Page
Contents
General guide
Power supply
Keyboard
Display formats
Display symbols
2ndF
Floating point display format
Scientific display format
Order of operations
Engineering display format
Accuracy and Capacity
Correction
Capacity
Functions Input range
RÆP
Stat
Overflow / Error conditions
Mixed arithmetic calculation
Basic calculation
Parentheses calculations
Constant calculation
Memory calculation
Percentage calculation
Scientific calculation
Square, Square / Cubic Root, Power, Root
Reciprocal, Factorial
Logarithms and Antilogarithms
Trigonometric / Inverse trigonometric functions
Angular units conversion
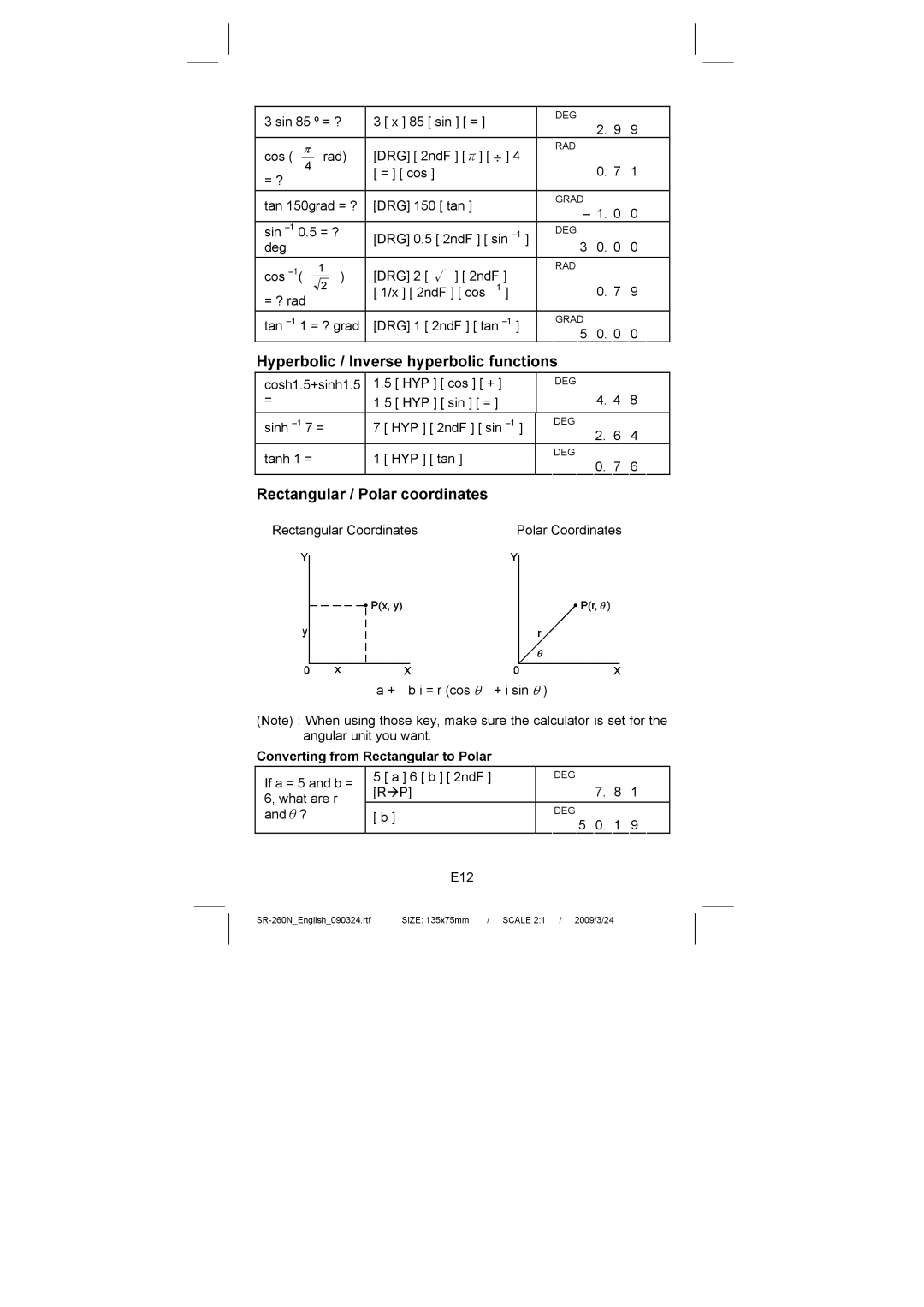
Rectangular / Polar coordinates
Hyperbolic / Inverse hyperbolic functions
Converting from Rectangular to Polar
Sexagesimal ↔ Decimal form conversion
Permutations, Combinations
Converting from Polar to Rectangular
Converting from Sexagesimal to Decimal
Complex numbers calculation
Base-n mode calculation
Converting between bases
Negative and Complements
Random numbers and Exchange key
Statistics calculation
Unit conversion
Computing single variable statistics
CPK
Adding a data entry
Viewing statistics data
Editing statistics data
Delete error
Weighted data entry method
Calculo Básico
Guia General
Calculo Científico
Calculo Estadístico
EL Teclado
Suministro DE Energia
1ras. Funciones
2dos Funciones
LOS Formatos
LOS Símbolos
Formato Científico
Orden DE Operaciones
Exactitud & Capacidad
Corrección
Funciones Rango de entrada
RÆP
Condiciones DEL DESBORDAMIENTO/DE Error
Calculo Entre Paréntesis
Calculo Aritmético Mixto
Calculo Constante
Calculo Porcentual
Calculo Memorizado
CUADRADO, Raíz CUADRADA/ CÚBICO, POTENCIA, Raíz
RECIPROCO, Factorial
Logaritmos Y Antilogaritmos
Calculo Fraccionario
Conversión DE Unidades Angulares
Hiperbólico / Funciones Inversas Hiperbólicas
Trigonométrico / Funciones Inversas Trigonométricas
Rectangular / Polares Coordinados
Sexagesimal ↔ Conversión Decimal
PERMUTACIONES, Combinaciones
Convirtiendo Entre Bases
Calculo DE Modo BASE-N
Números Aleatorios Y Tecla DE Cambio
Calculo DE Números Complejos
Unidad DE Conversión
Computar EL Único Variable Estadístico
Muestra de desviación estadística
VER Datos Estadísticos
Editar Datos Estadísticos
Borrar Error
Método DE Ingreso Dato Peso
Cálculo básico
Guia geral
Cálculo científico
Cálculo de estatísticas
Suprimento de energia
Guia geral
Teclado
Formato de exibição
Exibição de símbolos
Formato de exibição de ponto flutuante
Formato de exibição de ponto fixo
Formato de exibição científica
Ordem de operações
Formato de exibição para engenharia
Exatidão e Capacidade
Correção
Capacidade
Funções Variação de Entrada
≤ r 1 x 10
Condições de Excesso / Erro
Cálculo de aritmética misturado
