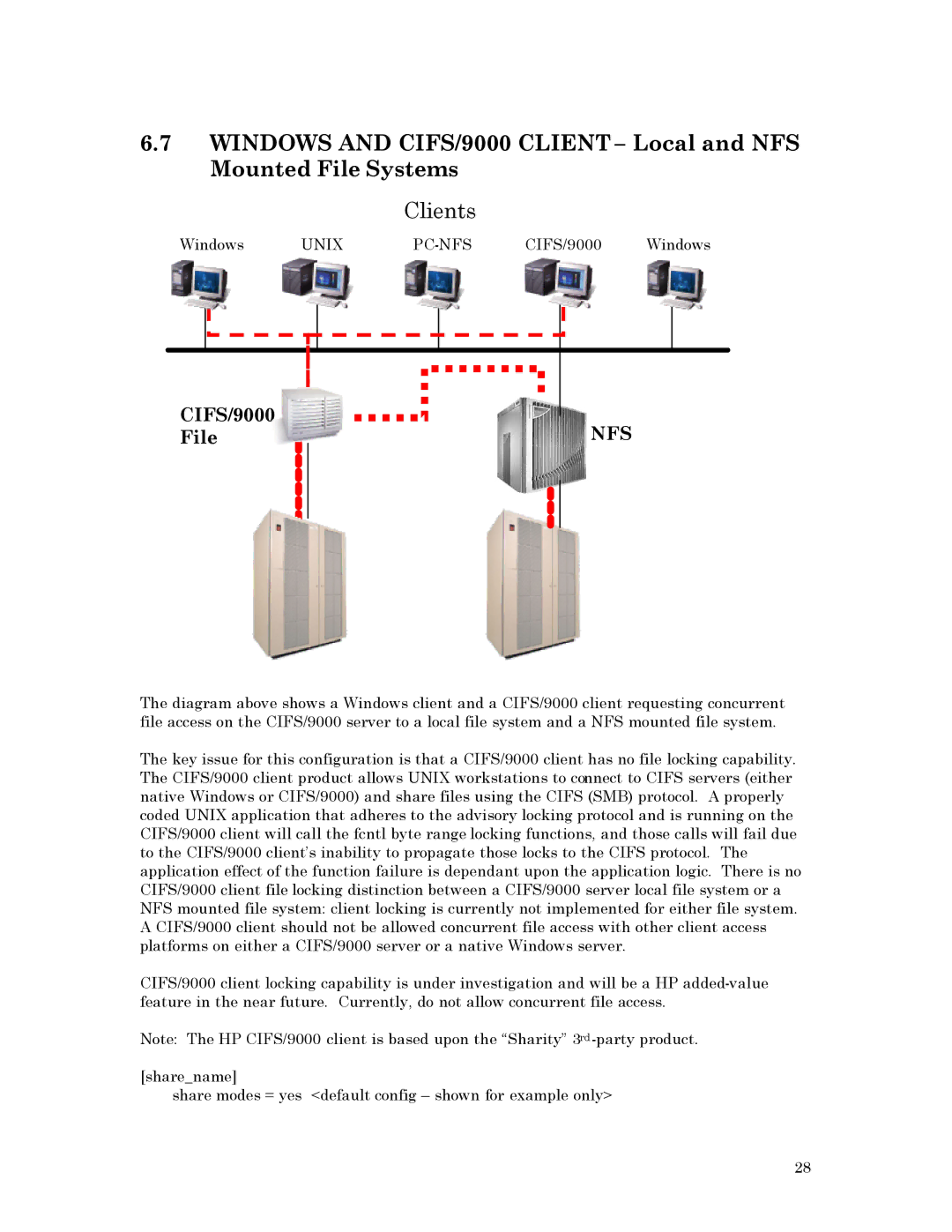
6.7WINDOWS AND CIFS/9000 CLIENT – Local and NFS Mounted File Systems
Clients
Windows | UNIX | CIFS/9000 | Windows |
CIFS/9000 | NFS |
File |
The diagram above shows a Windows client and a CIFS/9000 client requesting concurrent file access on the CIFS/9000 server to a local file system and a NFS mounted file system.
The key issue for this configuration is that a CIFS/9000 client has no file locking capability. The CIFS/9000 client product allows UNIX workstations to connect to CIFS servers (either native Windows or CIFS/9000) and share files using the CIFS (SMB) protocol. A properly coded UNIX application that adheres to the advisory locking protocol and is running on the CIFS/9000 client will call the fcntl byte range locking functions, and those calls will fail due to the CIFS/9000 client’s inability to propagate those locks to the CIFS protocol. The application effect of the function failure is dependant upon the application logic. There is no CIFS/9000 client file locking distinction between a CIFS/9000 server local file system or a NFS mounted file system: client locking is currently not implemented for either file system. A CIFS/9000 client should not be allowed concurrent file access with other client access platforms on either a CIFS/9000 server or a native Windows server.
CIFS/9000 client locking capability is under investigation and will be a HP
Note: The HP CIFS/9000 client is based upon the “Sharity” 3rd
[share_name]
share modes = yes <default config – shown for example only>
28