Abstract
HP Fortran Programmer Guide
Page
Contents
Performance and optimization
Using the on statement
Controlling data storage
Debugging
Migrating to HP Fortran 131
Using Fortran directives 123
Writing HP-UX applications 107
Calling C routines from HP Fortran 110
Fortran 2003 Features 151
Porting to HP Fortran 141
Documentation Feedback 153 Glossary 154 Index 159
HP secure development lifecycle
An overview of HP Fortran
HP Fortran compiler environment
An overview of HP Fortran
+preinclude= file
Driver
Options for controlling the f90 driver
+dryrun
Options for controlling the C preprocessor
Preprocessor
Options for controlling the front end
Front-end
+moddir=directory
Options for controlling optimization
Back-end
+DAmodel
Options for controlling code generation
+Onooptimization
Optimization
Options for controlling the Linker
Linker
+FPflags
Ldirectory
Ooutfile
Tools
HP-UX operating system
Wl ,options
$ f90 hello.f90
Compiling with the f90 command
F90 command syntax
Compiling and linking
Example 2 hello.f90
Command-line options
F90 command syntax
Command-line options
+save
Command-line options by category
Commonly-used options
Commonly-used options
Options listed by category
Option descriptions
Example 3 Example
Do I+1, N
+allowunaligned
Boption
Data type sizes and +autodbl4
14164
+autodbl +autodbl4
+nocfc
+cpp=default
+charlit77
+check=bounds
Datamodelare
Name=def
+DAmodel
+DDdatamodel
Native
Blended
Itanium
Itanium2
Values for the +FP option
Signals recognized by the +fpexception option
Gformat77
+hugecommon
Example 4 % f90 +hugecommon=results pcvals.f90
+initheapinteger=ival
/usr/include directory +noimplicitnone
+indirectcommonlist=file
+initheapcomplex=rvalival
+nolibs
+io77
Ipo
+nocheckuf
+noobjdebug
Levels of optimization
Requires concurrent use of the +Oprofile=use option
With different values of optlevel
+pa1
+realconstant=single
+demandload option. The default is +nodemandload
+nodemandload the default
+r8
End.o
Tx,path
Tp,/usr/ccs/lbin/cpp
F90com
Wx,arg1,arg2,...,argN
Bhidden =symbol ,symbol
Symbol binding options
Bdefault=symbol,symbol
Bextern =symbol ,symbol
Using optimization options
Reviewing general optimization options
F90 +O3 +Osize myprog.f90
+Oautopar and omit +Oparallel
+Oconservative
+Onoall
+Onoautopar
F90 +O3 +Onomoveflops +Ofltacc myprog.f90
Fine-tuning optimization options
+Onocxlimitedrange
Default is +Onocxlimitedrange
Default is +Odataprefetch
+Ocachepadcommon option
+Onofailsafe
+Onofenvaccess
+Onofastaccess
+Onoentrysched
Optimizations performed by +Onofltacc
+Onoinline=function1,function2
+Oinlinebudget=n +Oinlinebudget enables
+Onoinline
+Onoinlinefilename
Millicode versions of intrinsic functions
Values for the +Oinlinebudget option
+Onoloopunrolljam
+inlinelevel num
+Onoloopunroll=factor
+Oloopunroll=4
+Onopipeline
Default is+Onoparmsoverlap
+Oparallelintrinsics
+Onoparmsoverlap
For +Oprofile=collectarc,stride
