Battery Connection
Connect your Inverter to your batteries using the following procedures:
•Connect DC Wiring: Though your Inverter is a
should be used when continuously operating heavy draw equipment under these conditions. Tighten your Inverter and battery terminals to approximately 3.5
Recommended Cable Sizing.
•Connect Ground: Using a
section to locate the Main Ground Screw. All installations must comply with national and local codes and ordinances.
•Connect Fuse: Tripp Lite recommends that you connect your Inverter’s positive DC Terminal directly to a fuse(s) and fuse block(s) within 45 cm (18 inches) of the battery. The fuse’s rating must equal or exceed the Minimum DC Fuse Rating listed in your Inverter’s specifications. See Specifications for fuse recommendations. See diagrams below for proper fuse placement.
WARNING!
•Failure to properly ground your Inverter to a vehicle’s chassis or earth ground may result in a lethal electrical shock hazard.
•Never attempt to operate your Inverter by connecting it directly to output from an alternator rather than a battery or battery bank.
•Observe proper polarity with all DC connections.
Vehicular Applications
Your Inverter’s Nominal DC Input Voltage must match the voltage of your battery or
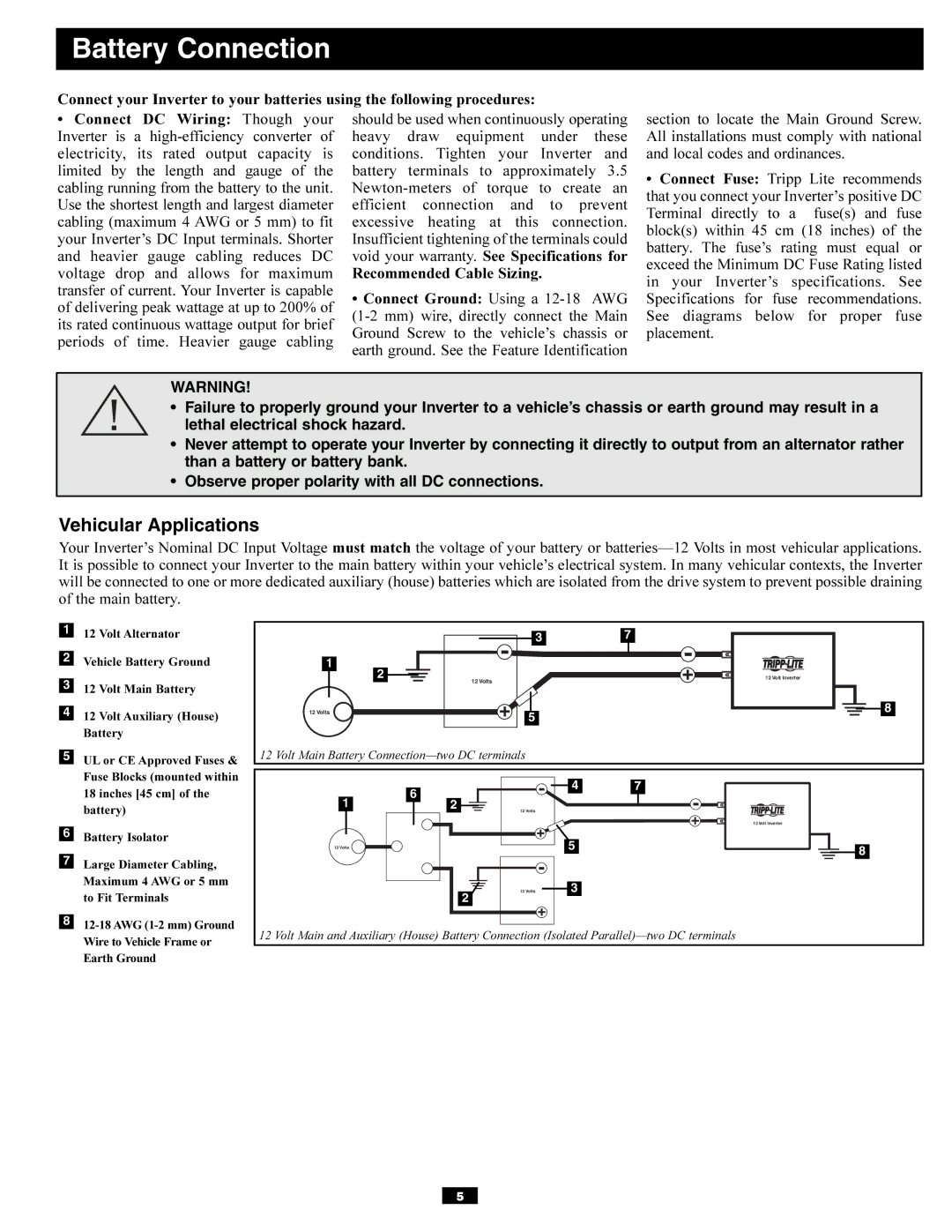
112 Volt Alternator
2Vehicle Battery Ground
312 Volt Main Battery
412 Volt Auxiliary (House) Battery
5UL or CE Approved Fuses & Fuse Blocks (mounted within 18 inches [45 cm] of the battery)
6Battery Isolator
7Large Diameter Cabling, Maximum 4 AWG or 5 mm to Fit Terminals
8
| 3 | 7 |
1 | 2 |
|
| 12 Volt Inverter | |
| 12 Volts |
|
12 Volts | 5 | 8 |
|
| |
12 Volt Main Battery |
| |
| 4 | 7 |
1 | 6 |
|
2 |
| |
12 Volts
12 Volt Inverter
12 Volts | 5 | 8 |
|
|
12 Volts | 3 |
2 |
|
12 Volt Main and Auxiliary (House) Battery Connection (Isolated
5