Overview of IBM Networking
STUN and BSTUN
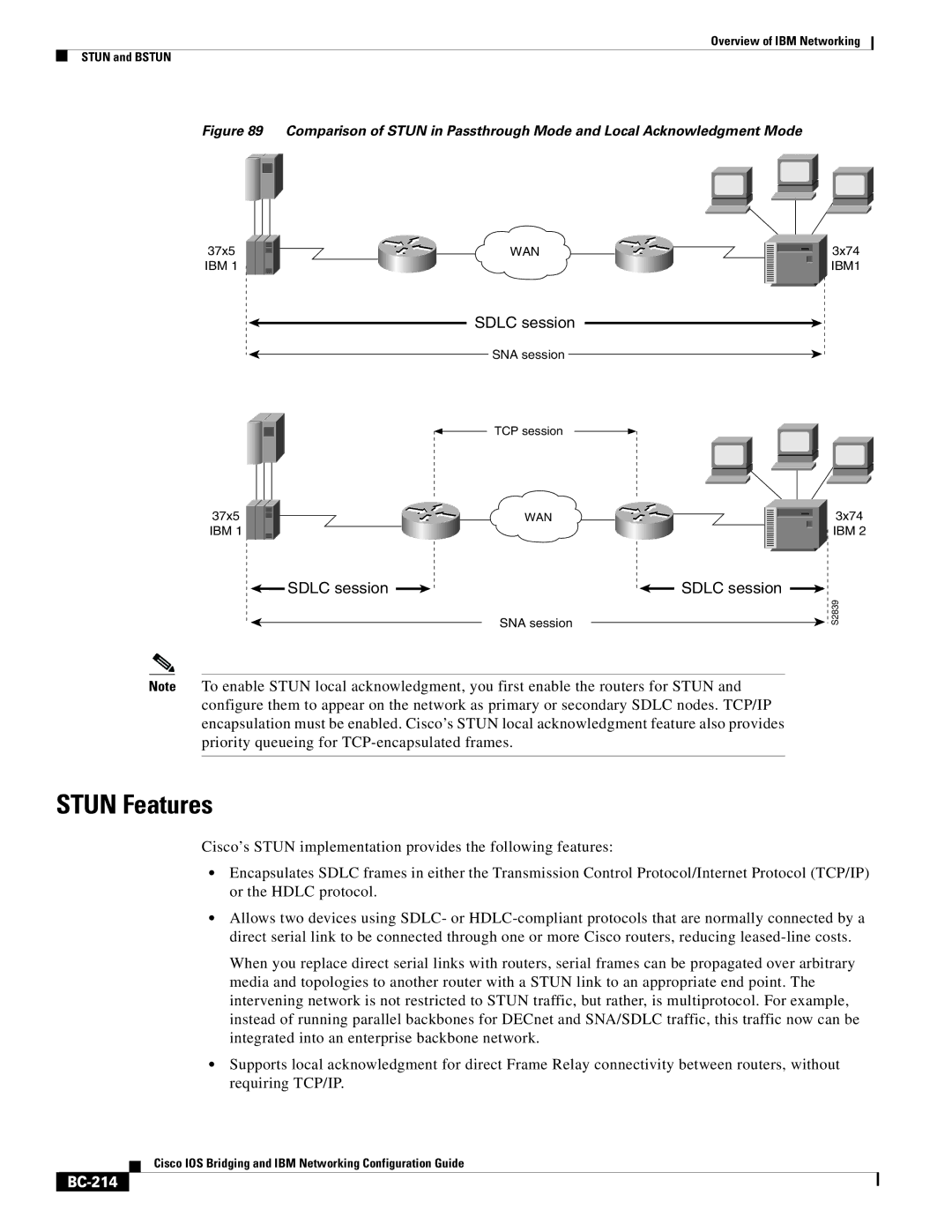
Figure 89 Comparison of STUN in Passthrough Mode and Local Acknowledgment Mode
37x5 | WAN |
IBM 1 |
|
SDLC session
SNA session
TCP session
37x5 | WAN |
IBM 1 |
|
3x74
IBM1
3x74
IBM 2
SDLC session |
| SDLC session |
|
SNA session
Note To enable STUN local acknowledgment, you first enable the routers for STUN and configure them to appear on the network as primary or secondary SDLC nodes. TCP/IP encapsulation must be enabled. Cisco’s STUN local acknowledgment feature also provides priority queueing for
S2839
STUN Features
Cisco’s STUN implementation provides the following features:
•Encapsulates SDLC frames in either the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) or the HDLC protocol.
•Allows two devices using SDLC- or
When you replace direct serial links with routers, serial frames can be propagated over arbitrary media and topologies to another router with a STUN link to an appropriate end point. The intervening network is not restricted to STUN traffic, but rather, is multiprotocol. For example, instead of running parallel backbones for DECnet and SNA/SDLC traffic, this traffic now can be integrated into an enterprise backbone network.
•Supports local acknowledgment for direct Frame Relay connectivity between routers, without requiring TCP/IP.
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide