Chapter 1 About Cisco IP Solution Center
Overview of ISC
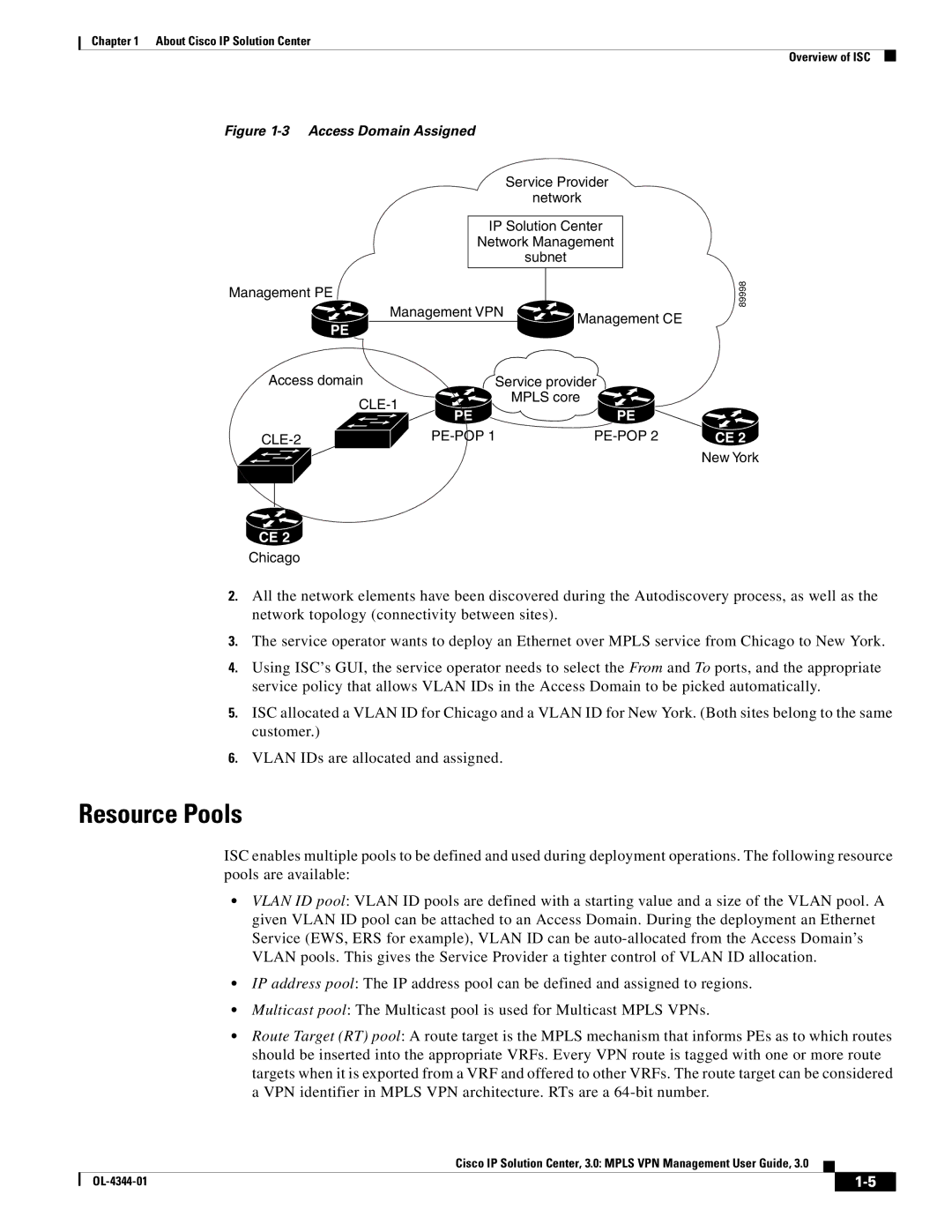
Figure 1-3 Access Domain Assigned
Service Provider
network
IP Solution Center
Network Management
subnet
Management PE
Management VPN | Management CE | |
PE | ||
|
89998
Access domain | Service provider |
| |
| MPLS core |
| |
PE | PE |
| |
|
| ||
CE 2 | |||
New York
CE 2
Chicago
2.All the network elements have been discovered during the Autodiscovery process, as well as the network topology (connectivity between sites).
3.The service operator wants to deploy an Ethernet over MPLS service from Chicago to New York.
4.Using ISC’s GUI, the service operator needs to select the From and To ports, and the appropriate service policy that allows VLAN IDs in the Access Domain to be picked automatically.
5.ISC allocated a VLAN ID for Chicago and a VLAN ID for New York. (Both sites belong to the same customer.)
6.VLAN IDs are allocated and assigned.
Resource Pools
ISC enables multiple pools to be defined and used during deployment operations. The following resource pools are available:
•VLAN ID pool: VLAN ID pools are defined with a starting value and a size of the VLAN pool. A given VLAN ID pool can be attached to an Access Domain. During the deployment an Ethernet Service (EWS, ERS for example), VLAN ID can be
•IP address pool: The IP address pool can be defined and assigned to regions.
•Multicast pool: The Multicast pool is used for Multicast MPLS VPNs.
•Route Target (RT) pool: A route target is the MPLS mechanism that informs PEs as to which routes should be inserted into the appropriate VRFs. Every VPN route is tagged with one or more route targets when it is exported from a VRF and offered to other VRFs. The route target can be considered a VPN identifier in MPLS VPN architecture. RTs are a
Cisco IP Solution Center, 3.0: MPLS VPN Management User Guide, 3.0
|
| ||
|
|