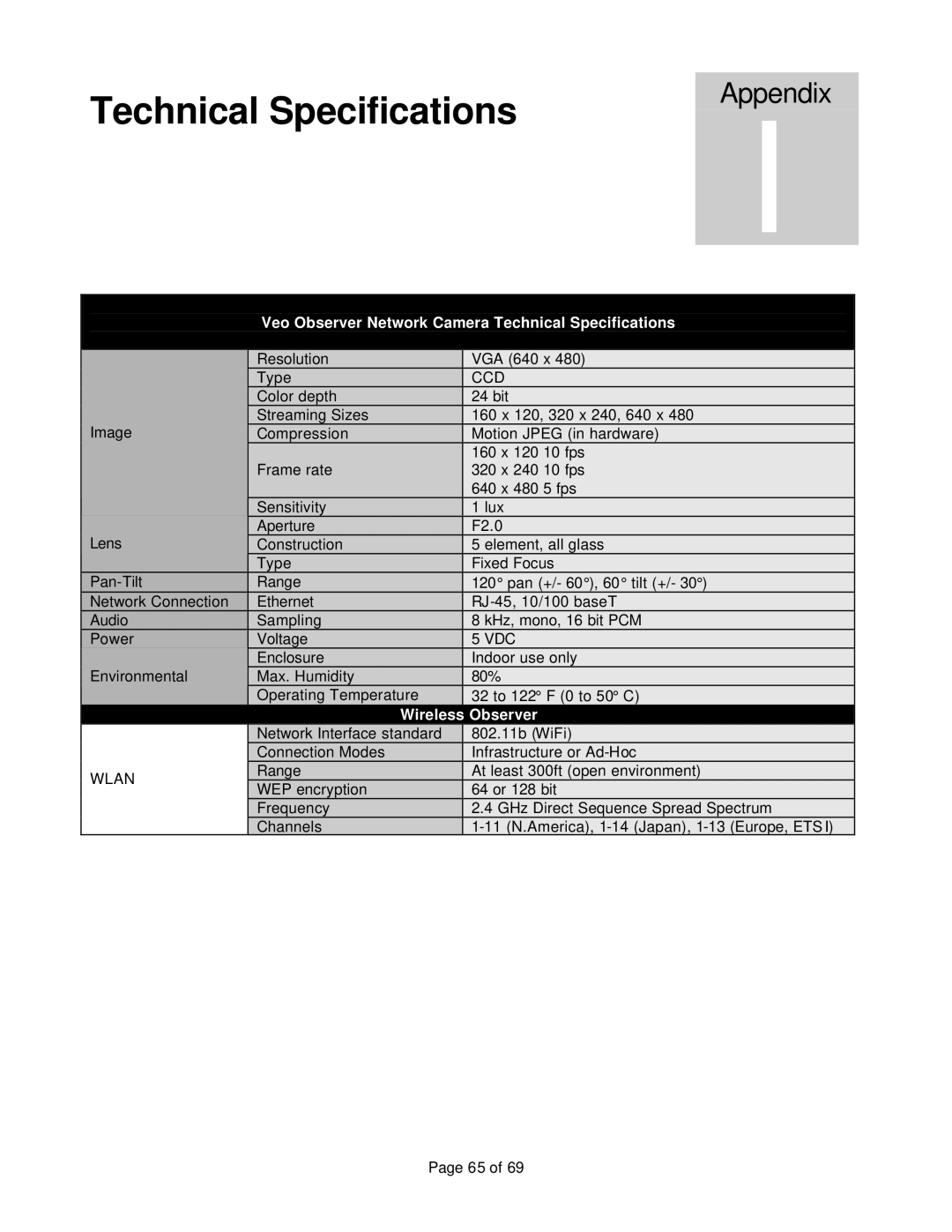
802.11b specifications
The Veo 802.11b is a notable wireless networking standard that emerged in the late 1990s as one of the first widely adopted protocols for local area networks (LANs). Operating in the 2.4 GHz frequency band, 802.11b provided users with the ability to connect to the internet and share resources without the constraints of wired connections.One of the primary features of 802.11b is its maximum data transfer rate of 11 Mbps, which was impressive at the time of its release. This speed allowed for basic internet usage, file sharing, and general network connectivity. While this might seem slow by today’s standards, it laid the foundation for the rapid evolution of wireless technologies.
Veo 802.11b utilized Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) technology, which enhanced the reliability of the connection by spreading the signal over a wider frequency range. This technique helped to reduce interference, particularly in environments with multiple wireless devices operating on the same frequency. The standard also included mechanisms for ensuring data integrity, such as the use of cyclic redundancy check (CRC) algorithms.
In terms of range, Veo 802.11b offered coverage of approximately 100 to 300 feet indoors, and up to 1000 feet outdoors depending on environmental factors. This range made it suitable for home networks and small office environments, allowing users to access the internet from different locations within a building without the need for cumbersome cabling.
Another characteristic of the 802.11b standard was its compatibility with the earlier 802.11 standard, ensuring that devices using both protocols could operate together. This backward compatibility facilitated a smoother transition for users upgrading their systems, as they could maintain connectivity with older devices while enjoying the benefits of faster wireless networking.
Security was also an important aspect, though initially limited. The standard employed Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) for data encryption, which provided a basic level of security to protect wireless communications. However, as vulnerabilities were discovered in WEP, the need for stronger security protocols became evident, leading to further developments in later standards.
Ultimately, the Veo 802.11b played a pivotal role in revolutionizing wireless communications. It established the groundwork for further advancements such as 802.11g and 802.11n, which provided higher speeds and greater efficiency. While newer standards have since eclipsed its capabilities, 802.11b remains a significant milestone in the evolution of wireless networking technology. Its influence can still be seen in the pervasive use of wireless networks in homes, offices, and public spaces around the world today.