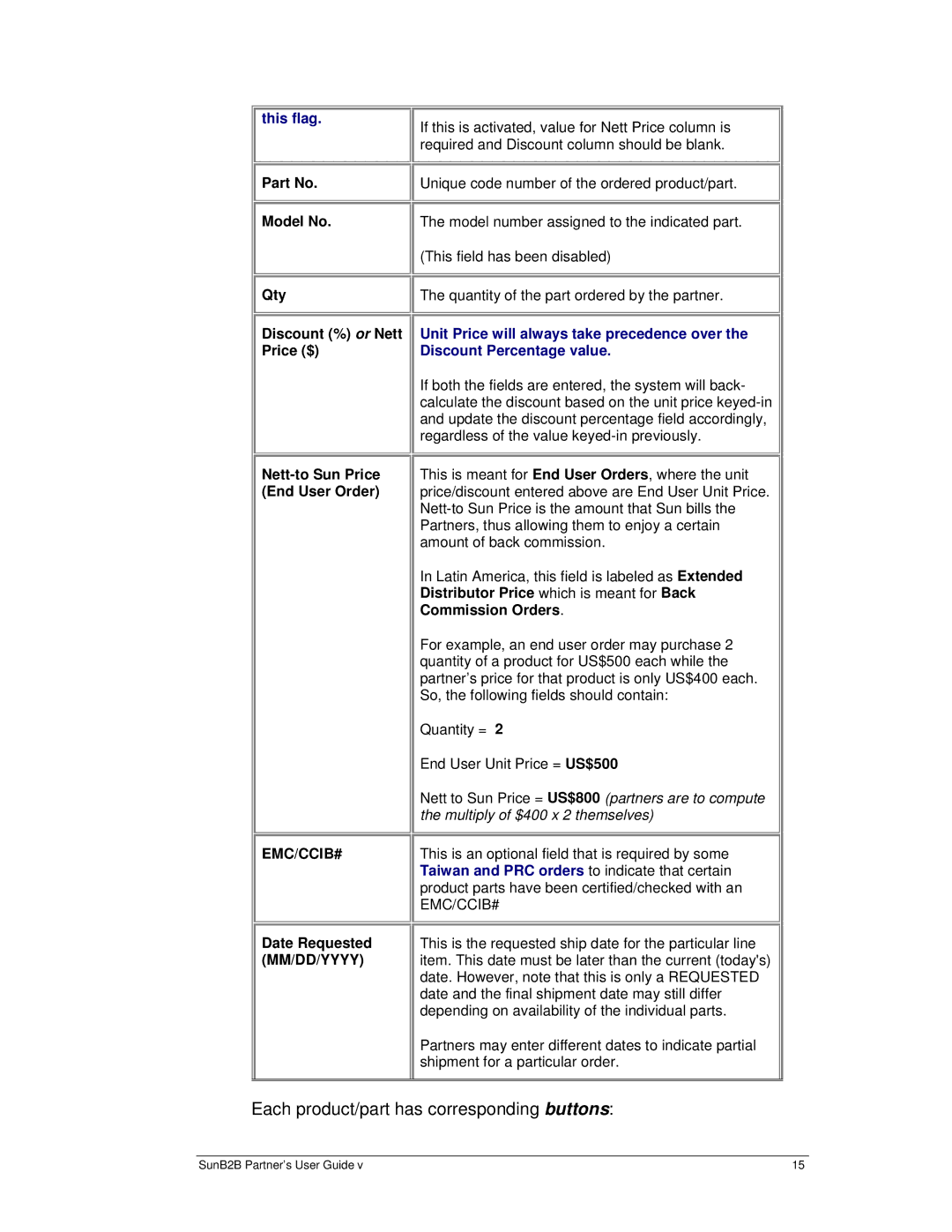
B2B specifications
Sun Microsystems, founded in 1982, was a standout technology company that made significant contributions to the landscape of computing and networking, particularly in the business-to-business (B2B) domain. Initially focused on high-performance workstations and servers running the Solaris operating system, Sun became a pivotal player in the server market, known for its powerful hardware and software solutions designed for enterprises.One of the major features of Sun Microsystems' B2B offerings was their commitment to open standards. The company was a proponent of open systems architecture, which allowed businesses to integrate various hardware and software products without being locked into proprietary solutions. This focus on interoperability made Sun's products highly attractive to companies looking to create flexible IT environments that could adapt and evolve with changing business needs.
In terms of technology, Sun was known for its innovations in computing hardware and software. The introduction of the SPARC (Scalable Processor Architecture) architecture enabled the development of powerful, scalable servers that could handle demanding enterprise applications. Paired with the Solaris OS, businesses could achieve high levels of performance, security, and reliability, which were critical for B2B operations.
Another cornerstone of Sun's B2B technology was its networked computing approach. The company popularized the concept of thin clients and server-based computing, where data processing occurs on centralized servers, and users access applications via lightweight client devices. This architecture not only improved overall efficiency but also simplified management and reduced total costs for organizations.
Sun Microsystems also played a crucial role in the development of Java, which has become a ubiquitous programming language for building enterprise-level applications. Java's "write once, run anywhere" capability enables businesses to deploy applications across diverse platforms effortlessly. This flexibility was especially beneficial in B2B environments, where various systems often needed to communicate and work together seamlessly.
Additionally, Sun's commitment to high-performance storage solutions reinforced its B2B capabilities. With advanced technologies like the Network File System (NFS) and Storage Area Networks (SAN), companies could manage vast amounts of data efficiently, ensuring fast and reliable access to critical business information.
In conclusion, Sun Microsystems made substantial impacts in the B2B realm through its commitment to open standards, innovative hardware solutions, and influential software technologies like Java. Although the company was acquired by Oracle in 2010, its legacy continues to shape the way businesses approach technology and collaboration today.