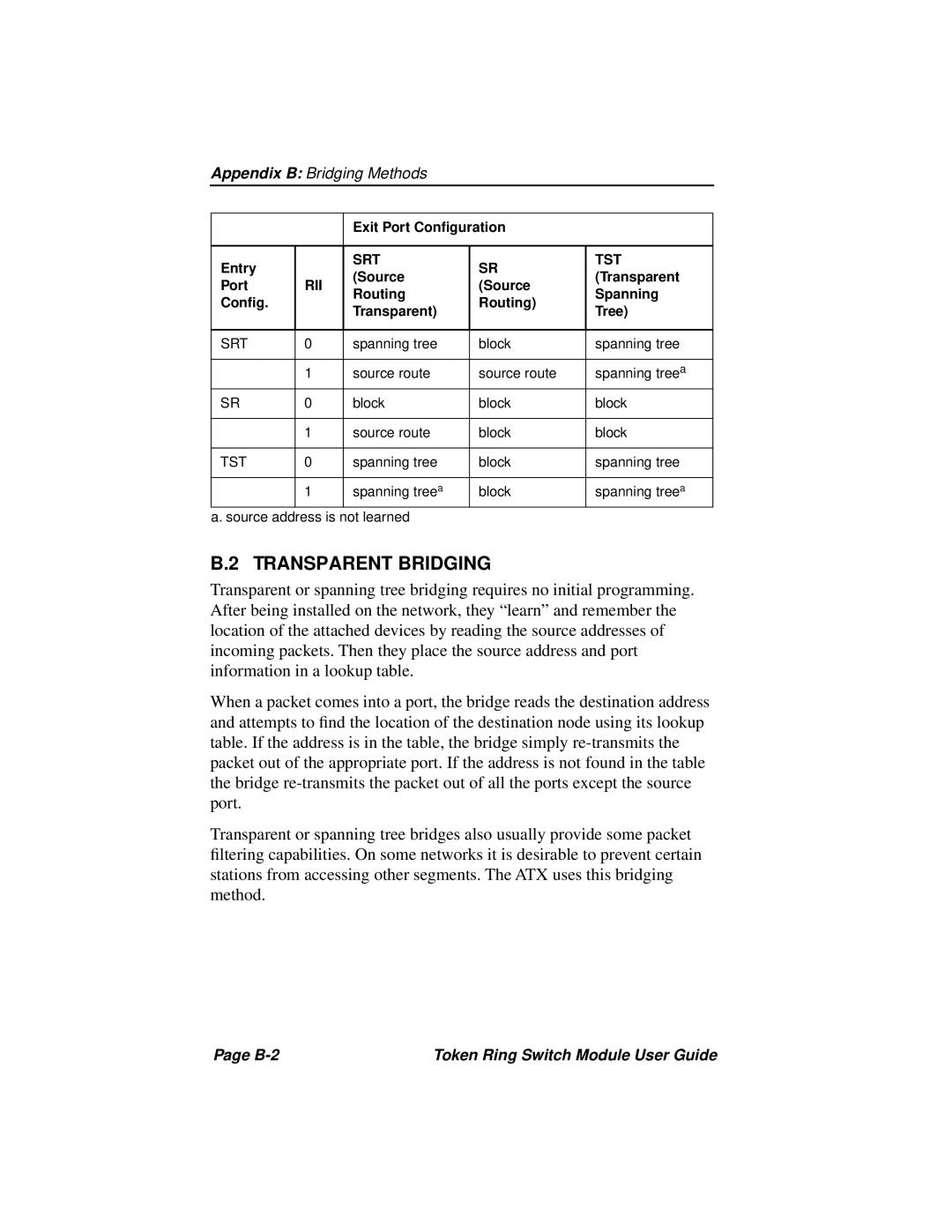
3T02-04 specifications
Cabletron Systems, a notable name in the networking industry, gained prominence for its pioneering products and innovative technologies. One of its formidable offerings is the Cabletron Systems 3T02-04, an advanced network switching device designed to cater to the evolving demands of high-performance networking environments.The Cabletron Systems 3T02-04 excels in facilitating seamless data transfer within various network infrastructures. At its core, this device is engineered with key features that enhance its performance and adaptability. With a robust switching architecture, it provides high throughput and low latency, ensuring efficient handling of data traffic. This is particularly crucial for organizations that rely on rapid communication and data exchange for their operations.
One of the defining characteristics of the 3T02-04 is its multi-port configuration, which allows multiple devices to connect simultaneously. This enables the device to support a wide range of applications, from standard office networking to intensive data center operations. Equip with support for various data transmission protocols, including Ethernet, the 3T02-04 is highly versatile, meeting the diverse needs of modern networking tasks.
Additionally, Cabletron Systems incorporated advanced technologies such as Virtual LAN (VLAN) support in the 3T02-04, enhancing network segmentation and improving security measures. This feature allows network administrators to partition the network into different segments, ensuring that sensitive data remains separate and secure from other less critical services.
The 3T02-04 is also notable for its scalability. As organizations grow and their networking requirements evolve, the 3T02-04 can adapt. This scalability is crucial for businesses looking to future-proof their infrastructure investments, allowing them to add bandwidth and enhance connectivity without a complete overhaul of their existing systems.
Moreover, the robustness and reliability of the device ensure that it can withstand the rigors of demanding environments. Its durable design and comprehensive management features enable efficient monitoring and maintenance.
In conclusion, the Cabletron Systems 3T02-04 stands out as a powerful and versatile networking solution that combines cutting-edge technologies, multi-port capabilities, VLAN support, and excellent scalability, making it a valuable asset for any organization aiming to optimize its network infrastructure.