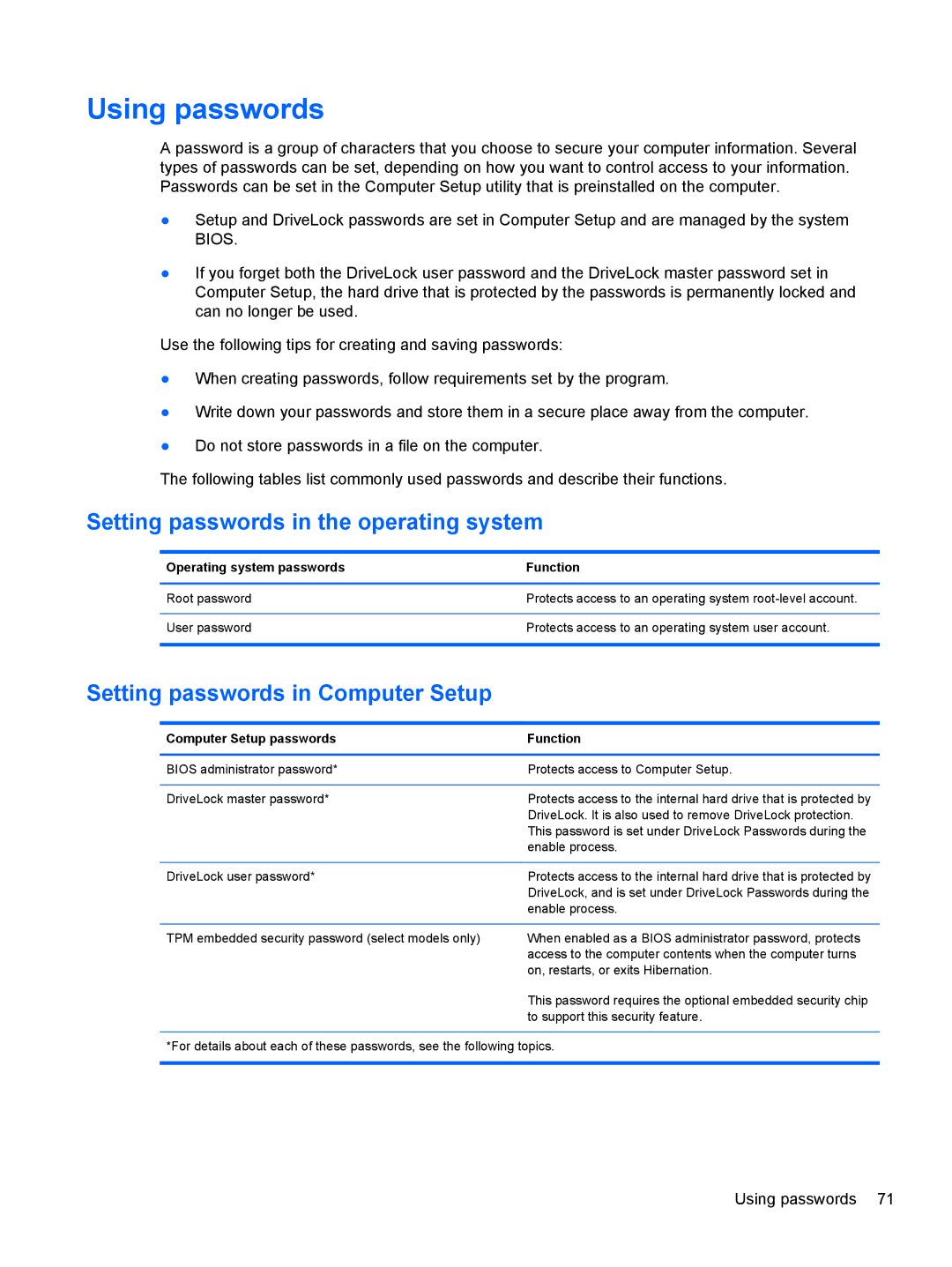
C1E67UT specifications
The HP C1E67UT is a dynamic and robust notebook designed for professionals and everyday users who seek reliability and performance in their computing experience. This laptop stands out due to its powerful specifications and innovative technologies that cater to a wide range of tasks, from business applications to multimedia usage.One of the key features of the HP C1E67UT is its powerful processor. Equipped with an Intel Core i5 or i7 processor, this laptop ensures a seamless performance that can handle multiple applications simultaneously. This level of processing power makes it suitable for multitasking, allowing users to run demanding applications like graphics software, video editors, and even more straightforward tasks like browsing the web and creating documents without slowdowns.
The display on the HP C1E67UT is another highlight, offering a vibrant and crisp graphics experience. With a Full HD resolution, users can enjoy sharp images and vivid colors, making it ideal for watching movies or viewing high-resolution photos. The anti-glare screen technology further enhances usability, allowing work in varied lighting conditions without straining the eyes.
In terms of storage, the HP C1E67UT provides ample space to accommodate large files and applications. With options for SSD storage, it offers faster boot times and quicker access to data compared to traditional hard drives. This speed is invaluable for users who rely on quick file access for their daily activities.
Connectivity is well catered for with multiple USB ports, HDMI output, and Wi-Fi capabilities. This laptop also includes Bluetooth technology, facilitating seamless connections with various peripherals such as printers, mice, and headphones. The presence of an integrated webcam and dual-array microphones support video conferencing, enhancing productivity for remote work or virtual meetings.
Durability is essential for any professional device, and the HP C1E67UT does not disappoint. Built with robust materials, it withstands everyday wear and tear, making it a reliable companion for users who travel frequently or work in dynamic environments.
In conclusion, the HP C1E67UT is a powerful, feature-rich notebook designed to meet the needs of both professionals and casual users. Its combination of a strong processor, vibrant display, generous storage options, and durable build makes it an excellent choice for anyone seeking a reliable computing solution. With its array of features, the HP C1E67UT is well-equipped for any task, from business applications to entertainment, catering to a diverse audience.