DIM Code Checkpoints
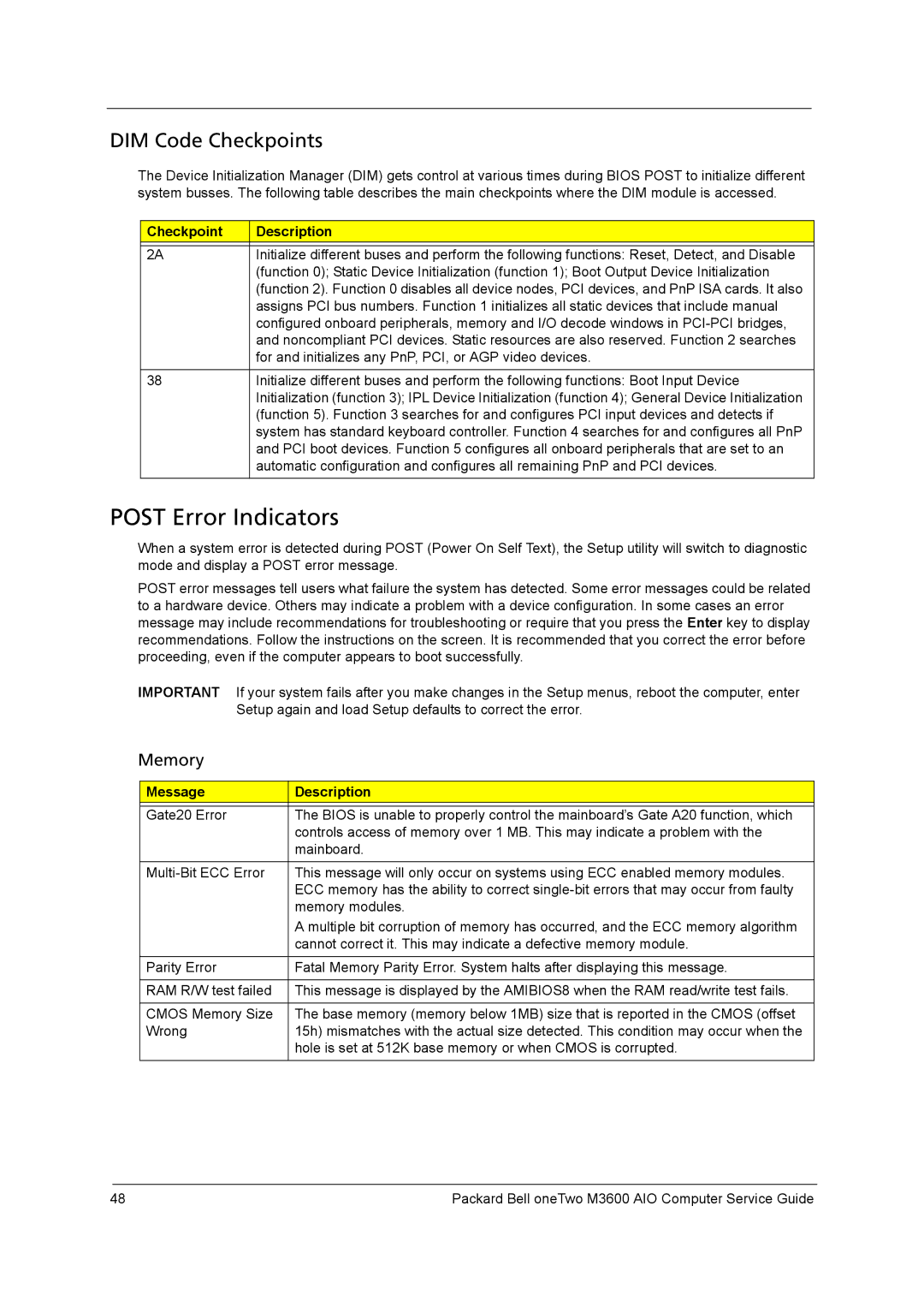
The Device Initialization Manager (DIM) gets control at various times during BIOS POST to initialize different system busses. The following table describes the main checkpoints where the DIM module is accessed.
Checkpoint | Description |
|
|
2A | Initialize different buses and perform the following functions: Reset, Detect, and Disable |
| (function 0); Static Device Initialization (function 1); Boot Output Device Initialization |
| (function 2). Function 0 disables all device nodes, PCI devices, and PnP ISA cards. It also |
| assigns PCI bus numbers. Function 1 initializes all static devices that include manual |
| configured onboard peripherals, memory and I/O decode windows in |
| and noncompliant PCI devices. Static resources are also reserved. Function 2 searches |
| for and initializes any PnP, PCI, or AGP video devices. |
|
|
38 | Initialize different buses and perform the following functions: Boot Input Device |
| Initialization (function 3); IPL Device Initialization (function 4); General Device Initialization |
| (function 5). Function 3 searches for and configures PCI input devices and detects if |
| system has standard keyboard controller. Function 4 searches for and configures all PnP |
| and PCI boot devices. Function 5 configures all onboard peripherals that are set to an |
| automatic configuration and configures all remaining PnP and PCI devices. |
|
|
POST Error Indicators
When a system error is detected during POST (Power On Self Text), the Setup utility will switch to diagnostic mode and display a POST error message.
POST error messages tell users what failure the system has detected. Some error messages could be related to a hardware device. Others may indicate a problem with a device configuration. In some cases an error message may include recommendations for troubleshooting or require that you press the Enter key to display recommendations. Follow the instructions on the screen. It is recommended that you correct the error before proceeding, even if the computer appears to boot successfully.
IMPORTANT If your system fails after you make changes in the Setup menus, reboot the computer, enter Setup again and load Setup defaults to correct the error.
Memory
Message | Description |
|
|
Gate20 Error | The BIOS is unable to properly control the mainboard’s Gate A20 function, which |
| controls access of memory over 1 MB. This may indicate a problem with the |
| mainboard. |
|
|
This message will only occur on systems using ECC enabled memory modules. | |
| ECC memory has the ability to correct |
| memory modules. |
| A multiple bit corruption of memory has occurred, and the ECC memory algorithm |
| cannot correct it. This may indicate a defective memory module. |
|
|
Parity Error | Fatal Memory Parity Error. System halts after displaying this message. |
|
|
RAM R/W test failed | This message is displayed by the AMIBIOS8 when the RAM read/write test fails. |
|
|
CMOS Memory Size | The base memory (memory below 1MB) size that is reported in the CMOS (offset |
Wrong | 15h) mismatches with the actual size detected. This condition may occur when the |
| hole is set at 512K base memory or when CMOS is corrupted. |
|
|
48 | Packard Bell oneTwo M3600 AIO Computer Service Guide |