16 Recovery Using ZMC | Sun Microsystems, Inc. |
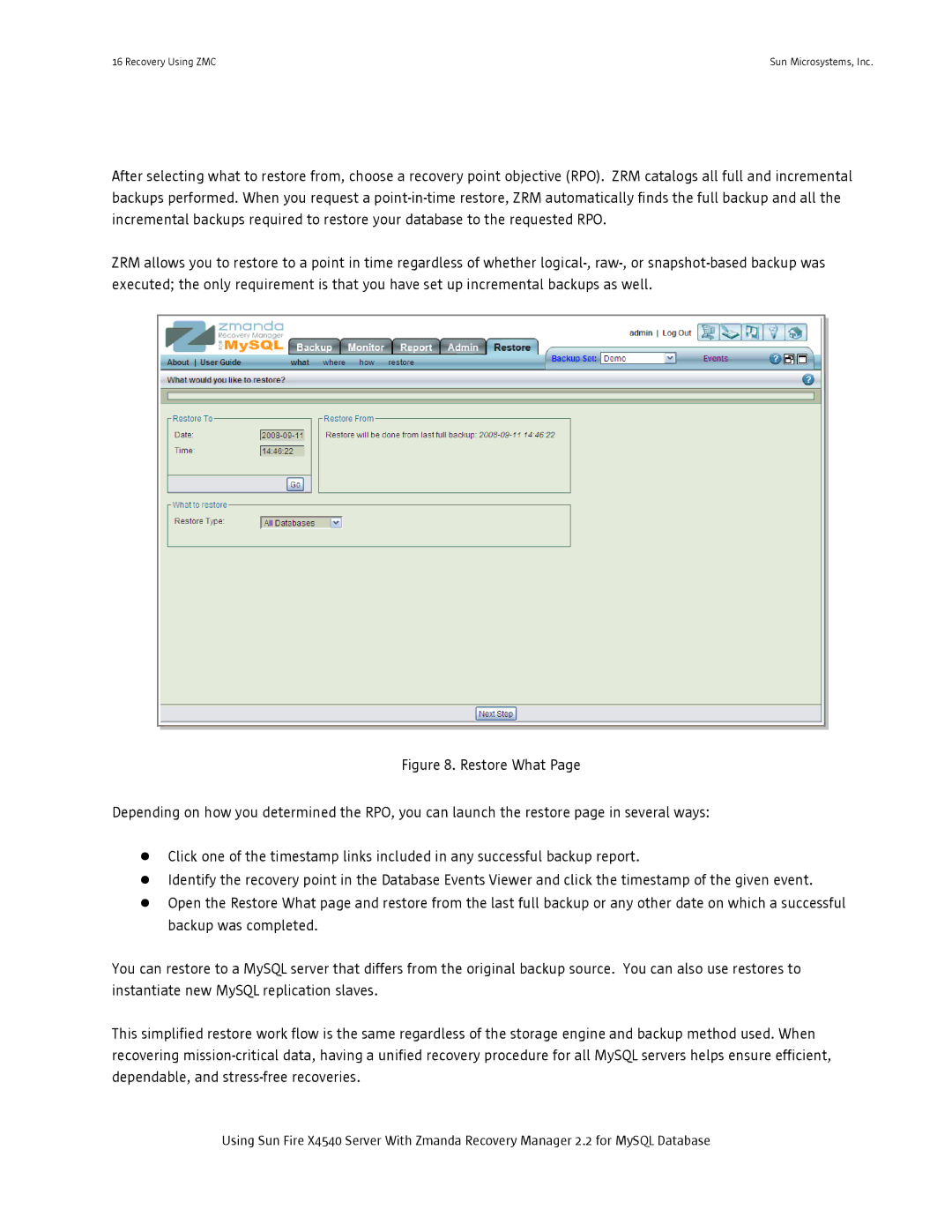
After selecting what to restore from, choose a recovery point objective (RPO). ZRM catalogs all full and incremental backups performed. When you request a
ZRM allows you to restore to a point in time regardless of whether
Figure 8. Restore What Page
Depending on how you determined the RPO, you can launch the restore page in several ways:
●Click one of the timestamp links included in any successful backup report.
●Identify the recovery point in the Database Events Viewer and click the timestamp of the given event.
●Open the Restore What page and restore from the last full backup or any other date on which a successful backup was completed.
You can restore to a MySQL server that differs from the original backup source. You can also use restores to instantiate new MySQL replication slaves.
This simplified restore work flow is the same regardless of the storage engine and backup method used. When recovering mission-critical data, having a unified recovery procedure for all MySQL servers helps ensure efficient, dependable, and stress-free recoveries.
Using Sun Fire X4540 Server With Zmanda Recovery Manager 2.2 for MySQL Database