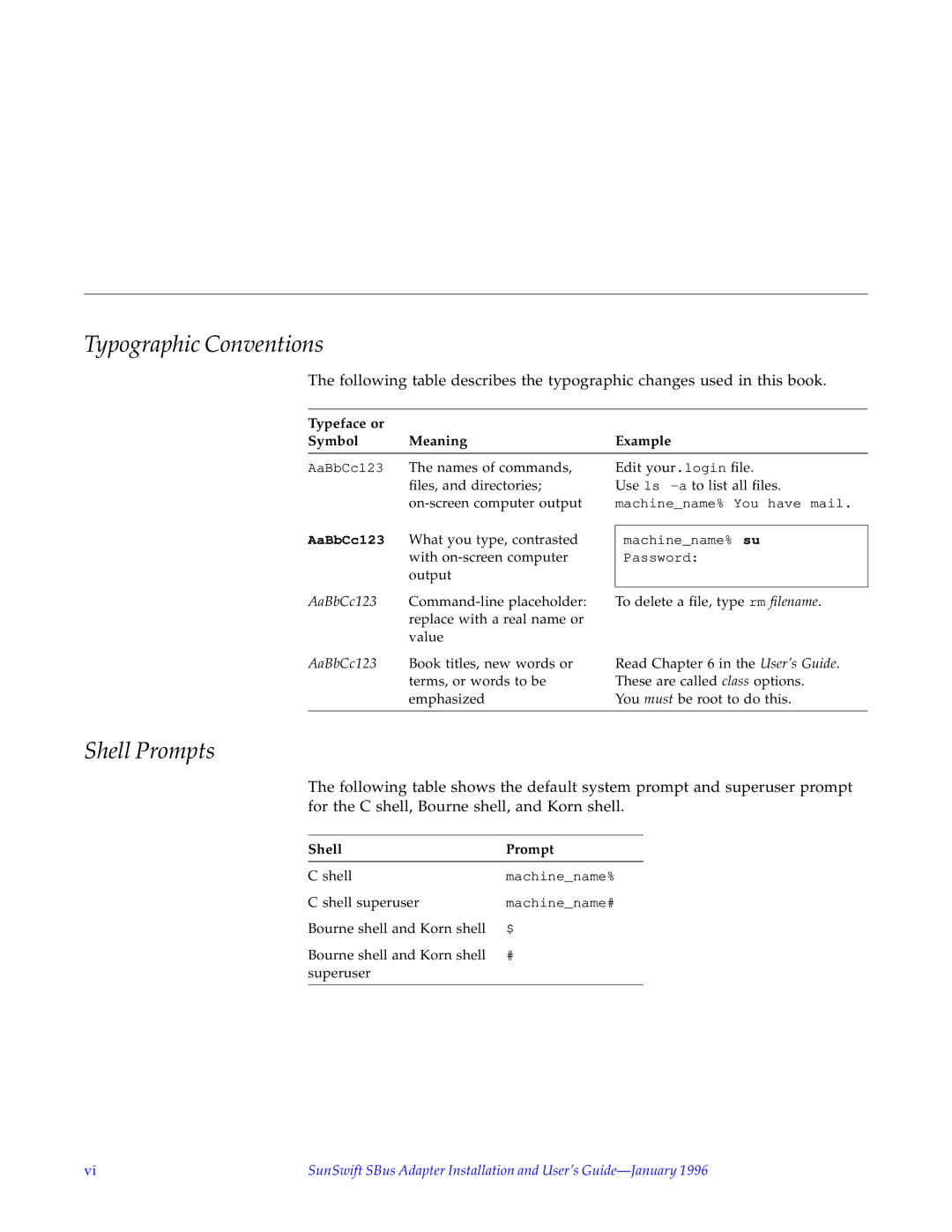
SunSwiftTM specifications
Sun Microsystems introduced the SunSwiftTM, a series of advanced networking interfaces and I/O technology designed to enhance the performance of their workstations and servers. SunSwift interfaces were built to address the increasing demand for high-speed data transfer and connectivity in enterprise environments. The architecture was characterized by a focus on achieving higher bandwidth, lower latency, and improved reliability.One of the main features of SunSwift is its ability to support high-speed data communication through various Ethernet and token ring implementations. The SunSwift cards were designed to be compatible with multiple Sun systems, ensuring wide applicability across different server models. This compatibility allowed users to upgrade their network interfaces without needing to invest in new hardware, promoting cost efficiency and flexibility in network design.
Incorporating the latest advancements in technology, SunSwift leveraged technologies such as PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) to enhance data throughput capabilities. The use of PCI enabled the SunSwift to keep pace with the evolving standards of computing, allowing it to handle the demands of modern applications and workloads.
Another key characteristic of SunSwift is its support for network protocols essential for enterprise functionality, including TCP/IP, which provided a robust framework for network communication. The interface achieved high-performance levels while maintaining compatibility with various operating systems, thereby simplifying network management and deployment.
The reliability of SunSwift was further evidenced through advanced error detection and correction mechanisms. This focus on quality ensured that data integrity was preserved, reducing the chances of packet loss during transmission. Additionally, Sun Microsystems incorporated features that facilitated ease of use, such as simple installation processes that required minimal configuration, making SunSwift accessible even to users with limited technical expertise.
Overall, SunSwift represented a significant advancement in network interface technology during its era, showcasing Sun Microsystems' commitment to delivering high-performance solutions that cater to the demands of enterprise networking. Its blend of speed, reliability, and compatibility made it a valuable asset for organizations seeking to enhance their networking infrastructure and support their growing data communication needs. With its innovative features and robust technology, SunSwift played a crucial role in the evolution of networking capabilities within the Sun Microsystems product lineup.