Cálculo básico
Cálculo de parênteses
Cálculo constante
Cálculo de memória
Cálculo de porcentagem
Recíproco, Factorial
Cálculo científico
Logaritmos e Anti-logaritmos
Cálculo fracionário
Conversão de unidades angulares
Funções Hiperbólicas /Hiperbólicas Inversas
Funções Trigonométricas /Trigonométricas Inversas
Conversão de forma Sexagesimal ↔ Decimal
Permutações, Combinações
Cálculo de números complexos
Cálculo de modo Base-n
Convertendo entre bases
Negativo e Complementos
Números randômicos e Tecla de comutação
Cálculo de estatísticas
Conversão de unidade
Computando estatísticas de variáveis simples
Divergência da Amostra Padrão
Visualização de dados estatísticos
Editando dados estatísticos
Somando uma entrada de dado
Apague erro
Método de entrada de dados carregado
Statistische Berechnungen
Allgemeine Hinweise
Die Stromversorgung
Allgemeine Hinweise
Die Tastatur
Bildschirmanzeigen
Bildschirmsymbole
Bildschirmanzeige im wissenschaftlichen Stil
Bildschirmanzeige mit fixiertem Komma
Bildschirmanzeige im Ingenieurstil
Korrekturen
Reihenfolge der Rechenoperationen
Kapazität
Korrektheit und Kapazität
Funktionen Grenzen bei der Eingabe
≤ x 1 x 10 10 100, x ≠ ≤ x ≤ 69, x ist eine ganze Zahl
Möglichkeit von Overflows und Fehlern
Grundlegende Berechnungen
Gemischte arithmetische Berechnungen
Rechnen mit Klammern
Rechnen mit Prozentsätzen
Rechnen mit Konstanten
Wiederholung der zuletzt eingegebenen Zahl
Wiederholung der arithmetischen Rechenoperation
Rechnen mit dem Speicher
Wissenschaftliche Berechnungen
Berechnung von Kehrwerten und Faktoren
Quadrat-/ Kubik- Potenzen und Wurzeln, Potenzen
Berechnung von Brüchen
Berechnung von Logarithmen und Antilogarithmen
Trigonometrische und invers-trigonometrische Funktionen
Umrechnung von Winkeleinheiten
Rechteckige und polare Koordinaten
Hyperbolische und invers-hyperbolische Funktionen
Permutationen und Kombinationen
Rechnen mit dem Mode Basis n
Umrechnungen der sexagesimalen Form in die dezimale Form
Umrechnungen der dezimalen Form in die sexagesimale Form
Negative Zahlen und Ergänzungen
Rechnen mit komplexen Zahlen
Zufallszahlen und Austausch von Zahlen
Statistische Berechnungen
Umrechnung zwischen anderen Einheiten
Verarbeitung einfach-variabler Statistiken
Standard Bevölkerungs-Abweichung
Eingabe durch Addition von Daten
Anschauen von statistischen Daten
Unbeabsichtigtes Löschen
Erstellung von statistischen Daten
Methode der Eingabe von gewichteten Daten
Calcul scientifique
Calcul simple
Calcul statistiques
Source d’alimentation
Informations générales
Le clavier
Affichage des formats
Affichage des symboles
Affichage en format virgule flottante
Affichage en format virgule fixée
Affichage Format scientifique
Ordre des opérations
