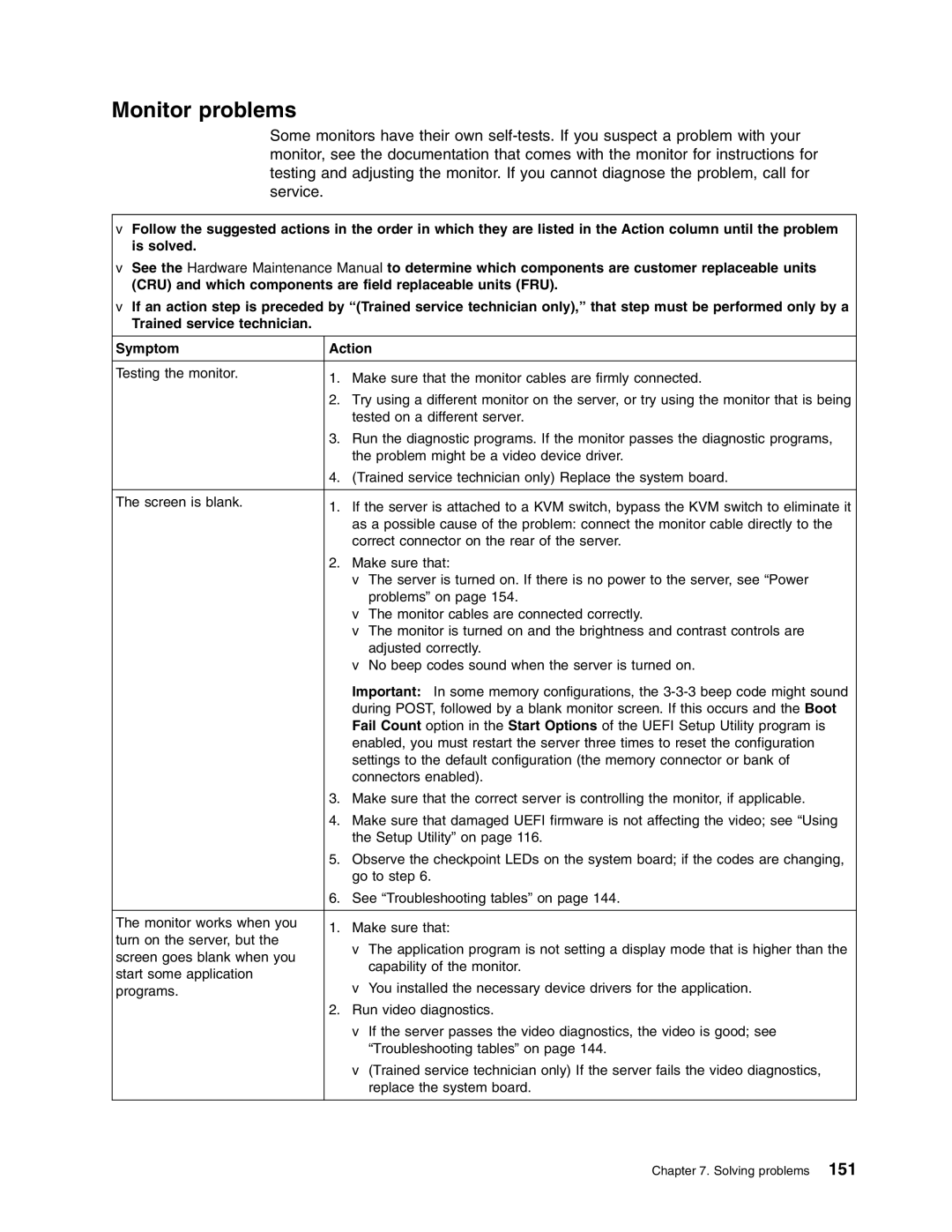
RD210 specifications
The Lenovo RD210 is a powerhouse in the realm of entry-level rack servers, designed to deliver high performance and reliability for small to medium businesses. With its compact 1U form factor, the RD210 is an ideal choice for organizations looking to maximize space in their data center while still benefiting from robust computing capabilities.One of the standout features of the RD210 is its support for the latest Intel Xeon processors, which provide exceptional performance for demanding workloads. This server can be equipped with multiple processor options, allowing businesses to select the configuration that best meets their needs. Its impressive memory capacity, supporting up to 192 GB of DDR3 RAM, ensures that users can run multiple applications simultaneously without experiencing any slowdowns.
Storage flexibility is another strong point of the RD210. The server supports a variety of configurations, accommodating up to four hot-swap drive bays for SAS or SATA drives. This feature allows for easy upgrades and replacements, reducing downtime and increasing overall efficiency. Additionally, organizations can opt for SSDs for enhanced performance, particularly valuable for applications that require rapid data access.
The RD210 also boasts a range of advanced technologies that enhance its performance and reliability. For instance, Lenovo's Intelligent Cooling technology helps maintain optimal operating temperatures, which can extend the life of the server components. Furthermore, with features like redundant power supplies and advanced error correction, the RD210 is designed to minimize system failures and ensure business continuity.
In terms of connectivity, the RD210 comes equipped with multiple Ethernet ports, supporting options for faster networking speeds and redundancy. It also integrates easily into existing infrastructure, with support for various operating systems, including Windows Server and Linux distributions.
For management, the Lenovo RD210 includes advanced tools like Lenovo XClarity, providing real-time monitoring and management capabilities. This feature simplifies server administration, making it easier for IT teams to manage workloads efficiently.
In conclusion, the Lenovo RD210 combines scalability, performance, and reliability in a compact package suitable for diverse computing needs. Its powerful processors, ample memory, and storage options make it a smart investment for businesses aiming to enhance their IT infrastructure. As organizations increasingly rely on secure and efficient solutions, the RD210 stands out as a reliable choice for robust server performance.