Default is +Onopromoteindirectcalls
+Onorecovery
Default is +Oshortdata=8
Filenames recognized by f90
Filenames
Linking with f90 vs. ld
Linking HP Fortran programs
$ f90 -c hello.f90 # compile
Libraries linked by default on PA-RISC
Libraries linked by default on Itanium
Linking to libraries
Linking HP Fortran 90 routines
Linking to nondefault libraries
Additional HP Fortran libraries
Linking to shared libraries
Opt/fortran90/lib/pa2064/ -lF90 -lisamstub
$ f90 -Wl,-a,archive prog.f90 -lm
Special-purpose compilations
Compiling programs with modules
Library search rules
Special-purpose compilations
Example 7 Example 2-3 code.f90
Examples
Example
Example 6 Example 2-2 main.f90
$ dostats
Compiling with make
Example 8 Example 2-4 data.f90
$ f90 -o dostats data.f90 code.f90 main.f90
$ make
Compiling for different PA-RISC machines
Managing .mod files
Example 9 Example 2-5 makefile
Compiling with +pic
Creating shared libraries
Linking with -b
Using the C preprocessor
$ f90 +cpp=yes -D Debug cppdirect.f90
Using the C preprocessor
Processing cpp directives
Example 13 Example 2-9 cppdirect.f90
Creating demand-loadable executables
Creating shared executables
Saving the cpp output file
HP Fortran environment variables
Compiling in 64-bit mode
Using environment variables
$ f90 +noshared prog.f90
$ f90 +list hello.f90
F90ROOT environment variable
STF90COM64 environment variable
HPF90OPTS environment variable
Mpnumberofthreads environment variable
Floating installation
Floating installation
Lpath environment variable
Alternate-path/opt/fortran90.3.6.1
Setting up floating installation
Disabling implicit typing
Controlling data storage
Disabling implicit typing
Automatic and static variables
Controlling data storage
Contains
Increasing the precision of constants
Increasing default data sizes
Increasing default data sizes
Increasing default data sizes
Sharing data among programs
Usr/lib/libpthread.sl
Which creates multiple threads
Sharing data among programs
$ gotosleep
Modules vs. common blocks
$ wakeup
Im up
Modules vs. common blocks
Using the HP WDB debugger
Debugging
Stripping debugging information
Floating-point exceptions
Signals recognized by +fpexception
Signal
Handling runtime exceptions
Bus error exception
Floating-point exceptions
= 1.0/0.0
Segmentation violation exception
Illegal instruction exception
Bad argument exception
Using debugging lines
Exceptions handled by the on statement
Using the on statement
Exceptions handled by the on statement
On REAL8 DIV 0 Call divzerotrap
Actions specified by on
On Double Precision DIV 0 Call divzerotrap
Exceptions handled by the on statement
Example 15 Example5-2 ignore.f90
Ignoring errors
Terminating program execution
Example 14 Example5-1 abort.f90
On Double Precision Overflow Call trap
Calling a trap procedure
Trapping floating-point exceptions
Trapping integer overflow exceptions
Trapping +Ctrl-C trap interrupts
Allowing core dumps
Example 17 Example5-4 callitrap.f90
On Real Overflow Ignore
Example 18 Example 5-5 allowcore.f90
HP Caliper
Using profilers
Using profilers
Performance and optimization
Programprogramarguments
Comparing Program Performance
Opt/ansic/bin/cc -Aa +O3 -o program +Oprofile=collect
Program.c
$ gprof prog gprof.out
Using Options to Control Data Collection
Gprof
Specifying PBO file names and locations
$ f90 +O4 file.f90
Using options to control optimization
Using +O to set optimization levels
Prof
+O4
Using the optimization options
+O2, -O
+O3
Packaged optimization options
Fine-tuning optimization options
$ f90 +02 +Oaggressive +Osize prog.f90
$ f90 +O4 +Oaggressive +Ofltacc prog.f90
+Ofltacc=relaxed
Is +Onofastaccess at
+Ofastaccess at level
+O2
+Ofltacc=relaxed . This
Fast
+Onoinitcheck
+Onoloopunroll=n
+Oinlinelevel num
+Onolibcalls
+Olibcalls
+Opipeline
+Onoparminit
+Orecovery
+Ovectorize option on
+Oregreassoc
+Onoreturn
+Oshortdata=8
Conservative vs. aggressive optimization
+Onowholeprogrammode
+Owholeprogrammode
F90 +O3 +Oparallel -c x.f90 y.f90 F90 +O3 -c z.f90
Conservative, aggressive, and default optimizations
Parallelizing HP Fortran programs
Compiling for parallel execution
Calling routines with side effects parallellization
Performance and parallelization
Profiling parallelized programs
Conditions inhibiting loop parallelization
Data dependences
Indeterminate iteration counts
Vector routines called by +Ovectorize
Using the +Ovectorize option
Vectorization
F90 +O3 +Ovectorize prog.f90
Vecdmultadd
Controlling vectorization locally
Saxpy
Sdot
Industry-wide standard Vectorization
Calling Blas library routines
Example 19 Example 6-1 axpy.f90
REAL, External sdot
Controlling code generation for performance
Example 20 Example 7-1 getargs.f90
Accessing command-line arguments
Writing HP-UX applications
$ fprog arg1 another arg
Calling HP-UX system and library routines
Using HP-UX file I/O
Stream I/O using Fstream
Performing I/O using HP-UX system calls
Obtaining an HP-UX file descriptor
Using HP-UX file I/O
Calling C routines from HP Fortran
Data types
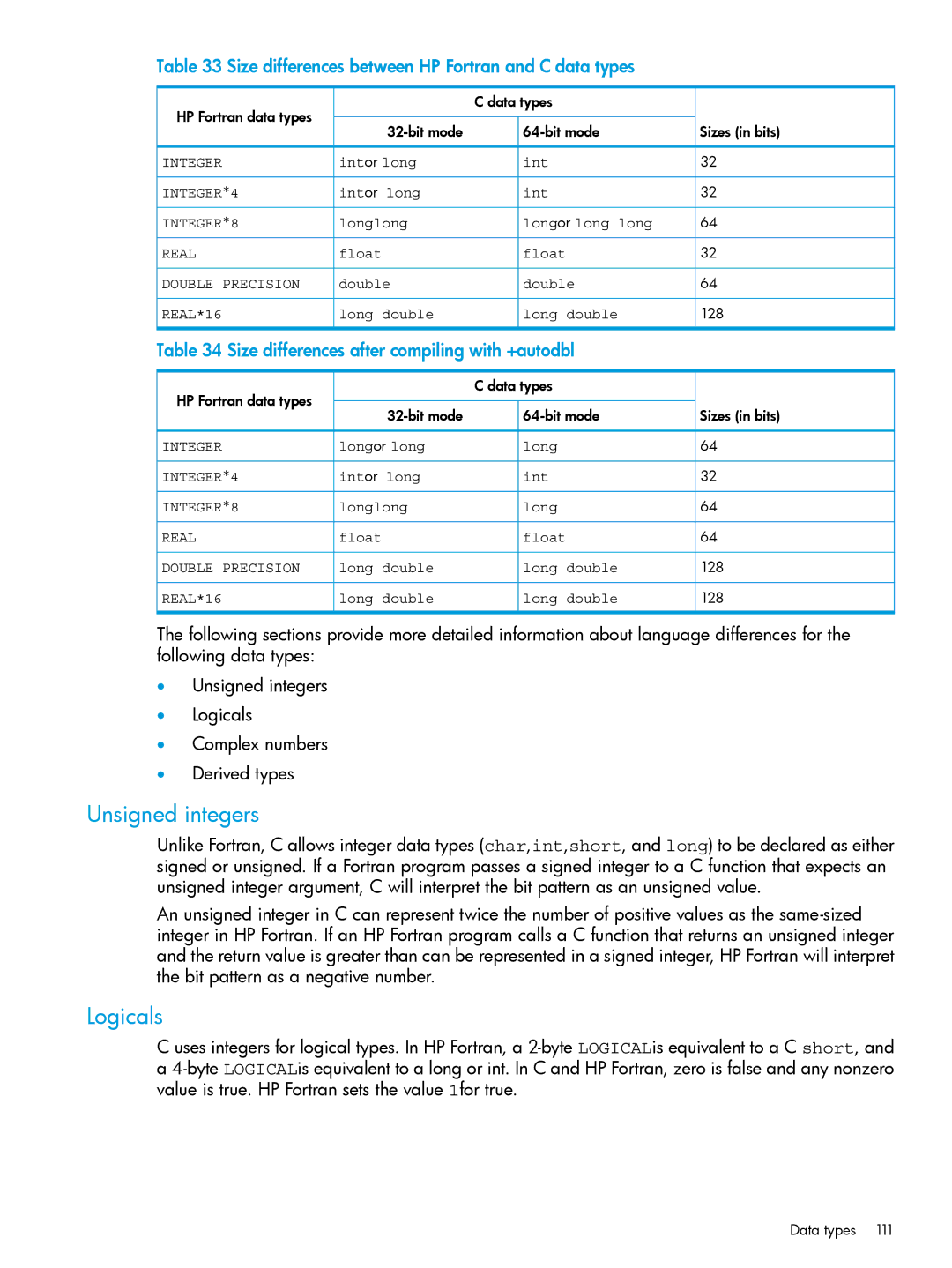
Data type correspondence for HP Fortran and C
Size differences after compiling with +autodbl
Unsigned integers
Logicals
Size differences between HP Fortran and C data types
Complex numbers
Complex sqrcomplexCOMPLEX cmxval
Example 21 Example 8-1 passcomplex.f90
Example 22 Example 8-2 sqrcomplex.c
Argument-passing conventions
Derived types
Pointers
Call foo%REFptr, %REFiarray, %VALi
Integer ptr INTEGER, DIMENSION100 iarray
Case sensitivity
Void fooint *ptr, int iarray100, int
Case sensitivity
Example 23 Example 8-3 sortem.c
$HP$ Alias bubblesort = BubbleSort%REF,%VAL
Example 24 Example 8-4 testsort.f90
Int
Memory layout of a two-dimensional array in Fortran and C
REAL, DIMENSION2,3,4
Arrays
