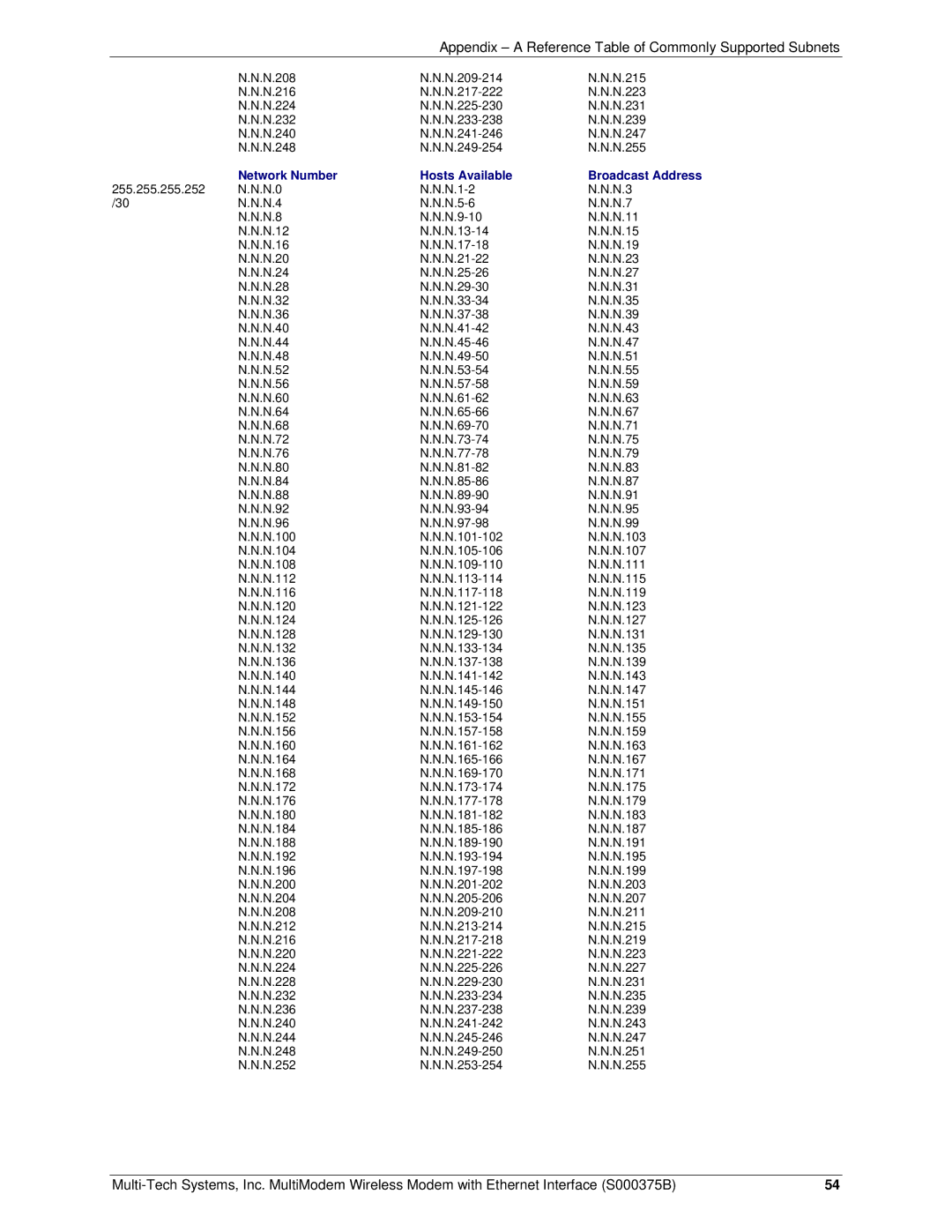
RJ-9, RJ-45 specifications
Multi-Tech Systems offers a range of communication solutions, prominently featuring the RJ-45 and RJ-9 connectors that are crucial in networking and telecommunications. These connectors are foundational to many applications, enabling efficient data transfer and ensuring reliable voice communications.The RJ-45 connector is primarily used in Ethernet networks. It features eight pins and is designed for high-speed data transmission, making it the standard for wired local area networks (LANs). This connector supports various Ethernet standards including Fast Ethernet (100BASE-T), Gigabit Ethernet (1000BASE-T), and even 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10GBASE-T). An essential characteristic of the RJ-45 is its versatility, as it can be used with both straight-through and crossover cable configurations. This flexibility allows for straightforward connectivity between devices such as computers, routers, and switches.
Multi-Tech Systems employs advanced technology in their RJ-45 connectors, including support for Power over Ethernet (PoE). This innovation permits electrical power and data to be transmitted over the same cable, simplifying installations and reducing the need for additional wiring. The robust design of these connectors ensures durability and minimizes signal interference, thereby maximizing data integrity during transmission.
On the other hand, the RJ-9 connector, also known as the RJ-9 or RJ-10 connector, is typically used in telephone and headset applications. Characterized by its smaller size and four or six pins, the RJ-9 is optimized for voice frequency communication. It connects devices such as telephones, headsets, and other VoIP equipment, delivering clear audio quality that is essential for effective communication.
One standout feature of the RJ-9 connector is its ability to provide superior noise resistance, making it ideal for environments with significant electromagnetic interference. Multi-Tech Systems' RJ-9 connectors are designed for ease of use, allowing quick and simple connections. These connectors can often be found in various telephony devices, ensuring that they remain a staple in personal, commercial, and industrial communication systems.
In conclusion, Multi-Tech Systems continues to lead in the provision of reliable RJ-45 and RJ-9 connectors, integrating innovative technologies that enhance performance in data and voice communication. Whether in a high-speed networking environment or in everyday telephony applications, these connectors deliver the functionality and quality demanded by modern users. Their design and engineering reflect a commitment to excellence, helping users stay connected in an increasingly digital world.