Maintenance and Service Guide
Product notice
Safety warning notice
Iii
Iv Safety warning notice
Table of contents
Removal and replacement procedures Microtower MT chassis
Sata data cable
System board callouts
100
101
102
114
116
System board callouts 118
120
168
169
170
173
224
225
228
230
Standard Configuration Features
Standard Configuration Features
Microtower Small form factor
Product Features
Desktop mini
Front panel components, microtower
Front panel components, microtower
Front panel components, small form factor
Front panel components, desktop mini
Front panel components, desktop mini
Rear panel components, microtower
Rear panel components, small form factor
Rear panel components, small form factor
Rear panel components, desktop mini
Green USB 3.0 Ports blue
Serial Number Location
Serial Number Location
Computer major components
Microtower MT chassis spare parts
Illustrated parts catalog
Microtower MT chassis spare parts
Cables
Item Description Front I/O assembly Sata drive power cable
Sata data cable, 14 inch, 1 straight end, 1 angled end
Misc parts
USB Wireless Washable Smart card
Antenna for use with Wlan card
Description Hard drives/Solid-state drives
Drives
Optical drives
Misc boards
Item Description
Small Form Factor SFF chassis spare parts
Small Form Factor SFF chassis spare parts
Item Description Front bezel Bezel blank
Illustrated parts catalog
Item Description Front I/O assembly Power switch assembly
Sata data cable, 19.5 inch, 2 straight ends
Misc parts
Clamp lock, includes universal cable plate not included
USB USB, mini Washable Smart card
Drives
Misc boards
Power supply, 120W
Item Description Access panel
Desktop Mini DM chassis spare parts
Desktop Mini DM chassis spare parts
Mouse USB, laser USB, optical Washable Wireless
Item Description Keyboards
Description
Solid-state drives
Drive
Generating static
Electrostatic discharge information
Relative Humidity Event 55% 40% 10%
Preventing electrostatic damage to equipment
Personal grounding methods and equipment
Grounding the work area
Static Shielding Protection Levels
Operating guidelines
Recommended materials and equipment
General cleaning safety precautions
Cleaning the Computer Case
Cleaning the keyboard
Routine care
Service considerations
Cleaning the monitor
Cleaning the mouse
Power supply fan
Cables and connectors
Lithium coin cell battery
Screws
Hard Drives
Serial ATA Hard Drive Characteristics
Sata hard drives
Sata hard drive cables
Smart ATA drives
Cable management
Removal and replacement procedures Microtower MT chassis
Preparation for disassembly
Access panel
Front bezel
Optical drive bezel blank
Battery
Type
Type
Memory
DIMMs
DDR3-SDRAM DIMMs
Populating Dimm sockets
Installing DIMMs
Page
Expansion cards
Page
Page
Page
Drives
DVD±RW drive DVD-ROM drive Blu-ray BD-Writer XL Drive
Page
Drive positions
Removing a slim optical drive
Installing a slim optical drive
Removing a hard drive
Installing a hard drive
Page
Page
Page
Drive power cable
Front I/O and power switch assembly
Removal and replacement procedures Microtower MT chassis
Heat sink
Processor
Speaker
Page
Rear chassis fan
Power supply
Power supply
To install the power supply, reverse the removal procedure
System board
Page
Sys Bd Label Color Component Connector
System board callouts
Password Green Clear system
Parallel port Black Optional parallel Jumper Passwords Port
Front I/O Black Front I/O/power
Input Silver Headphone Switch Output jacks Microphone jacks
Preparation for disassembly
Access panel
Front bezel security
Bezel blanks
Bezel blanks
Battery
Type
Memory
Installing DIMMs
Page
Expansion card
Page
Page
Page
Drives
Installing and Removing Drives
Page
Removing a 3.5-inch device
Installing a 3.5-inch device
Page
Page
Removing a slim optical drive
Installing a slim optical drive
Page
Removing and replacing a 3.5-inch hard drive
Page
Page
Removing a 2.5-inch hard drive
Page
Drive power cable
To install the baffle, reverse the removal procedure Baffle
