Overview of IBM Networking
IBM Network Media Translation
QLLC Conversion
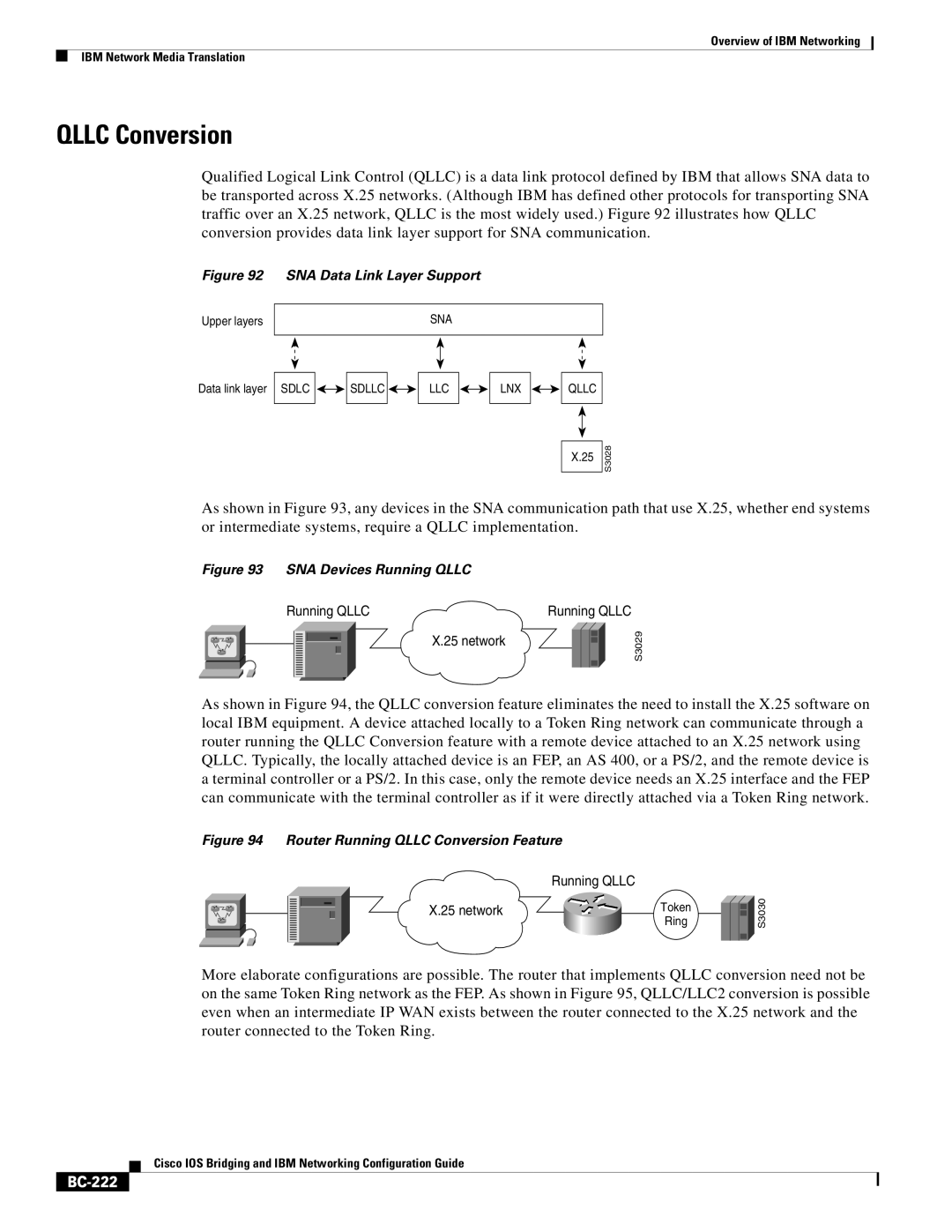
Qualified Logical Link Control (QLLC) is a data link protocol defined by IBM that allows SNA data to be transported across X.25 networks. (Although IBM has defined other protocols for transporting SNA traffic over an X.25 network, QLLC is the most widely used.) Figure 92 illustrates how QLLC conversion provides data link layer support for SNA communication.
Figure 92 SNA Data Link Layer Support
Upper layers
SNA
Data link layer SDLC
![]()
![]() SDLLC
SDLLC ![]()
![]()
LLC
LNX
QLLC
X.25
S3028
As shown in Figure 93, any devices in the SNA communication path that use X.25, whether end systems or intermediate systems, require a QLLC implementation.
Figure 93 SNA Devices Running QLLC
Running QLLC
X.25 network
Running QLLC
S3029
As shown in Figure 94, the QLLC conversion feature eliminates the need to install the X.25 software on local IBM equipment. A device attached locally to a Token Ring network can communicate through a router running the QLLC Conversion feature with a remote device attached to an X.25 network using QLLC. Typically, the locally attached device is an FEP, an AS 400, or a PS/2, and the remote device is a terminal controller or a PS/2. In this case, only the remote device needs an X.25 interface and the FEP can communicate with the terminal controller as if it were directly attached via a Token Ring network.
Figure 94 Router Running QLLC Conversion Feature
| Running QLLC |
X.25 network | Token |
| Ring |
![]()
![]() S3030
S3030
More elaborate configurations are possible. The router that implements QLLC conversion need not be on the same Token Ring network as the FEP. As shown in Figure 95, QLLC/LLC2 conversion is possible even when an intermediate IP WAN exists between the router connected to the X.25 network and the router connected to the Token Ring.
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide