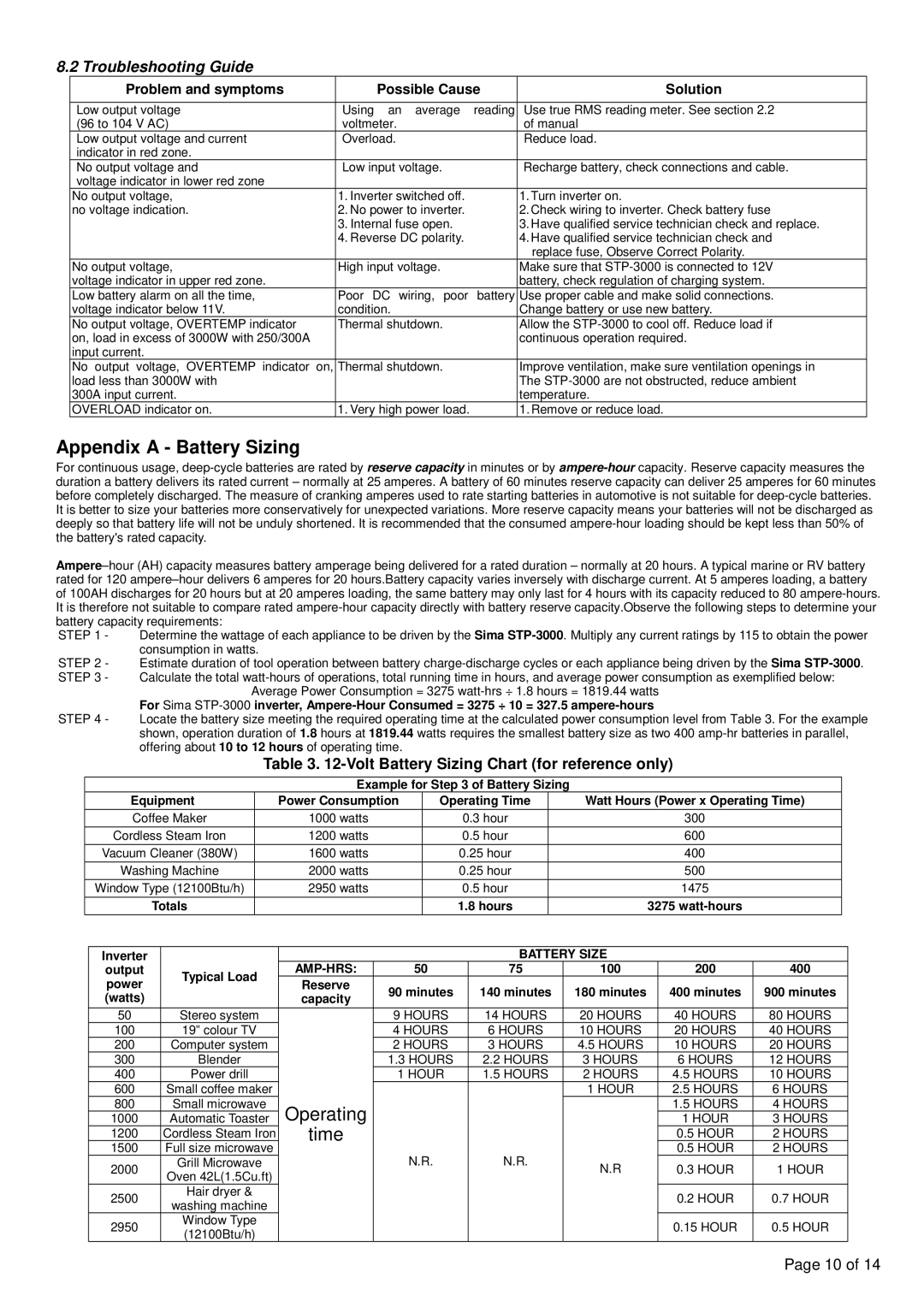
8.2 Troubleshooting Guide
Problem and symptoms | Possible Cause | Solution |
|
|
|
Low output voltage | Using an average reading | Use true RMS reading meter. See section 2.2 |
(96 to 104 V AC) | voltmeter. | of manual |
Low output voltage and current | Overload. | Reduce load. |
indicator in red zone. |
|
|
No output voltage and | Low input voltage. | Recharge battery, check connections and cable. |
voltage indicator in lower red zone |
|
|
No output voltage, | 1. Inverter switched off. | 1. Turn inverter on. |
no voltage indication. | 2. No power to inverter. | 2. Check wiring to inverter. Check battery fuse |
| 3. Internal fuse open. | 3. Have qualified service technician check and replace. |
| 4. Reverse DC polarity. | 4. Have qualified service technician check and |
|
| replace fuse, Observe Correct Polarity. |
No output voltage, | High input voltage. | Make sure that |
voltage indicator in upper red zone. |
| battery, check regulation of charging system. |
Low battery alarm on all the time, | Poor DC wiring, poor battery | Use proper cable and make solid connections. |
voltage indicator below 11V. | condition. | Change battery or use new battery. |
No output voltage, OVERTEMP indicator | Thermal shutdown. | Allow the |
on, load in excess of 3000W with 250/300A |
| continuous operation required. |
input current. |
|
|
No output voltage, OVERTEMP indicator on, | Thermal shutdown. | Improve ventilation, make sure ventilation openings in |
load less than 3000W with |
| The |
300A input current. |
| temperature. |
OVERLOAD indicator on. | 1. Very high power load. | 1. Remove or reduce load. |
Appendix A - Battery Sizing
For continuous usage,
STEP 1 - Determine the wattage of each appliance to be driven by the Sima
STEP 2 - Estimate duration of tool operation between battery
STEP 3 - Calculate the total
For Sima
