Configurations
1.4 Configurations
The M-LVDS EVM board allows the user to construct various bus configurations. The two devices on the EVM allow for point-to-point simplex, parallel-terminated point-to-point simplex, and two-node multipoint operation. All of these modes of operation can be configured through onboard jumpers, external cabling, and different resistor combinations. The devices which are delivered with the EVM change output operation but, configuration of jumpers to setup the transmission type is independent of the devices installed
1.4.1Point-to-Point
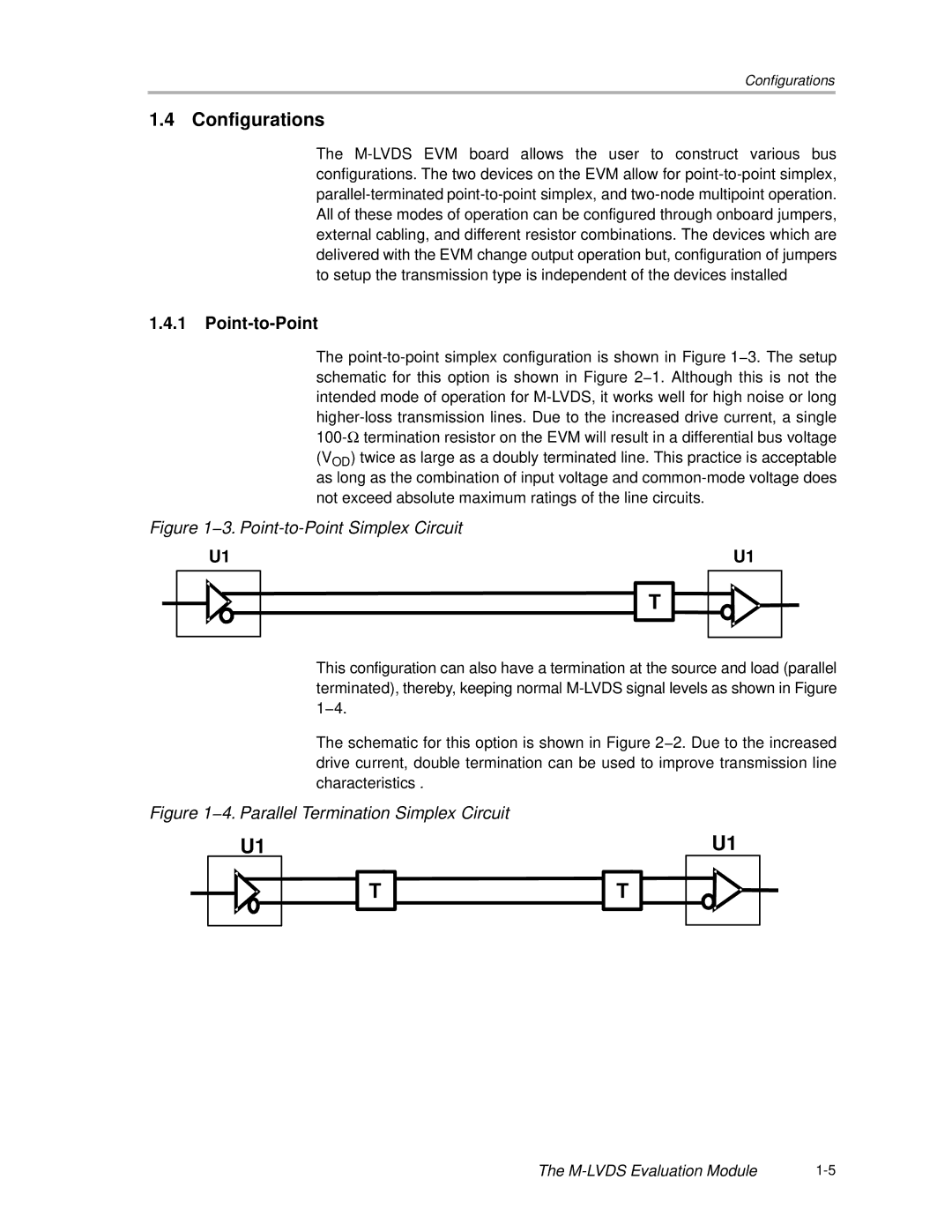
The point-to-point simplex configuration is shown in Figure 1−3. The setup schematic for this option is shown in Figure 2−1. Although this is not the intended mode of operation for M-LVDS, it works well for high noise or long higher-loss transmission lines. Due to the increased drive current, a single 100-Ωtermination resistor on the EVM will result in a differential bus voltage (VOD) twice as large as a doubly terminated line. This practice is acceptable as long as the combination of input voltage and common-mode voltage does not exceed absolute maximum ratings of the line circuits.
Figure 1−3. Point-to-Point Simplex Circuit
This configuration can also have a termination at the source and load (parallel terminated), thereby, keeping normal M-LVDS signal levels as shown in Figure 1−4.
The schematic for this option is shown in Figure 2−2. Due to the increased drive current, double termination can be used to improve transmission line characteristics .
Figure 1−4. Parallel Termination Simplex Circuit
The M-LVDS Evaluation Module | 1-5 |