Baffle
Hood sensor
Front I/O assembly
Page
Page
Power switch
Power switch
Speaker
Heat sink
Page
Page
Processor
Page
Power supply
Page
System board
Page
System board callouts
DIMM2
Using the Small Form Factor Computer in a Tower Orientation
Removal and replacement procedures desktop mini DM chassis
Access panel
Hard drive
Page
Page
Speaker
Page
Front bezel
DDR3-SDRAM SODIMMs
SODIMMs
GB, PC3-12800, Sodimm
Populating Sodimm sockets
Description System Board Label Socket Color
SODIMM1 socket, Channel B
SODIMM3 socket, Channel a
Replacing SODIMMs
Page
Replacing the battery
Type
Page
Heat sink
Processor
Fan
Drive cage
Page
Wlan module
Page
Solid-state drive
Page
External antennas select models only
External antennas select models only
Page
Page
Remove the solid-state drive M.2 solid-state drive on
Updating Smbios Information
System ID Setup
Setup Field Name Comment Label
Sys Bd Label Color Component
Wlan antennas
Page
Page
Page
Changing from desktop to tower configuration
Computer Setup F10 Utility
Computer Setup F10 Utilities
Using Computer Setup F10 Utilities
Computer Setup-File
Computer Setup-Storage
Computer Setup F10 Utility
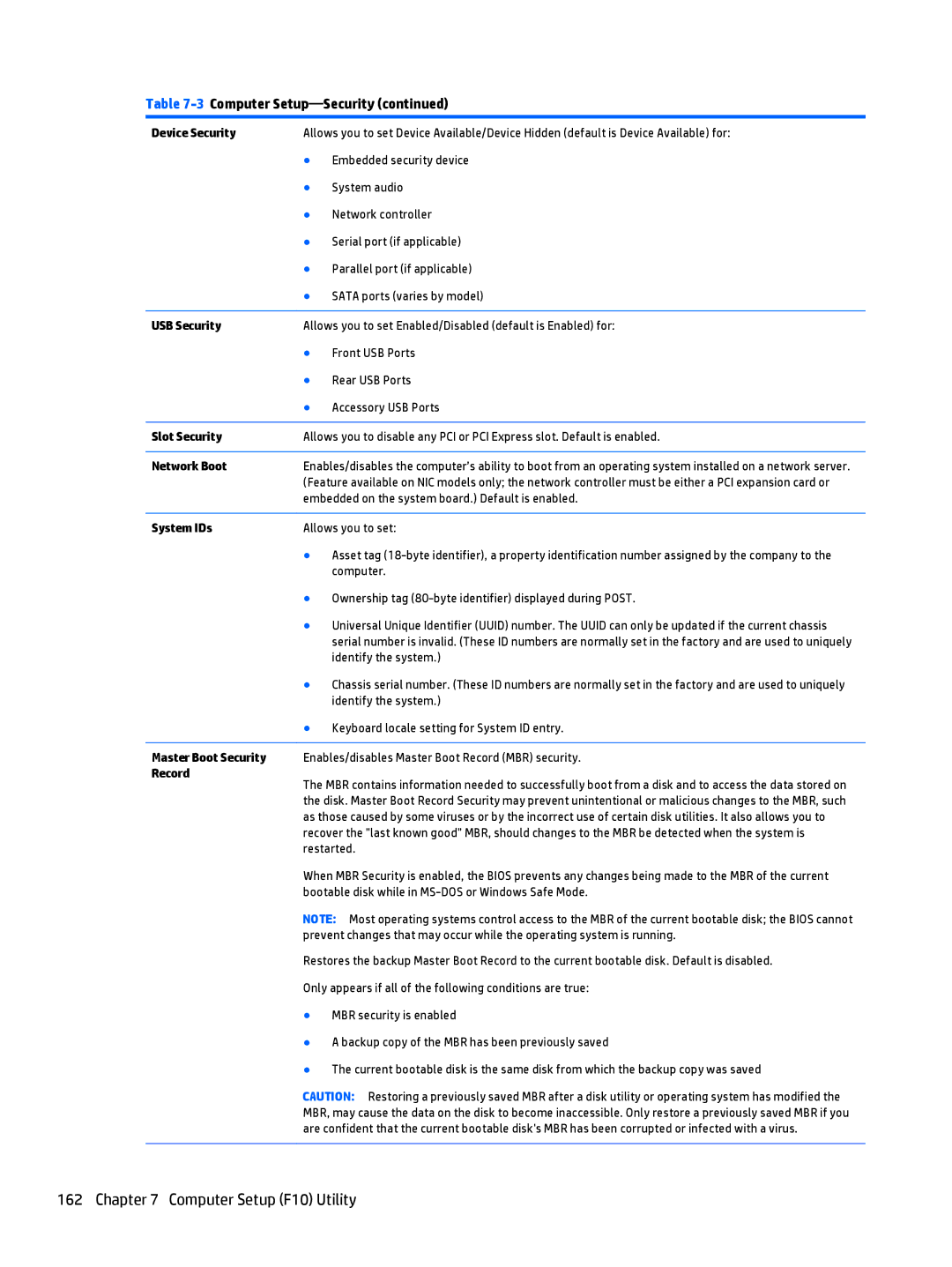
Computer Setup-Security
Network Boot
Master Boot Security
Device Security
USB Security
Secure Boot
Configuration
Legacy Support to disabled
System Security these
Computer Setup-Power
Hardware Power
Option Description
Management
Computer Setup-Advanced
Power-On Options
Bios Power-On
Option
PCI VGA Configuration
Using the Dash Terminal Type option
Connected Bios
Bus Options
Recovering the Configuration Settings
Safety and comfort Before you call for technical support
Troubleshooting without diagnostics
Helpful hints
Solving general problems
Computer will not respond to keyboard or mouse Cause
Solving general problems
Apps icon
Poor performance Cause Solution
Under Windows System, click Run
Solving power problems
Processor thermal protection activated
Power supply shuts down intermittently Cause Solution
Solving hard drive problems
Solving hard drive problems
Nonsystem disk/NTLDR missing message Cause Solution
Storage Boot Order list
Computer will not boot from hard drive Cause Solution
Storage Boot Order
Solving media card reader problems
Solving media card reader problems
Can not write to the media card Cause
Solving display problems
Inserted media card has boot capability
Blank screen no video Cause Solution
To the electrical outlet
Solving display problems
Blank screen no video Cause
Dim characters Cause Solution
Install the video drivers included in the upgrade kit
Be sure the monitor cable is securely connected to
Monitor needs to be degaussed
Image is not centered Cause Solution
Position may need adjustment
No Connection, Check Signal Cable displays on screen Cause
Horizontal or vertical position of the image
Certain typed symbols do not appear correct Cause
Solving audio problems
Sound cuts in and out Cause Solution
Solving audio problems
Solving printer problems
Printer will not print Cause Solution
Line-in jack is not functioning properly Cause
Control Panel , and then select Device Manager
Solving keyboard and mouse problems
Solving keyboard and mouse problems
Printer prints garbled information Cause Solution
Make the proper network connections to the printer
Keyboard connector is not properly connected
Program in use has stopped responding to commands
Shut down the computer using the keyboard
Computer, and then restart the computer
Solving Hardware Installation Problems
Solving Hardware Installation Problems
That pins in the connector are not bent down
Mouse may need repair
Computer will not start Cause Solution
Solving Network Problems
Solving Network Problems
Network status link light never flashes Cause Solution
Correct operating mode
Diagnostics reports a failure Cause Solution
Settings for the board
Cable Correctly
Solving memory problems
New network card will not boot Cause Solution
Solving memory problems