STEP 4 - Locate the battery size meeting the required operating time at the calculated power consumption level from Table 3. For the example shown, operation duration of 1.8 hours at 1819.44 watts requires the smallest battery size as two 400
Table 3. 12-Volt Battery Sizing Chart (for reference only)
Example for Step 3 of Battery Sizing
Equipment | Power Consumption | Operating Time | Watt Hours (Power x Operating Time) |
Coffee Maker | 1000 watts | 0.3 hour | 300 |
Cordless Steam Iron | 1200 watts | 0.5 hour | 600 |
Vacuum Cleaner (380W) | 1600 watts | 0.25 hour | 400 |
Washing Machine | 2000 watts | 0.25 hour | 500 |
Window Type (12100Btu/h) | 2950 watts | 0.5 hour | 1475 |
Totals
1.8 hours
3275
Inverter |
|
|
| BATTERY SIZE |
|
| ||
output | Typical Load |
| 50 | 75 | 100 | 200 | 400 | |
power | Reserve | 90 minutes | 140 minutes | 180 minutes | 400 minutes | 900 minutes | ||
| ||||||||
(watts) |
| capacity | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
50 | Stereo system |
| 9 HOURS | 14 HOURS | 20 HOURS | 40 HOURS | 80 HOURS | |
100 | 19” colour TV |
| 4 HOURS | 6 HOURS | 10 HOURS | 20 HOURS | 40 HOURS | |
200 | Computer system |
| 2 HOURS | 3 HOURS | 4.5 HOURS | 10 HOURS | 20 HOURS | |
300 | Blender |
| 1.3 HOURS | 2.2 HOURS | 3 HOURS | 6 HOURS | 12 HOURS | |
400 | Power drill |
| 1 HOUR | 1.5 HOURS | 2 HOURS | 4.5 HOURS | 10 HOURS | |
600 | Small coffee maker |
|
|
| 1 HOUR | 2.5 HOURS | 6 HOURS | |
800 | Small microwave | Operating |
|
|
| 1.5 HOURS | 4 HOURS | |
1000 | Automatic Toaster |
|
|
| 1 HOUR | 3 HOURS | ||
1200 | Cordless Steam Iron | time |
|
|
| 0.5 HOUR | 2 HOURS | |
1500 | Full size microwave |
| N.R. | N.R. |
| 0.5 HOUR | 2 HOURS | |
2000 | Grill Microwave |
| N.R | 0.3 HOUR | 1 HOUR | |||
Oven 42L(1.5Cu.ft) |
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
2500 | Hair dryer & |
|
|
|
| 0.2 HOUR | 0.7 HOUR | |
washing machine |
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
2950 | Window Type |
|
|
|
| 0.15 HOUR | 0.5 HOUR | |
(12100Btu/h) |
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Page 10 of 14