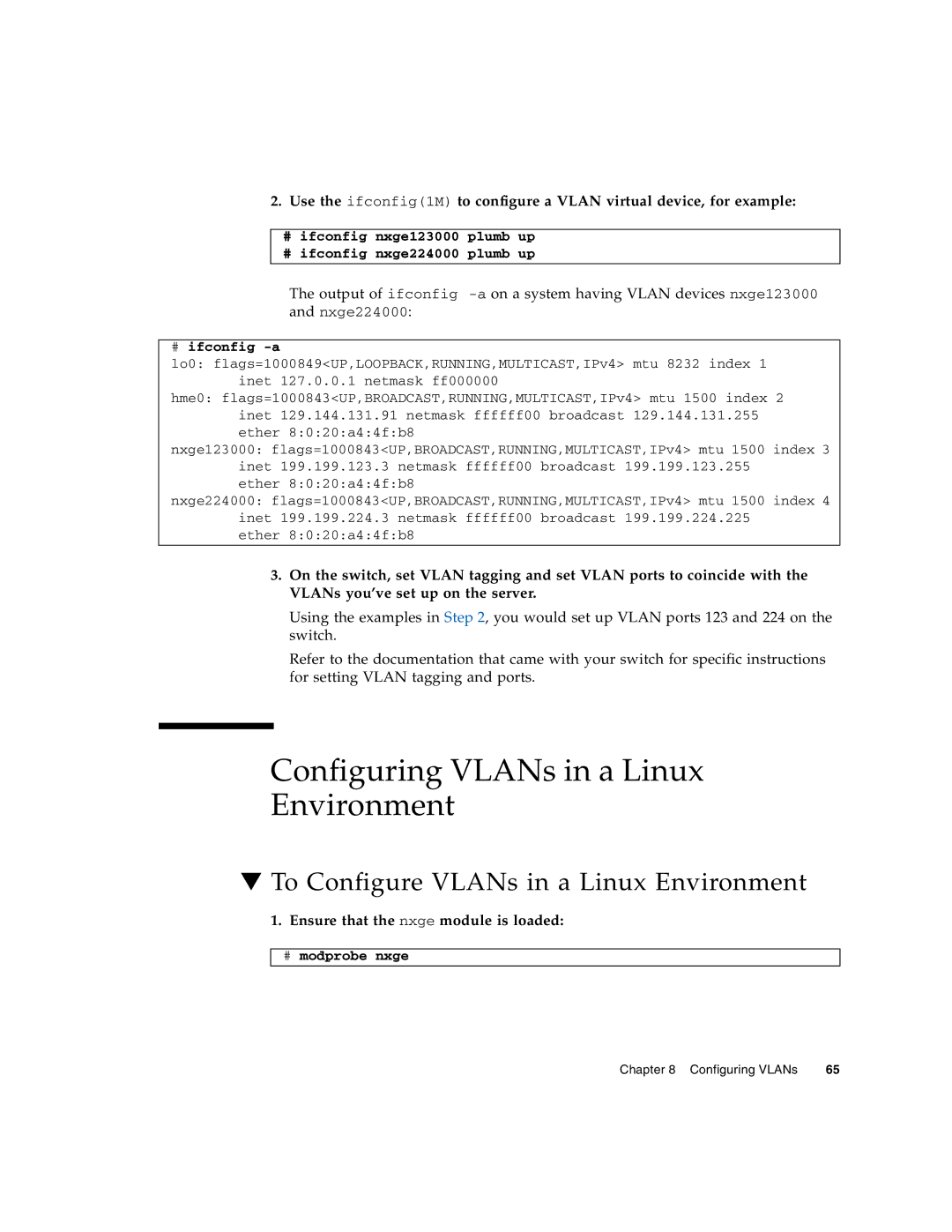
2.Use the ifconfig(1M) to configure a VLAN virtual device, for example:
#ifconfig nxge123000 plumb up
#ifconfig nxge224000 plumb up
The output of ifconfig
#ifconfig -a
lo0: flags=1000849<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING,MULTICAST,IPv4> mtu 8232 index 1 inet 127.0.0.1 netmask ff000000
hme0: flags=1000843<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST,IPv4> mtu 1500 index 2 inet 129.144.131.91 netmask ffffff00 broadcast 129.144.131.255 ether 8:0:20:a4:4f:b8
nxge123000: flags=1000843<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST,IPv4> mtu 1500 index 3 inet 199.199.123.3 netmask ffffff00 broadcast 199.199.123.255
ether 8:0:20:a4:4f:b8
nxge224000: flags=1000843<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST,IPv4> mtu 1500 index 4 inet 199.199.224.3 netmask ffffff00 broadcast 199.199.224.225
ether 8:0:20:a4:4f:b8
3.On the switch, set VLAN tagging and set VLAN ports to coincide with the VLANs you’ve set up on the server.
Using the examples in Step 2, you would set up VLAN ports 123 and 224 on the switch.
Refer to the documentation that came with your switch for specific instructions for setting VLAN tagging and ports.
Configuring VLANs in a Linux
Environment
▼To Configure VLANs in a Linux Environment
1.Ensure that the nxge module is loaded:
#modprobe nxge
Chapter 8 Configuring VLANs | 65 |