Out of memory error Cause
Memory count during Post is wrong Cause Solution
Insufficient memory error during operation Cause Solution
Computer Setup utility
Solving CD-ROM and DVD problems
Security Network Boot
Movie will not play in the DVD drive Cause Solution
Solving CD-ROM and DVD problems
Cannot eject compact disc tray-load unit Cause
Solving USB flash drive problems
USB flash drive not found identified Cause Solution
System will not boot from USB flash drive Cause Solution
Security USB Security
Solving Internet access problems
Solving front panel component problems
Solving front panel component problems
Solving software problems
Delete button
Log on to your ISP and launch the desired program
System files may be damaged
Advanced startup, click Restart now
Solving software problems
Select Automatic Repair
Post numeric codes and text messages
Post error messages
Control panel message Description Recommended action
Download to Disable to prevent PXE
Post numeric codes and text messages
Flash Screen Image Corrupted Flash Screen image has errors
ECC Memory Module Detected ECC
Ensure that none of the keys are
Depressed
Power Supply fan not detected
Reseat power supply fan
Reconfigure card resources and/or run
Computer Setup or Windows utilities
Sata Cabling Error One or more Sata devices are improperly
Reboot the computer
Functionality contained in the system Bios
System Bios version
Activity Beeps Possible cause Recommended action
Causing the failure. Continue adding devices
Pre-video graphics error For systems with a graphics card
Red Power LED flashes seven
Times, once every second Unable to boot
Press and hold the power button for less than
Check that both power supply cables are
Replace the power button harness. If
Problem persists, replace the system board
Password security and resetting Cmos
Resetting the password jumper
Changing a Setup or Power-On password
Clearing and resetting the Cmos
Deleting a Setup or Power-On password
Press Enter
Page
Why run HP PC Hardware Diagnostics
How to access and run HP PC Hardware Diagnostics
Diagnostic section, click HP Uefi Support Environment
Creating recovery media and backups
Restoring and recovering using Windows tools
Using Reset when the system is not responding
Select Reset Follow the on-screen instructions to continue
Backing up, restoring, and recovering in Windows
Creating recovery media
Click All Programs
To create recovery discs Close all open programs
To create the Windows DVD System backup and recovery
System Restore
Follow the on-screen instructions to set up your backup
System Recovery
System Recovery when Windows is responding
System Recovery when Windows is not responding
Select Install now
Page
Japanese Power Cord Requirements
General Requirements
Country-Specific Requirements
Country-Specific Requirements
Country Accrediting Agency
Statement of Volatility
Appendix B Statement of Volatility
Enter the F10 setup utility
MT Specifications
Appendix C Specifications
Plus Platinum
MT Specifications
Rated Input Current Current Leakage Nfpa
240W active PFC
240W active PFC 280W active PFC 87/90/87% efficient at
240W active PFC 89/91/90% efficient at
280W active PFC 280W active PFC 90/92/89% efficient at
DM Specifications
DM Specifications
Approximate Weight Temperature Range
DC Output
Disassembly preparation
205 Illustrated Processor removal Audio problems 182
Drive cage removal
Hard drive removal
Front panel problems 197
Downloading DM removal and replacement
HP Recovery Disc Creator, using
Fan, MT Installation
Recovery discs, steps for creating
Removal and replacement DM battery
Media card reader
Socket population 42, 78
MT heat sink MT power supply
SFF front bezel SFF front I/O, power switch Assembly 103
SFF power supply 114 SFF power switch 106 SFF processor 112
MT battery blank MT bezel blank
Creating backups 217
Creating system restore points
Flash drive 218 System Recovery 220
DM removal and replacement Wlan module Index