can detect the presence/absence of ambient light, or the intensity of ambient light.
Like amorphous silicon solar cells, amorphous optical sensor use the photovoltaic effect in semiconductors.
Light
Amorphous optical sensor spectral sensitivity
Visible wavelength amorphous optical sensor
Human visual sensitivity
|
|
| Amorphous optical sensor pattern examples |
Measured at FL (for color illuminator): 1 to 10 kLx at SS (Solar Simulator)
When light hits a semiconductor, electrons and holes are created, the electrons diffuse in the
![]() (+) Anode
(+) Anode
Transparent electrode |
+ |
sensitivity | 1 |
| |
Relative | 0.5 |
400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 | 1000 |
Isc(A)
![]()
![]()
1
10 | 100 | 1,000 | 10,000 | 100,000 |
2.1 1.2
2.0
0.88
0.84
[AM-30-26]
two semiconductor types are connected externally.
p | + | + + | + |
|
| + |
|
|
| + |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| + |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| + |
| + |
|
|
|
| + |
|
|
|
|
| + |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| + |
|
| + |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
i | + |
|
|
|
|
|
| + |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| + |
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| + |
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| + |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| + |
|
|
| + |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||
n |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
Metallic electrode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Electron | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Wavelength [nm]
High sensitivity in the visible region
The human eye is sensitive to light with wavelengths from about 400 nm to about 700 nm. Since these amorphous optical sensors have sensitivity to essentially the same wavelengths, they provide sensing that is close to that of the
Illumination [Lux]
The output current is proportional
to the illumination
Since the output current changes proportionally to the light striking the sensor, these devices provide precise detection.
Flexible pattern geometries and sizes
These devices support designs with sizes and shapes that correspond to the target application.
+ Electron hole
Amorphous Optical Sensor Circuit Examples
human eye.
With an operational amplifier
Without an operational amplifier
Amorphous Optical Sensor Application Examples
Automatic adjustment of LCD backlight and operating panel buttons
A/D
A/D converter
These sensors can be used to sense the ambient illumination level and automatically turn off these lamps in bright operating environments. This reduces unnecessary power consumption and creates LCD screen display that is easy to see whatever the ambient lighting.
Cell phone with built-in optical sensor
Bright environments |
| Dark environments |
LCD backlight OFF | LCD backlight ON | LCD backlight ON |
Amorphous Optical Sensor
converter
C
Amorphous
Optical Sensor
R
●Increased operating time for portable electronic equipment due to reduced power consumption!
●LCD backlight level automatically adjusted to just the right level for viewing according to the ambient illumination level
Bright environments | Dark environments |
| LCD backlight |
OFF | Automatic brightness adjustment ON |
| Button lamps |
| About 300Lx | About 3Lx |
| |
Button lamps OFF | Button lamps OFF | Button lamps ON | ||
| 5 to 20mA | 55 to 70mA | 95 to 110mA | |
|
|
|
| |
| Cell phone without |
|
| |
| Bright environments | Dark environments | ||
LCD backlight ON | LCD backlight ON | LCD backlight ON | ||
| Unnecessary power | Unnecessary power |
| |
| consumption occurs | consumption occurs |
| |
Button lamps ON | Button lamps ON | Button lamps ON | ||
| 95 to 110mA | 95 to 110mA | 95 to 110mA | |
The current output from the amorphous optical sensor is | The amorphous optical sensor is connected to a resistor and the |
converted to a voltage, and signal processing is applied to that | voltage is input directly to an A/D converter for discrimination. |
voltage. |
|
Normally, an operational amplifier is used for linear amplification. |
|
Amorphous Optical Sensor Product Lineup
Type No. | External dimensions (mm) | Dark current (VR = 50 mV) MAX. | ||
| 2.1 ⋅ 2.0 mm2 | 1.2 A *1 | 10 pA | |
(glass thickness: 0.4 mm) | ||||
|
|
| ||
|
|
| ||
|
| *1 : at 1000Lux, Fluorescent Light for color illuminator | ||
Contact your SANYO sales representative for details on these products |
| |||
32 |
| 33 |
|
|
|