Affichage Format ingénieurie
Capacité
Précision et capacité
Functions Limite
Rad θ ≠ 2n-1
9999999999 Pour zéro, positif 9999999999 ≤ x ≤ Pour négatif
Surcharge / conditions d’erreur
Calcul simple
Calcul arithmétique mélangé
Calcul avec parenthéses
Calcul avec mémoire
Calcul de poucentage
Répéter le dernier nombre
Répéter la dernière opération arithmétique
Réciproque, factoriel
Calcul scientifique
Carré, racine carré / cubique, puissance, racine
Logarithmes et Antilogarithmes
Calcul de fraction
Fonctions de trigonométrie / de trigonométrie inversé
Conversion des unités angulaires
Fonctions hyperbolique / hyperbolique inversé
Permutations, combinaisons
Coordonnées rectangulaires / polaires
Conversion séxagésimal ↔ décimal
Mode de calcul en base-n
Convertir les séxadécimaux en décimaux
Convertir les décimaux en séxadécimaux
Nombres aléatoires et touche d’échange
Calcul nombres complexes
Négatif et complements
Nombres aléatoires
Conversion des unités
Calcul statistiques
Calcul statistiques à une seule variable
Pouce cm
En mode Stat 2ndF Stat
Ajouter une donnée
Aperçu des données statistiques
Edition des données statistiques
Méthode d’entrée des données pondérées
Effaçage d’erreur
SR-260NFrench090324.doc Size 135x75mm Scale 21 / 2009/3/26
Calcolo scientifico
Guida generale
Calcolo di statistica
Alimentazione di corrente
Guida generale
La tastiera
Formati di Visualizzazione
Visualizzazione di Simboli
Formato di visualizzazione di punto galleggiante
Formato di visualizzazione di punto fisso
Formato di visualizzazione scientifica
Ordine di operazioni
Formato di visualizzazione in ingegneria
Accuratezza e Capacità
Correzione
Accuratezza ±1 in 10a cifra Capacità
Funzioni Variazione di Entrata
Un numero intero
Condizioni di Traboccazione / Errore
Calcolo di aritmetica mista
Calcolo elementare
Calcoli delle parentesi
Calcolo costante
Calcolo della memoria
Calcolo di percentuale
Reciproco, Fattoriale
Calcolo scientifico
Calcolo frazionario
Conversione delle unità angolari
Coordinate Rettangolare / Polari
Funzioni Iperboliche / Iperboliche Inverse
Conversione Sessagesimale ↔ Decimale
Permutazioni, Combinazioni
Convertendo da Rettangolare a Polare
Convertendo da Polare a Rettangolare
Convertendo da Decimale al Sessagesimale
Modo di calcolo della Base-n
Convertendo tra basi
Negativo e Complementi
Calcolo di numeri complessi
Calcolo di statistica
Numeri casuali e tasto di Scambio
Conversione dellunità
Scarto quadratico medio del campione
Visualizzazione di dati di statistica
Editando dati di statistica
Cancellando errore
Metodo dentrata dei dati valutati
Statistische bewerkingen
Algemene inleiding
Voeding
Algemene inleiding
Het toetsenbord
Weergaveformaten
Statusindicatoren
Drijvende komma weergaveformaat
