WG311
Client attempting to connect
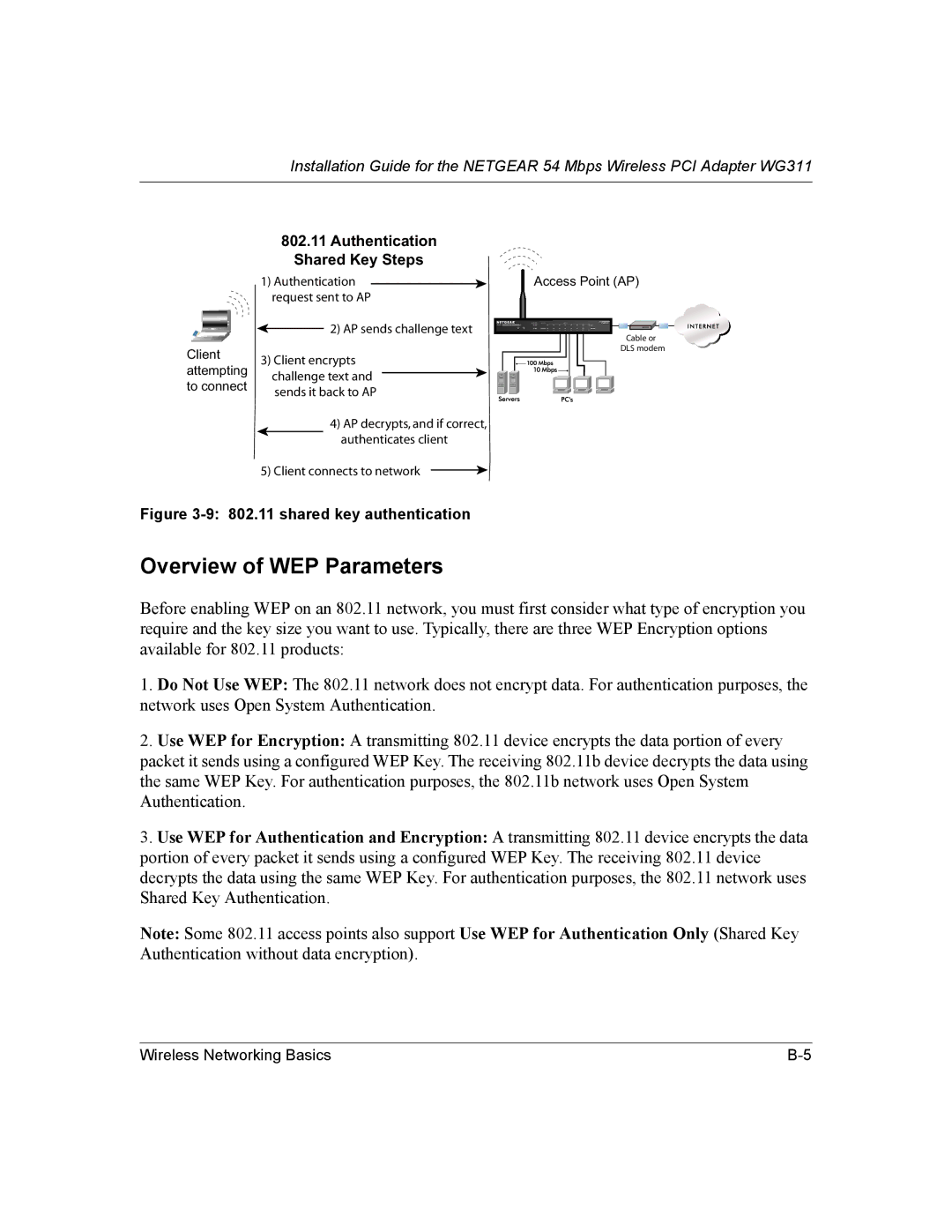
802.11 Authentication
Shared Key Steps
1) Authentication | Access Point (AP) |
request sent to AP |
|
2) AP sends challenge text | FVM318 |
|
Cable or
DLS modem
3) Client encrypts challenge text and sends it back to AP
4)AP decrypts, and if correct, authenticates client
5)Client connects to network ![]()
you
the
using
the data
portion of every packet it sends using a configured WEP Key. The receiving 802.11 device decrypts the data using the same WEP Key. For authentication purposes, the 802.11 network uses Shared Key Authentication.
Note: Some 802.11 access points also support Use WEP for Authentication Only (Shared Key Authentication without data encryption).
Wireless Networking Basics |