Example 26 Example 8-6 getarray.c
Example 25 Example 8-5 passarray.f90
Passing a string
Strings
Null-terminated string
Fortran hidden length argument
Strings
Following are example C and Fortran programs
File handling
Example 27 Example 8-7 passchars.f90
Example 28 Example 8-8 getstring.c
File handling
Example 29 Example 8-9 fnumtest.f90
Extern int globals100
Sharing data
Int somedata
Extern int somedata
HP Fortran directives
Using Fortran directives
Using HP Fortran directives
Directive syntax
Name
Syntax
Description and restrictions
$HP$ Alias name = external-name arg-pass-mode-list
Local and global usage
Case sensitivity
Argument-passing conventions
Example 32 Example 9-2 passstr.f90
Strings
For more information
Example 31 Example 9-1 prstr.c
Listing file
Disables the inclusion of source lines in the listing file
Specified on the command line
Example 33 Example
Vendor Directive Cray
Compatibility directives
Controlling vectorization
Compatibility directives recognized by HP Fortran
Compatibility directives
Controlling parallelization
Controlling dependence checks
Controlling checks for side effects
Using Fortran directives
Compiler limits
Command-line options not supported
Migrating to HP Fortran
Incompatibilities with HP Fortran
Double Precision x =
Format field widths
Floating-point constants
Intrinsic functions
Data types and constants
Procedure calls and definitions
KEY=
Input/output
Directives
Foo**REALbar, 8 ! foo**bar
Miscellaneous
Migration issues
Source code issues
Migration issues
HP Fortran 77 directives supported by f90 options
Directives
F77 options supported by f90
Command-line option issues
Intrinsic functions
Conflicting intrinsics and libU77 routine names
Data file issues
Object code issues
HP-supplied migration tools
Approaches to migration
$ fid +800 file.f $ fid +es program.f
END structure definition
Porting to HP Fortran
Compatibility extensions
Compatibility statements
+Oparallel or
Compiler directives
Compatibility directives
Pointer Cray-style
+Oparallel or +Ovectorize
Intrinsic procedures
Nonstandard intrinsic procedures in HP Fortran
Directive prefixes recognized by HP Fortran
Uninitialized variables
Using porting options
$ f90 testloop.f90
Using porting options
Large word size
One-trip do loops
Name conflicts
Example 34 Example 11-1 clash.f90
External int1
Source formats
Names with appended underscores
Porting from Tru64 to HP Fortran
Escape sequences
+cfc
Porting from Tru64 to HP Fortran
Enhancements
New options
Nof66alternate for +noonetrip
+nopadsrc Altparam
Check noboundsoptions for example, -nocheckbounds
Miscellaneous enhancements
Fortran 2003 Features
Interoperability with C
Input/output enhancements
Object orientation features
Fortran 2003 Features
Data enhancements
153
Documentation Feedback
Glossary
Glossary
155
So on. See also row-major order
Also filename extension
157
Memory fault
See ttv
Symbols
Index
159