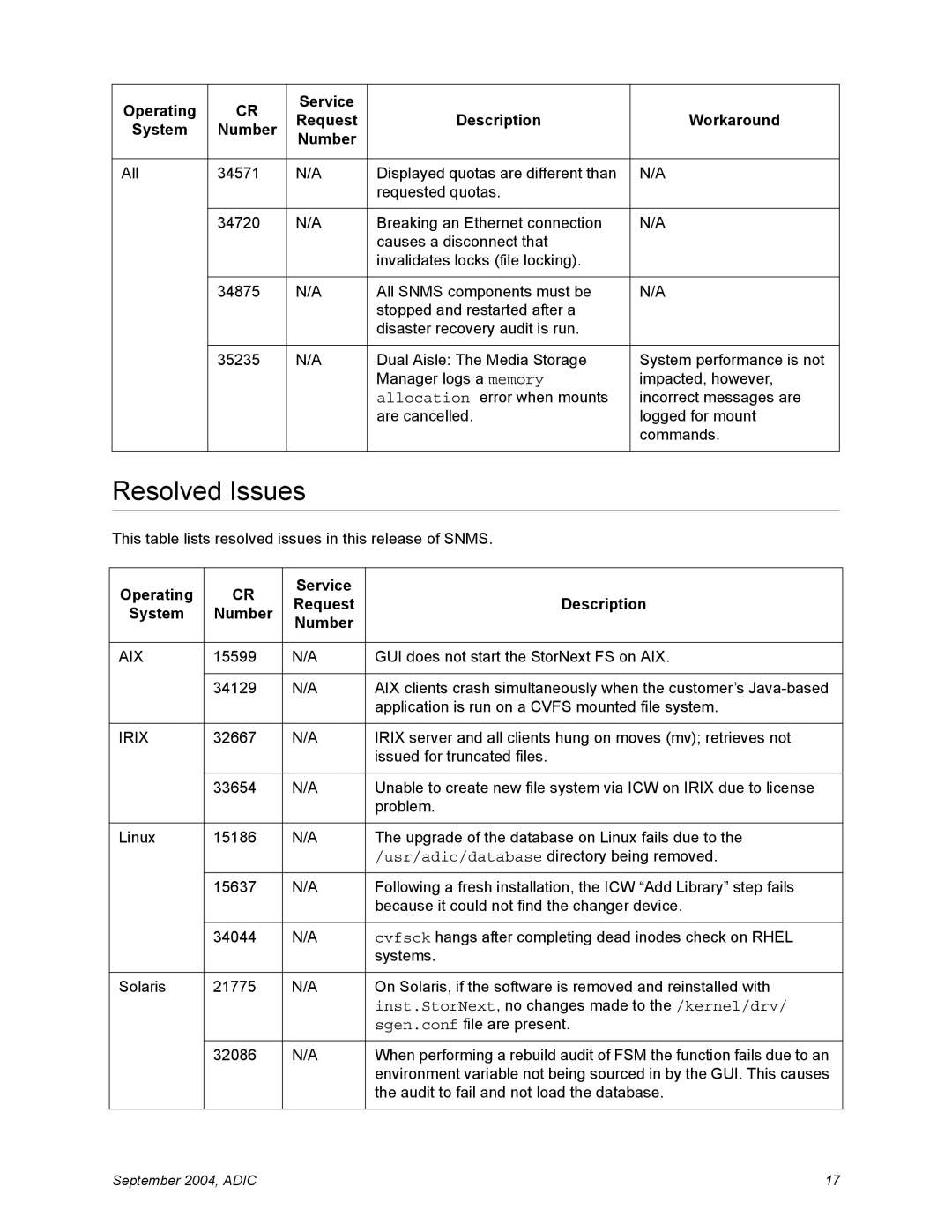
2.4.1 specifications
Quantum 2.4.1 is an exciting update in the realm of quantum computing frameworks, designed to enhance the capabilities and accessibility of quantum programming for developers and researchers. This version builds on its predecessors by introducing several significant features and improvements that streamline the quantum development process.One of the standout features of Quantum 2.4.1 is its enhanced simulation capabilities. The new simulation backend allows developers to run quantum algorithms on classical hardware with greater efficiency, making it easier to prototype and test quantum circuits. This feature is particularly beneficial for researchers who wish to experiment with quantum algorithms without requiring access to expensive quantum hardware.
Additionally, Quantum 2.4.1 introduces an upgraded library of quantum algorithms, which now includes implementations for various state-of-the-art algorithms such as Grover's Algorithm and the Quantum Fourier Transform. This extensive library not only provides ready-to-use components for developers but also serves as a valuable educational resource for those new to quantum computing.
The user interface has also seen significant improvements. Quantum 2.4.1 offers a more intuitive graphical user interface (GUI) that simplifies the process of building and testing quantum circuits. The drag-and-drop functionality allows users to visually assemble circuits, making quantum programming more accessible to beginners.
Moreover, Quantum 2.4.1’s support for hybrid algorithms has been expanded. Hybrid algorithms combine classical and quantum computing techniques to solve complex problems more efficiently. This version enhances integration with classical programming languages, making it easier for developers to build applications that leverage both classical and quantum resources.
Security is another area of focus in the 2.4.1 release. Enhanced protocols for quantum communication and error-correction techniques provide improved data integrity and security for quantum operations. This is crucial as the interest in quantum communication technology grows, driven by the need for secure communication channels in a digital landscape increasingly vulnerable to cyber threats.
Furthermore, the framework is built upon a modular architecture, allowing developers to easily extend and customize components. This flexibility encourages innovation and further experimentation within the quantum computing community.
In summary, Quantum 2.4.1 represents a significant leap forward in quantum programming, with its robust simulation capabilities, expanded algorithm library, improved user interface, hybrid computing support, enhanced security measures, and modular design. These characteristics make it a valuable tool for advancing research and application development in the burgeoning field of quantum computing. As the landscape evolves, Quantum 2.4.1 is well-positioned to support the next wave of breakthroughs in this transformative technology.