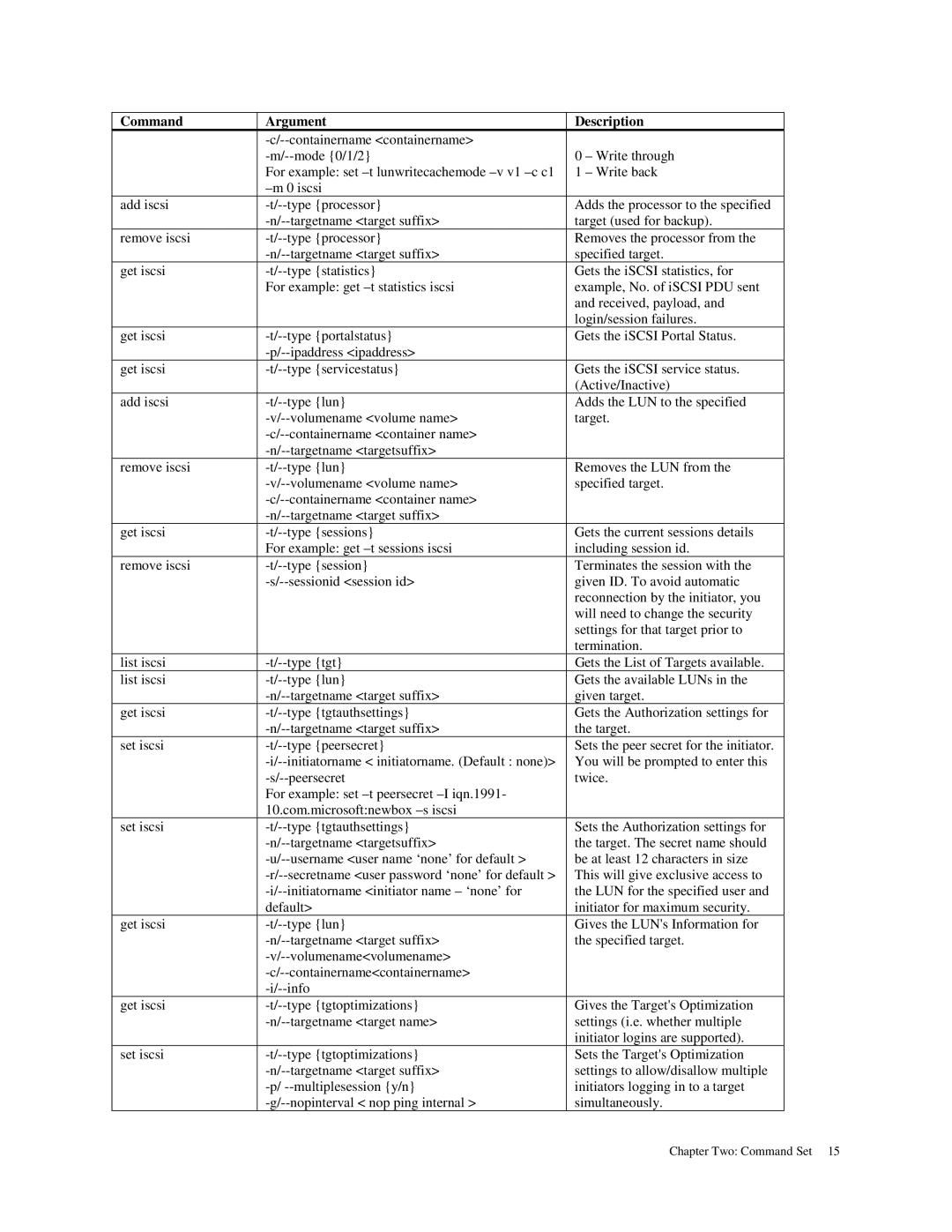
MAN-STOR-ITX27-CLI specifications
American Megatrends Inc. (AMI), a leader in the design and development of innovative hardware and firmware solutions, has made significant strides with its product line, notably with the MAN-STOR-ITX27-CLI model. This compact yet powerful storage solution is designed to meet the evolving needs of modern computing environments, making it a popular choice among tech enthusiasts, system integrators, and IT professionals.One of the main features of the MAN-STOR-ITX27-CLI is its form factor. Built in the Mini-ITX style, this storage system is optimized for space-saving applications without compromising performance. Its compact design allows it to be integrated into a variety of systems, from home media servers to business workstations, facilitating enhanced flexibility in deployment.
The MAN-STOR-ITX27-CLI utilizes advanced storage technologies to deliver reliable and high-speed data access. It supports multiple storage drives, including SSDs and traditional HDDs, providing users with a choice for speed or capacity according to their specific needs. The RAID configuration support enhances data redundancy and performance, ensuring that critical data remains accessible and secure.
In terms of connectivity, the MAN-STOR-ITX27-CLI is equipped with an array of ports, including USB 3.0, HDMI, and Ethernet, which facilitate seamless integration with other devices. High-speed data transfer rates are achieved, making it ideal for applications requiring quick data retrieval and storage, such as video editing and large-scale data analysis.
Another notable characteristic is its cooling system. The MAN-STOR-ITX27-CLI incorporates an efficient thermal management solution that helps maintain optimal operating temperatures, thus ensuring longevity and stability. This feature is particularly important in high-performance scenarios where excessive heat could impact system reliability.
Furthermore, the MAN-STOR-ITX27-CLI is designed with user-friendly features in mind. It allows for easy upgrades and expansions, making it a future-proof choice as storage demands continue to grow. The intuitive setup process and compatibility with a range of operating systems further simplify installation and management.
In conclusion, the American Megatrends MAN-STOR-ITX27-CLI is a versatile and powerful storage solution that excels in both performance and user convenience. Its advanced technology, compact design, and robust features make it a leading choice for anyone seeking reliable and efficient storage in a dynamic computing environment. With the increasing demand for data-driven solutions, products like the MAN-STOR-ITX27-CLI showcase AMI's commitment to innovation and quality in the field of technology.