Vaste komma weergaveformaat
Technisch weergaveformaat
Wetenschappelijke weergaveformaat
Verbeteringen maken
Volgorde van de bewerkingen
Nauwkeurigheid en capaciteit
Capaciteit
Functies Invoerbereik
Overflow en foutmeldingen
Gemengde rekenkundige bewerkingen
Basisbewerkingen
Bewerkingen met haakjes
Doorlopend berekenen
Geheugenbewerkingen
Procentberekening
De rekenkundige bewerking herhalen
Omgekeerde waarde en faculteit
Wetenschappelijke bewerkingen
Logaritmes en antilogaritmes
Bewerkingen met breuken
Hoekconversie
Hyperbolische / inverse hyperbolische functies
Trigonometrische / inverse trigonometrische functies
Permutaties en combinaties
Rechthoekige / polaire coördinaten
Conversie van sexagesimale ↔ decimale waarden
Conversie van rechthoekige naar polaire coördinaten
Converteren tussen getalbasissen
Bewerkingen met getalbasissen Base-N modus
Willekeurige getallen en de verwisseltoets
Bewerkingen met complexe getallen
Negatieve uitdrukking en complement
Willekeurige toets
Conversie van eenheden in↔cm
Statistische bewerkingen
Statische bewerkingen met één variabele
Voer alle Data
Gegevens toevoegen
Statistische gegevens weergeven
Statistische gegevens bewerken
De foutmelding dEL Error
Invoermethode voor herhalende waarden
Statistiske beregninger
Videnskabelige beregninger
Strømforsyning
Generel vejledning
Tastaturet
Displayformater
Displaysymboler
Flydende decimaltegn displayformat
Fast decimalpunkt displayformat
Videnskabeligt displayformat
Operationsrækkefølge
Teknisk displayformat
Nøjagtighed og kapacitet
Rettelser
Kapacitet
Funktioner Inputinterval
= 0 y Y = 2n+1, I/n, n er et heltal. n ≠ Da6
Overløb / Fejltilstande
Grundlæggende beregninger
Parentesberegninger
Blandede aritmetiske beregninger
Konstantberegninger
Gentagelse af det sidste tal
Hukommelsesberegninger
Procentberegning
Reciprok værdi, fakultet
Videnskabelige beregninger
Kvadrat, kvadrat- / kubikrod, opløftning, rod
Logaritmer og antilogaritmer
Trigonometriske / inverse trigonometriske funktioner
Konvertering mellem vinkelenheder
Rektangulære / Polære koordinater
Hyperbolske / inverse hyperbolske funktioner
Konvertering fra rektangulære til polære
Konvertering sexagesimalt ↔ decimalt format
Permutationer, kombinationer
Base-n-mode beregninger
Negative tal og komplementer
Beregninger med komplekse tal
Tilfældige tal og udskiftningstasten
Statistiske beregninger
Beregning af statistik med én variabel
Stikprøvestandardafvigelse Σ x 2 − Σ x 2 / n
Visning af statistiske data
Redigering af statistiske data
Tilføjelse af en datapost
Slet fejl
Vægtet dataindtastningsmetode
Статистическое вычисление
Научное вычисление
Электропитание
Общее руководство
Клавиатура
Формат экрана
Экранные символы
Формат экрана Плавающая точка
