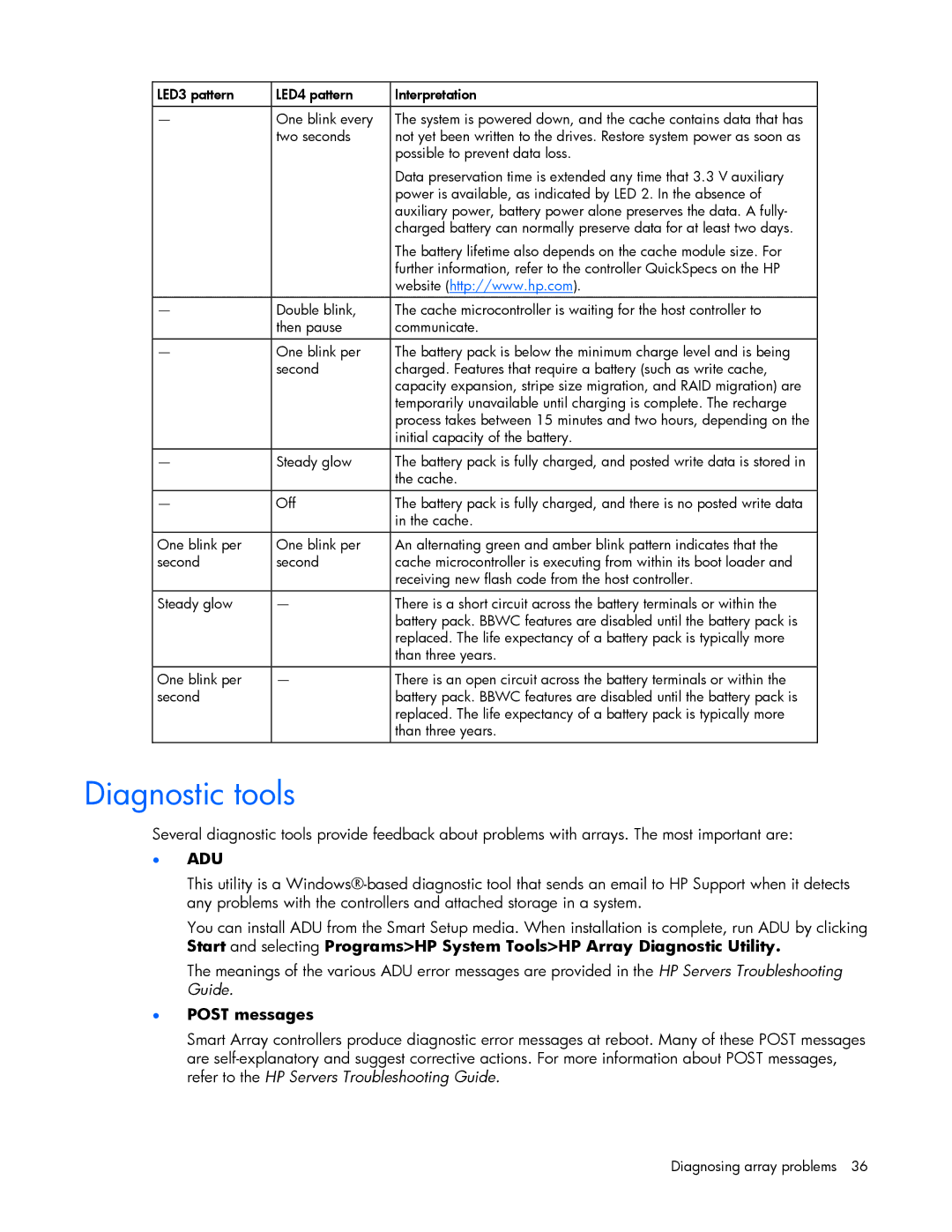
LED3 pattern | LED4 pattern | Interpretation |
|
|
|
— | One blink every | The system is powered down, and the cache contains data that has |
| two seconds | not yet been written to the drives. Restore system power as soon as |
|
| possible to prevent data loss. |
|
| Data preservation time is extended any time that 3.3 V auxiliary |
|
| power is available, as indicated by LED 2. In the absence of |
|
| auxiliary power, battery power alone preserves the data. A fully- |
|
| charged battery can normally preserve data for at least two days. |
|
| The battery lifetime also depends on the cache module size. For |
|
| further information, refer to the controller QuickSpecs on the HP |
|
| website (http://www.hp.com). |
— | Double blink, | The cache microcontroller is waiting for the host controller to |
| then pause | communicate. |
|
|
|
— | One blink per | The battery pack is below the minimum charge level and is being |
| second | charged. Features that require a battery (such as write cache, |
|
| capacity expansion, stripe size migration, and RAID migration) are |
|
| temporarily unavailable until charging is complete. The recharge |
|
| process takes between 15 minutes and two hours, depending on the |
|
| initial capacity of the battery. |
— | Steady glow | The battery pack is fully charged, and posted write data is stored in |
|
| the cache. |
|
|
|
— | Off | The battery pack is fully charged, and there is no posted write data |
|
| in the cache. |
|
|
|
One blink per | One blink per | An alternating green and amber blink pattern indicates that the |
second | second | cache microcontroller is executing from within its boot loader and |
|
| receiving new flash code from the host controller. |
|
|
|
Steady glow | — | There is a short circuit across the battery terminals or within the |
|
| battery pack. BBWC features are disabled until the battery pack is |
|
| replaced. The life expectancy of a battery pack is typically more |
|
| than three years. |
|
|
|
One blink per | — | There is an open circuit across the battery terminals or within the |
second |
| battery pack. BBWC features are disabled until the battery pack is |
|
| replaced. The life expectancy of a battery pack is typically more |
|
| than three years. |
|
|
|
Diagnostic tools
Several diagnostic tools provide feedback about problems with arrays. The most important are:
•ADU
This utility is a
You can install ADU from the Smart Setup media. When installation is complete, run ADU by clicking Start and selecting Programs>HP System Tools>HP Array Diagnostic Utility.
The meanings of the various ADU error messages are provided in the HP Servers Troubleshooting Guide.
•POST messages
Smart Array controllers produce diagnostic error messages at reboot. Many of these POST messages are
Diagnosing array problems 36