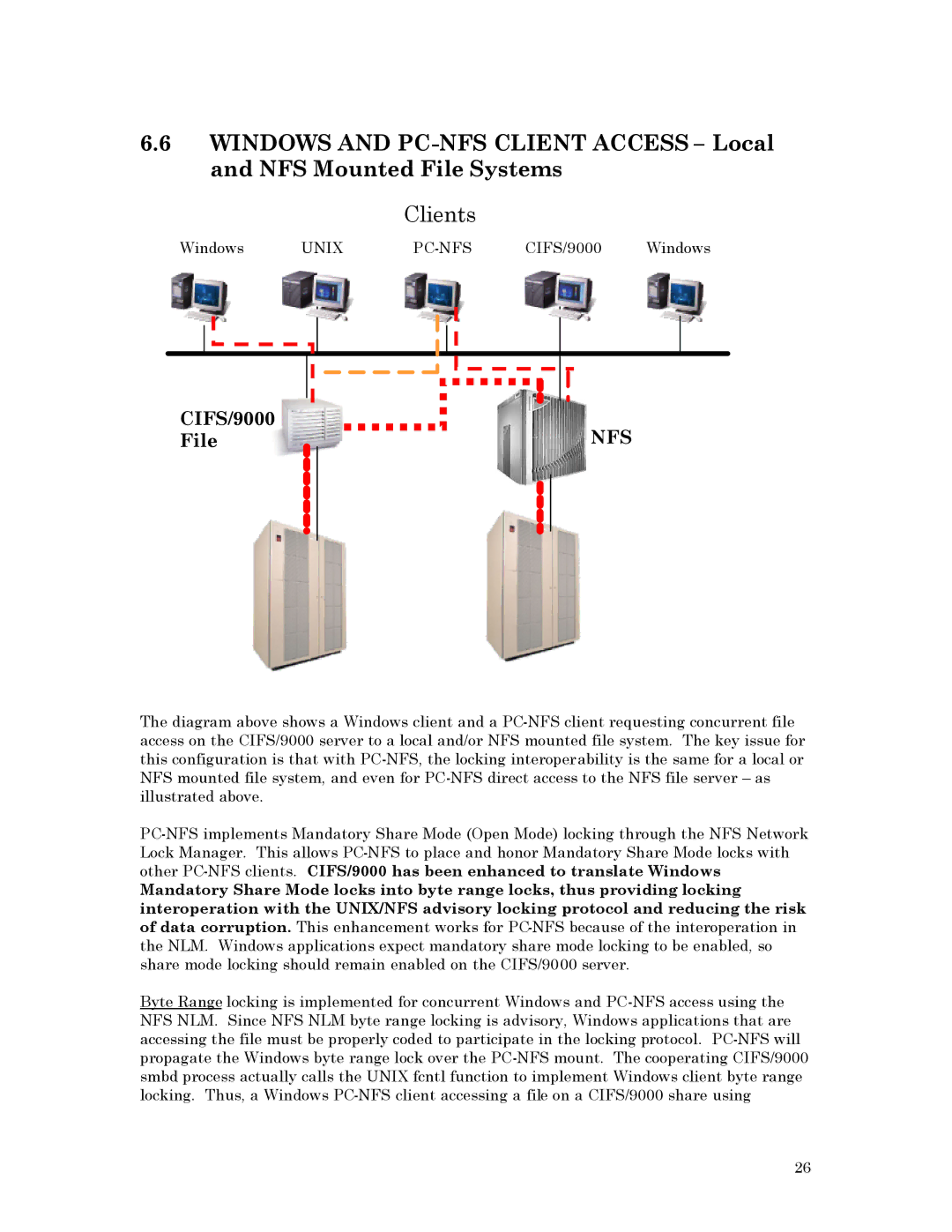
6.6WINDOWS AND PC-NFS CLIENT ACCESS – Local and NFS Mounted File Systems
Clients
Windows | UNIX | PC-NFS | CIFS/9000 | Windows |
The diagram above shows a Windows client and a PC-NFS client requesting concurrent file access on the CIFS/9000 server to a local and/or NFS mounted file system. The key issue for this configuration is that with PC-NFS, the locking interoperability is the same for a local or NFS mounted file system, and even for PC-NFS direct access to the NFS file server – as illustrated above.
PC-NFS implements Mandatory Share Mode (Open Mode) locking through the NFS Network Lock Manager. This allows PC-NFS to place and honor Mandatory Share Mode locks with other PC-NFS clients. CIFS/9000 has been enhanced to translate Windows
Mandatory Share Mode locks into byte range locks, thus providing locking interoperation with the UNIX/NFS advisory locking protocol and reducing the risk of data corruption. This enhancement works for PC-NFS because of the interoperation in the NLM. Windows applications expect mandatory share mode locking to be enabled, so share mode locking should remain enabled on the CIFS/9000 server.
Byte Range locking is implemented for concurrent Windows and PC-NFS access using the NFS NLM. Since NFS NLM byte range locking is advisory, Windows applications that are accessing the file must be properly coded to participate in the locking protocol. PC-NFS will propagate the Windows byte range lock over the PC-NFS mount. The cooperating CIFS/9000 smbd process actually calls the UNIX fcntl function to implement Windows client byte range locking. Thus, a Windows PC-NFS client accessing a file on a CIFS/9000 share using