Формат экрана Фиксированная точка
Формат экрана Инженерный
Формат экрана Научный
Исправление
Порядок действий
Точность и разрешение
Разрешение
Функции Диапазон ввода
NPr, nCr ≤r ≤n, n ≤9999999999, n, r целые числа
Состояния превышения / ошибки
Простое вычисление
Смешанное арифметическое вычисление
Вычисления со скобками
Вычисление с использованием памяти
Вычисление с процентами
Повторение последнего числа
Повторение арифметического действия
Обратная величина, факториал
Научное вычисление
Логарифмы и антилогарифмы
+ 3.75 =
Вычисление с дробями
Функции
Преобразование угловых единиц
Гиперболическая / обратная гиперболическая функции
Перестановки, сочетания
Прямоугольные / полярные координаты
Преобразование из прямоугольных координат в полярные
Преобразование из полярных координат в прямоугольные
Преобразование из шестидесятеричной формы в десятичную
Вычисление в режиме изменяющейсясистемы счисления
Преобразование из десятичной формы в шестидесятеричную
Преобразование между системами счисления
Кнопки Случайные числа и Замена
Вычисление с комплексными числами
Отрицательные и дополняющие числа
Кнопка Случайные
Статистический расчет с одной переменной
Статистическое вычисление
Преобразование единиц Дюймы ↔ см
Режиме Stat 2ndF Stat
Добавочный ввод данных
Просмотр статистических данных
Редактирование статистических данных
Удаление ошибки
Метод ввода средневзвешенных данных
Obliczenia naukowe
Instrukcja obsługi
Obliczenia statystyczne
Zasilanie
Instrukcja obsługi
Klawisze
Formaty wyświetlania
Wskaźniki ekranu
Format zmiennoprecinkowy
Format stalej liczby miejsc po przecinku
Format naukowy
Kolejność operacji
Format inżynierski
Dokładność i pojemność
Dokonywanie korekt
Pojemność
Funkcje Predział określoności funkcji
Grad θ ≠ 100 2n-1 n liczba całkowita
Przepełnienie / Błąd
Mieszane obliczenia arytmetyczne
Obliczenia podstawowe
Obliczenia z wykorzystaniem nawiasów
Obliczenia z użyciem stałych
Obliczenia wykorzystujące pamięć
Obliczenia procentów
Odwrotność, silnia
Obliczenia naukowe
Logarytmy i antylogarytmy
Działania na ułamkach
Konwersja jednostek miar kątów
Funkcje hiperboliczne i odwrotne hiperboliczne
Funkcje trygonometryczne i odwrotne trygonometryczne
Współrzędne prostokątne i polarne
Konwersja liczby sześćdziesiętnej do dziesiętnej
Permutacje i kombinacje
Konwersja liczby dziesiętnej do sześćdziesiętnej
Obliczenia w trybie Base-n
Konwersja układów liczbowych
Wartości ujemne i komplementy
Operacje na liczbach zespolonych
Obliczenia statystyczne
Liczby przypadkowe i klawisz wymiany
Konwersja jednostek in↔cm
Odchylenie standardowe próbki
Oglądanie statystyki danych
Edytowanie danych statystycznych
Wprowadzenie dodatkowych danych
Błąd kasowania
Wprowadzenie średiej ważonej
TypeScientific135x75mm