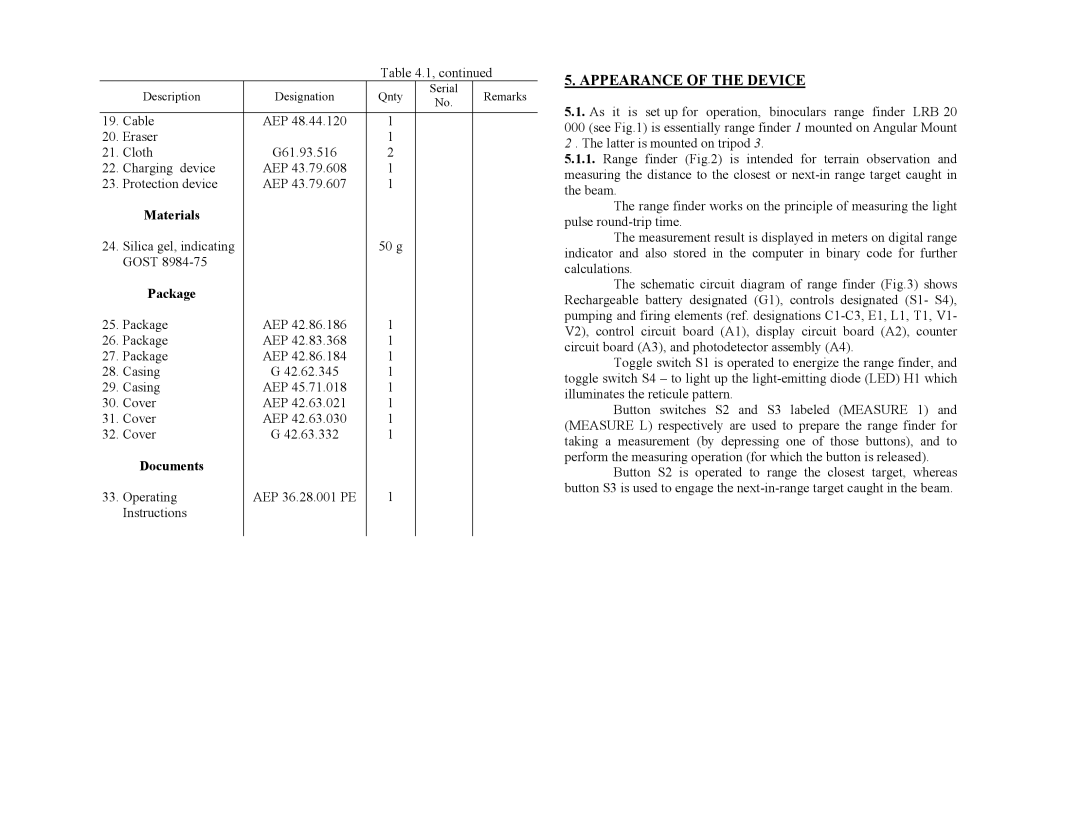
Table 4.1, continued
| Description | Designation | Qnty | Serial | Remarks |
| No. | ||||
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
19. | Cable | AEP 48.44.120 | 1 |
|
|
20. | Eraser |
| 1 |
|
|
21. | Cloth | G61.93.516 | 2 |
|
|
22. | Charging device | AEP 43.79.608 | 1 |
|
|
23. | Protection device | AEP 43.79.607 | 1 |
|
|
| Materials |
|
|
|
|
24. | Silica gel, indicating |
| 50 g |
|
|
| GOST |
|
|
|
|
| Package |
|
|
|
|
25. | Package | AEP 42.86.186 | 1 |
|
|
26. | Package | AEP 42.83.368 | 1 |
|
|
27. | Package | AEP 42.86.184 | 1 |
|
|
28. | Casing | G 42.62.345 | 1 |
|
|
29. | Casing | AEP 45.71.018 | 1 |
|
|
30. | Cover | AEP 42.63.021 | 1 |
|
|
31. | Cover | AEP 42.63.030 | 1 |
|
|
32. | Cover | G 42.63.332 | 1 |
|
|
| Documents |
|
|
|
|
33. | Operating | AEP 36.28.001 РE | 1 |
|
|
| Instructions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. APPEARANCE OF THE DEVICE
5.1.As it is set up for operation, binoculars range finder LRB 20
000 (see Fig.1) is essentially range finder 1 mounted on Angular Mount 2 . The latter is mounted on tripod 3.
5.1.1.Range finder (Fig.2) is intended for terrain observation and measuring the distance to the closest or
The range finder works on the principle of measuring the light pulse
The measurement result is displayed in meters on digital range indicator and also stored in the computer in binary code for further calculations.
The schematic circuit diagram of range finder (Fig.3) shows Rechargeable battery designated (G1), controls designated (S1- S4), pumping and firing elements (ref. designations
Toggle switch S1 is operated to energize the range finder, and toggle switch S4 – to light up the
Button switches S2 and S3 labeled (MEASURE 1) and (MEASURE L) respectively are used to prepare the range finder for taking a measurement (by depressing one of those buttons), and to perform the measuring operation (for which the button is released).
Button S2 is operated to range the closest target, whereas button S3 is used to engage the