POWER LEADER™ Ethernet Gateway
Chapter 1 – Introduction
1-3 Operational Description
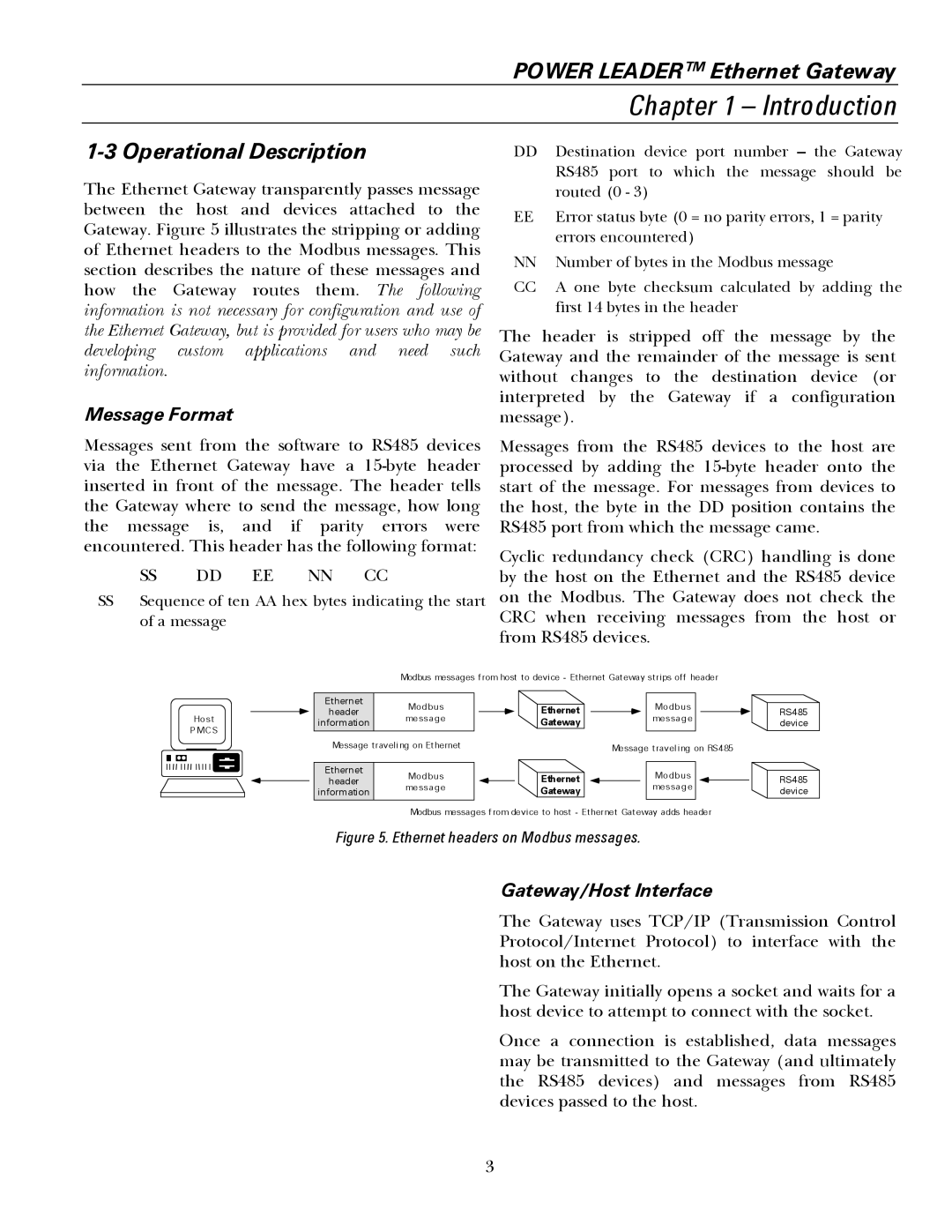
The Ethernet Gateway transparently passes message between the host and devices attached to the Gateway. Figure 5 illustrates the stripping or adding of Ethernet headers to the Modbus messages. This section describes the nature of these messages and how the Gateway routes them. The following information is not necessary for configuration and use of the Ethernet Gateway, but is provided for users who may be
developing custom applications and need such information.
Message Format
Messages sent from the software to RS485 devices via the Ethernet Gateway have a
the message is, and if parity errors were encountered. This header has the following format:
SS DD EE NN CC
SSSequence of ten AA hex bytes indicating the start of a message
DDDestination device port number – the Gateway RS485 port to which the message should be routed (0 - 3)
EEError status byte (0 = no parity errors, 1 = parity errors encountered)
NN Number of bytes in the Modbus message
CCA one byte checksum calculated by adding the first 14 bytes in the header
The header is stripped off the message by the Gateway and the remainder of the message is sent without changes to the destination device (or interpreted by the Gateway if a configuration message).
Messages from the RS485 devices to the host are processed by adding the
Cyclic redundancy check (CRC) handling is done by the host on the Ethernet and the RS485 device on the Modbus. The Gateway does not check the CRC when receiving messages from the host or from RS485 devices.
Ho s t
P MC S
Modbus messages f r om host to devi ce - Ether net Gat ewa y str i ps off header
Ethernet | Mo d b u s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Mo d b u s |
|
|
|
|
header |
|
|
|
|
|
| Ethernet |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
me ss a g e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| mes sa g e |
|
|
|
| |||
information |
|
|
|
|
|
| Gateway |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Message tr av el i ng on Et her net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Message t r av el i ng on RS485 |
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ethernet | Mo d b u s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Mo d b u s |
|
|
|
|
header |
|
|
|
|
|
| Ethernet |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| mes sa g e |
|
|
|
| |||||||
information | me ss a g e |
|
|
|
|
|
| Gateway |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Modbus messages f r om devi ce to host - Ether net Gat eway adds hea der
RS4 85 devi ce
RS4 85 devi ce
Figure 5. Ethernet headers on Modbus messages.
Gateway/Host Interface
The Gateway uses TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) to interface with the host on the Ethernet.
The Gateway initially opens a socket and waits for a host device to attempt to connect with the socket.
Once a connection is established, data messages may be transmitted to the Gateway (and ultimately the RS485 devices) and messages from RS485 devices passed to the host.
3