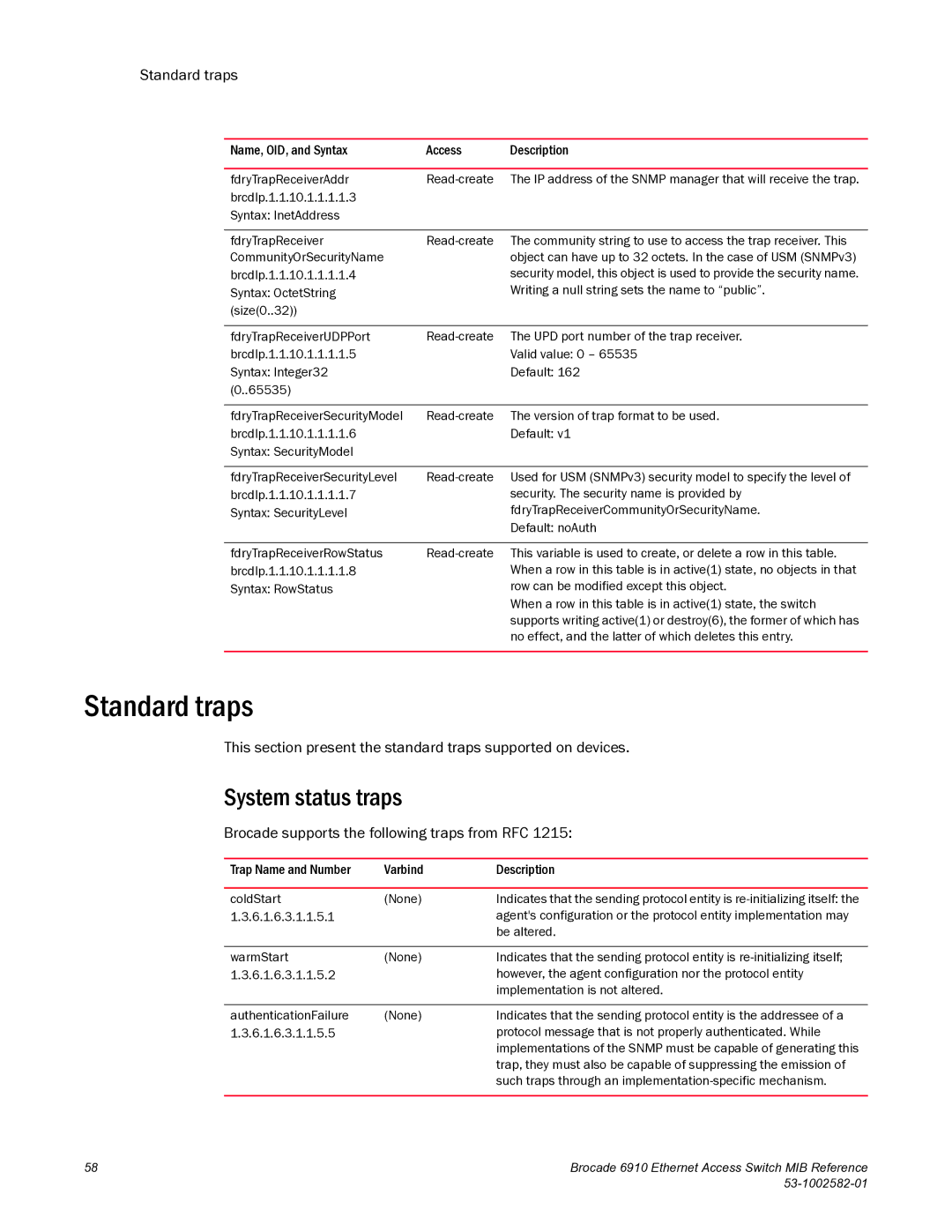
6910 specifications
Brocade Communications Systems, a leader in networking solutions, has established a strong presence in the data center and enterprise networking space with its various product offerings. One of its noteworthy products is the Brocade 6910 Switch, designed specifically for high-performance network environments.The Brocade 6910 is a high-density, compact Ethernet switch that operates at speeds up to 10 Gigabits per second. It is engineered to support the increasing data demands of modern enterprises while providing reliability and flexibility. With its compact form factor, the 6910 is suitable for space-constrained environments, making it an ideal choice for data centers and edge deployments.
One of the standout features of the Brocade 6910 is its support for both Layer 2 and Layer 3 networking, allowing for dynamic routing and switching capabilities that enhance overall network performance. This dual functionality enables organizations to optimize their network architecture, ensuring seamless data transfer and management.
Power over Ethernet (PoE) functionality is another significant characteristic of the Brocade 6910. This feature allows the switch to deliver power to connected devices, such as IP phones and wireless access points, eliminating the need for separate power sources and reducing cable clutter. This capability not only streamlines installations but also lowers operational costs.
In terms of scalability, the Brocade 6910 supports an extensive number of physical and virtual interfaces, which makes it versatile enough to grow with the needs of an organization. It can efficiently handle increasing traffic loads, enabling businesses to scale their network infrastructure without extensive upgrades.
The switch also incorporates advanced features like Virtual Chassis technology, allowing multiple switches to operate as a single logical entity. This simplifies management and improves redundancy, enhancing overall network reliability. Additionally, the Brocade 6910 includes comprehensive security features that protect network data through robust monitoring and access controls.
Furthermore, the Brocade 6910 is equipped with intelligent network management tools that provide visibility into network performance and health. This functionality helps IT teams to manage resources effectively, troubleshoot issues, and streamline maintenance tasks.
In conclusion, the Brocade 6910 Switch exemplifies modern networking solutions with its high performance, versatility, and advanced management capabilities. Organizations looking for reliable, scalable, and efficient networking solutions will find the Brocade 6910 to be an outstanding choice that meets the demands of today’s dynamic environments.