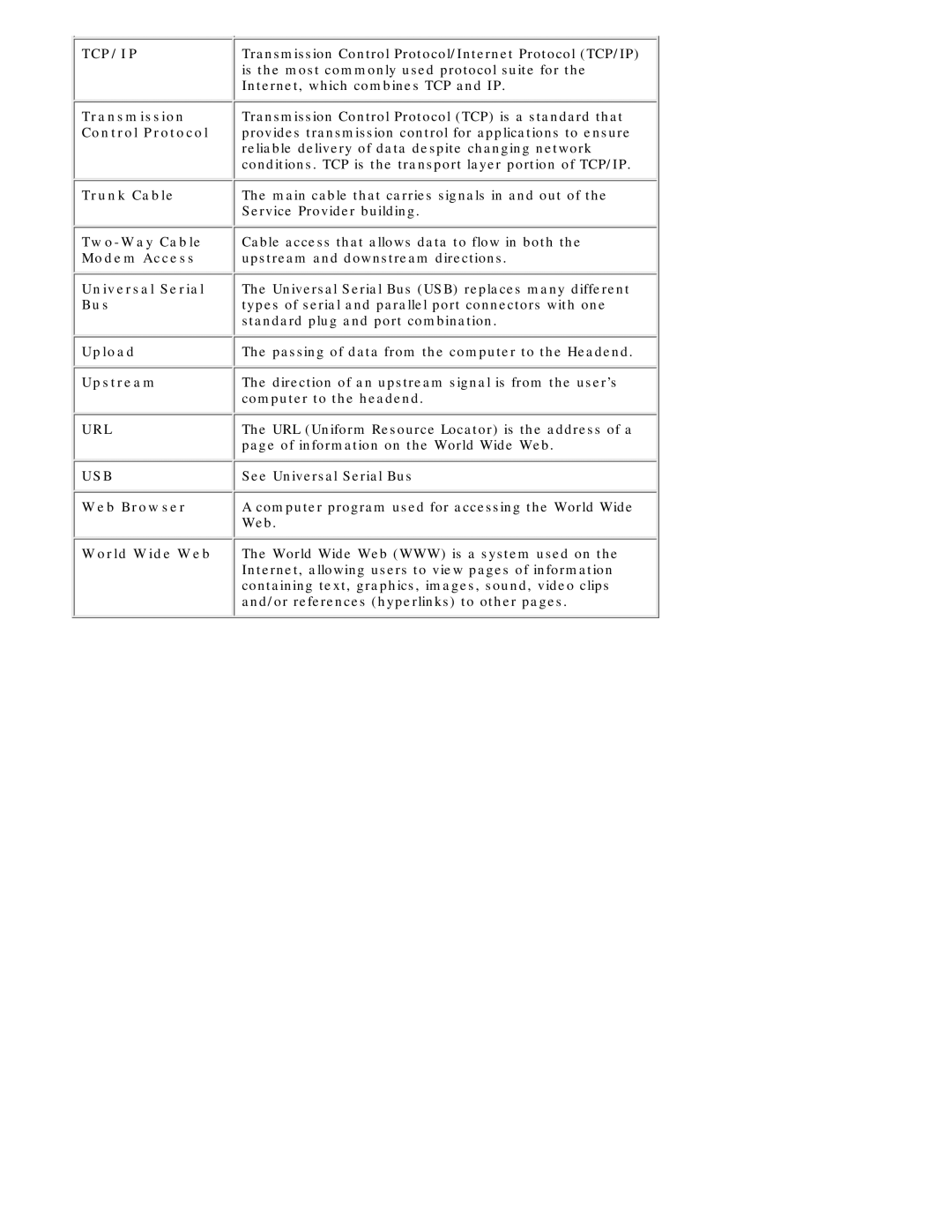
TCP/IP | Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) |
| is the most commonly used protocol suite for the |
| Internet, which combines TCP and IP. |
Transmission | Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is a standard that |
Control Protocol | provides transmission control for applications to ensure |
| reliable delivery of data despite changing network |
| conditions. TCP is the transport layer portion of TCP/IP. |
Trunk Cable | The main cable that carries signals in and out of the |
| Service Provider building. |
Cable access that allows data to flow in both the | |
Modem Access | upstream and downstream directions. |
Universal Serial | The Universal Serial Bus (USB) replaces many different |
Bus | types of serial and parallel port connectors with one |
| standard plug and port combination. |
Upload | The passing of data from the computer to the Headend. |
Upstream | The direction of an upstream signal is from the user’s |
| computer to the headend. |
URL | The URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the address of a |
| page of information on the World Wide Web. |
USB | See Universal Serial Bus |
Web Browser | A computer program used for accessing the World Wide |
| Web. |
World Wide Web | The World Wide Web (WWW) is a system used on the |
| Internet, allowing users to view pages of information |
| containing text, graphics, images, sound, video clips |
| and/or references (hyperlinks) to other pages. |